Xerox 701P21091 User Manual
Page 188
Using logical processing
3-8
Using LCDS Print Description Language
The characters used in the MASK parameter occupy numbered
positions, beginning with 0 and separated by commas. These
position numbers in the MASK parameter are used as type
numbers. Therefore, the associations of mask characters to type
that are listed in the following table are made for the above
TABLE command.
•
The data string characters that correspond positionally to
those occupied by @ in the CONSTANT parameter are tested
for type 2 (in the example, alphabetic A through Z or a
through z).
•
Characters that correspond positionally with a % are tested
for type 1 (numeric, 0 through 9).
•
If the string that is specified in the CONSTANT parameter
were to include a ?, the corresponding data character from
the input stream would be considered equal without any
comparison being made, because it is an “ignore” type mask
character.
Example 3
Assume the TABLE command in example 2 is changed as
follows.
When the first two character positions of the CONSTANT
parameter are checked for a mask character (as specified in the
MASK parameter), none is found. Exact character matches
between the input data string characters and the CONSTANT
parameter characters (in this case, A7) are required for those
two positions. Therefore, in this example, only data strings that
begin with A7 can possibly pass the entire test.
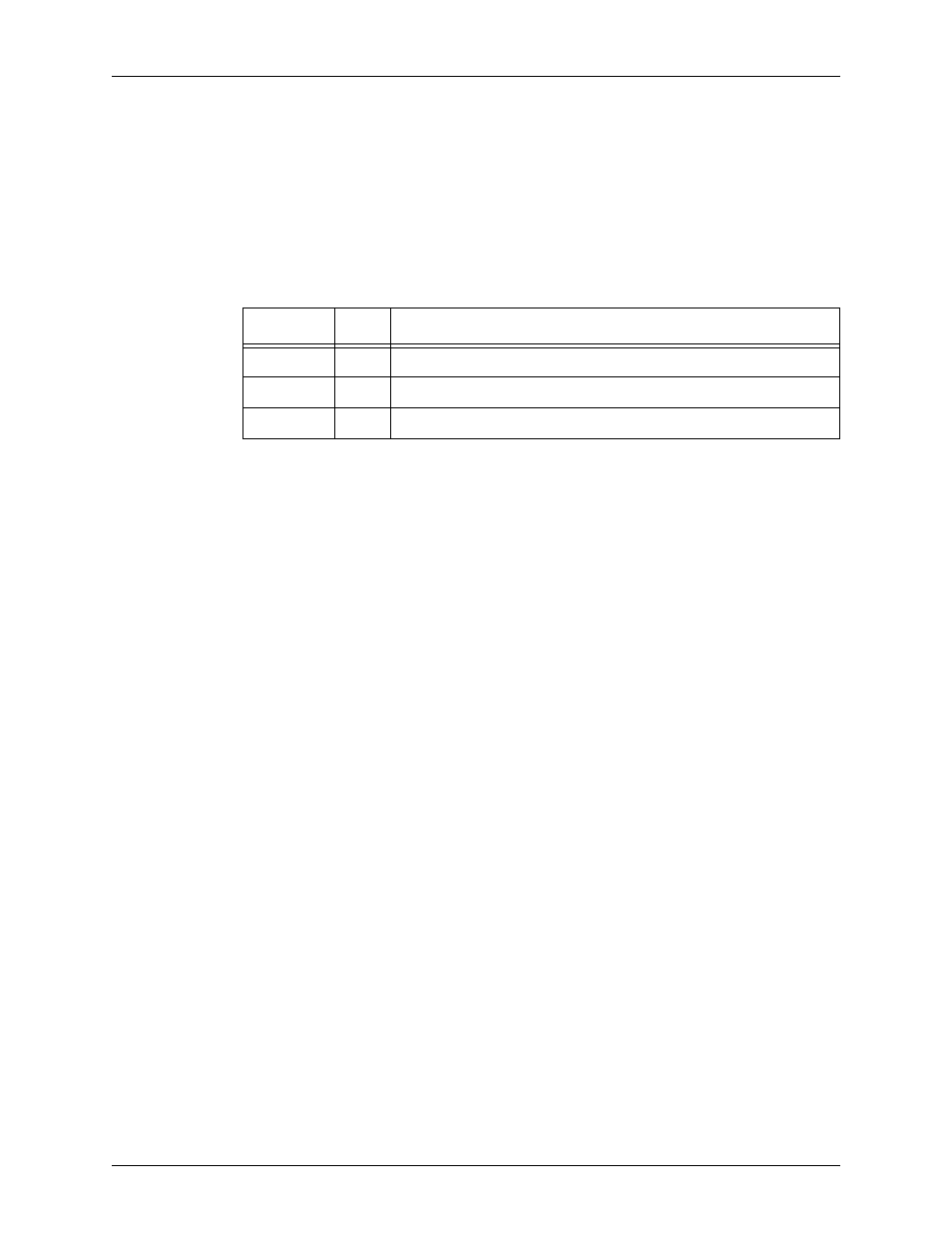
Table 3-5. Mask associations of character to type for the TABLE
command
Character
Type
Meaning
?
None
Make no comparison
%
1
Per standard default, any numeric (0 through 9)
@
2
Per standard default, any alphabetic (A through Z, a through z)
T2:
TABLE
MASK=('?','%','@'),
CONSTANT=('A7%%@%');
