Srg50 terminology – Nortel Networks SRG50 User Manual
Page 20
20
Chapter 2 SRG50 overview
NN40140-500
NN40140-500
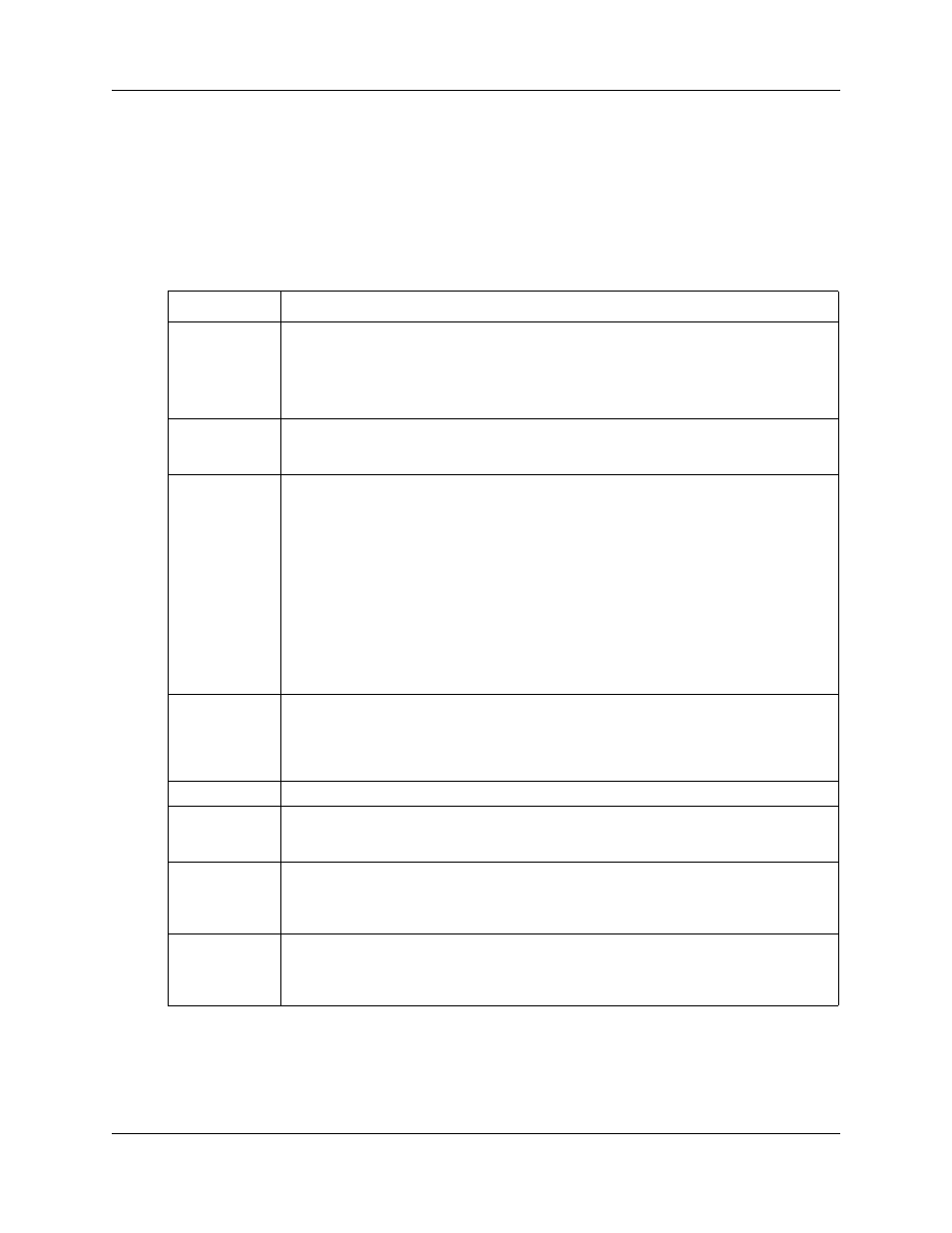
SRG50 terminology
The table
on page 20 identifies SRG terms that may be unfamiliar to main
office installers. They are provided to facilitate communications between SRG and main office
personnel. In the table, the Element Manager path where the term appears is provided for reference
and may not represent every appearance of the term.
Table 6 SRG50 terminology (Sheet 1 of 2)
Term
Description
Port
For telephony configuration (Configuration > Telephony), a port is an internal number that
identifies a physical termination point for a telephone set or a physical trunk.
For the configuration of resources (Configuration > Resources) and data services
(Configuration > Data Services), port is used in the context of the TCP/IP protocol suite.
IP Terminal
IP telephone
Configuration > Resources > Telephony Resources > IP & App Sets
Sets
Can refer to actual telephones, or to the directory number (DN) assigned to the port to
which a particular telephone is connected.
Telephone
Configuration > Resources > Telephony Resources > IP & App Sets
Mapping DN to Telephone
Configuration > Telephony > Sets
DN
Configuration > Telephony > Lines > Target Lines > Target Lines table > Control Set and
Prime Set columns
Trunks
Trunks refer to external facilities that are connected to the SRG and provide incoming and
outgoing communication paths. Paths can be physical (examples: loop; PRI; T1) or virtual
(VoIP trunks).
Configuration > Resources
Loop trunk
An analog loop (FXO) that connects to the PSTN: a POTS line.
Lines
A line is the generic term used for all communication paths, both internal and external.
Configuration > Telephony > Lines
Physical Lines
Physical trunks.
Configuration > Telephony > Lines > Active Physical Lines
(Lines 061 to 124)
VoIP Lines
VoIP trunks.
Configuration > Telephony > Lines > Active VoIP Lines
(Lines 001 to 024)
