3 configuring global settings for ospf – Planet Technology WGS3-2620 User Manual
Page 195
WGS3 Layer 3 Switch User’s Manual
- 187 -
Default Route
Advertisement
Disabled
Enables or disables advertising this switch as a default router.
Static Route
Advertisement
Disabled
Enables or disables advertisement of static routes.
5.7.5.2.3 Configuring Global Settings for OSPF
To implement OSPF for a large network, you must first organize the network into logical areas to limit the
number of OSPF routers that actively exchange Link State Advertisements (LSAs). You can then define
an OSPF interface by assigning an IP interface configured on this switch to one of these groups. This
OSPF interface will send and receive OSPF traffic to neighboring OSPF routers. You can further
optimize the exchange of OSPF traffic by specifying an area range that covers a large number of
subnetwork addresses. This is an important technique for limiting the amount of traffic exchanged
between Area Border Routers (ABRs). And finally, you must specify a virtual link to any OSPF area that
is not physically attached to the OSPF backbone. Virtual links can also be used to provide a redundant
link between contiguous areas to prevent areas from being partitioned, or to merge backbone areas.
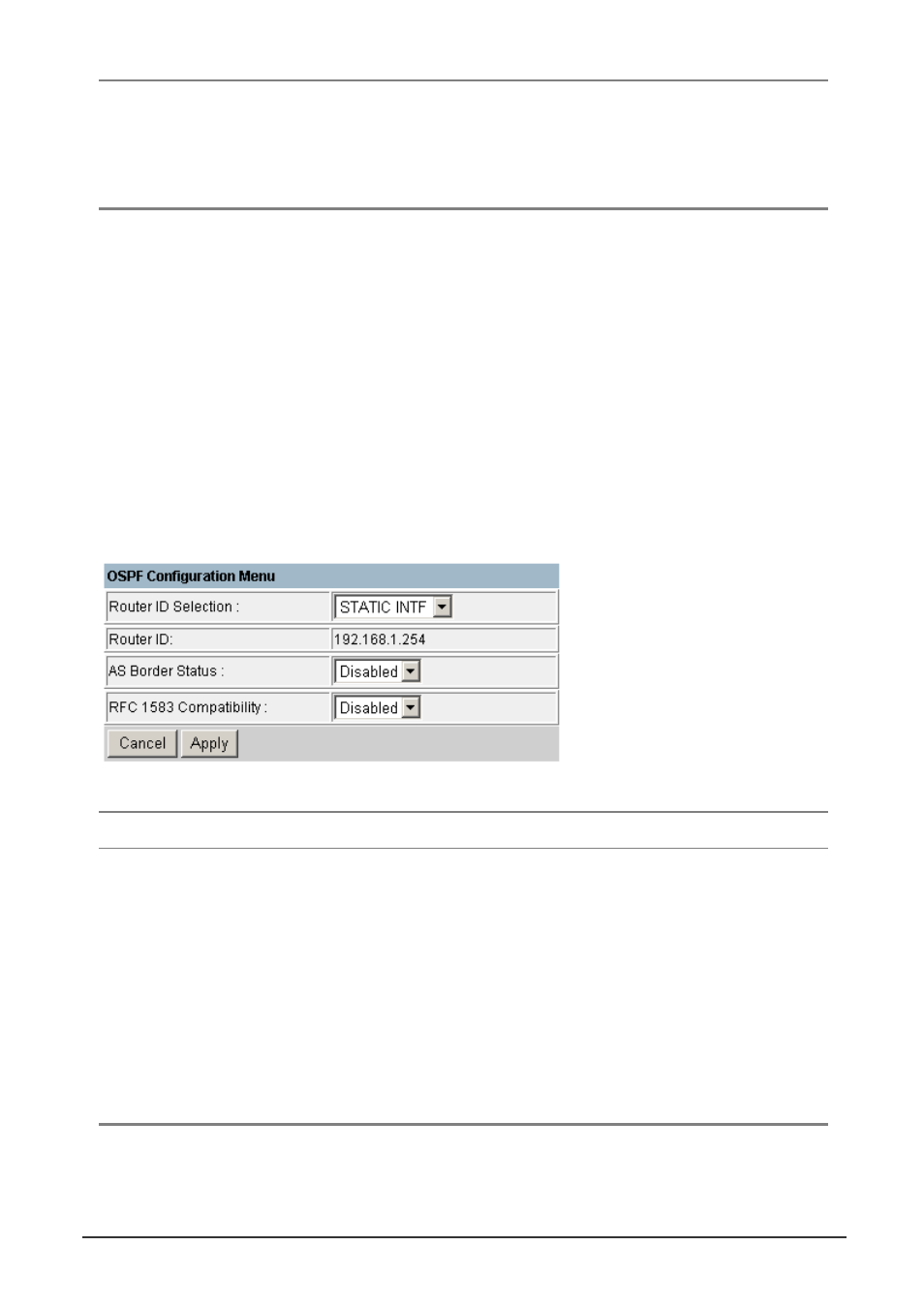
The OSPF global configuration consist a configuration page and a few sub-menu.
Parameter Default Description
Router ID
Selection
STATIC INTF Defines how the Router ID is determined: There are three options:
STATIC: User can manual configure the Router ID.
STATIC INTF: The VLAN 1 IP address will be used as Router ID
ACTIVE INTF: The first active interface will be used as Router ID
Router ID
VLAN 1 IP
A 32-bit number assigned to each router running the OSPF protocol.
This number uniquely identifies the router within an Autonomous
System.
RFC 1583
Compatibility
Disabled
Enable or disable the compatibility to RFC 1583 OSPF version 2
