KTI Networks KGS-2416 User Manual
Page 30
26
subnet is used to determine how to split an IP address to the network prefix and the
host address in bitwise basis. It is designed to utilize IP address more efficiently and
ease to manage IP network.
For a class B network, 128.1.2.3, it may have a subnet mask 255.255.0.0 in
default, in which the first two bytes is with all 1s. This means more than 60
thousands of nodes in flat IP address will be at the same network. It’s too large to
manage practically. Now if we divide it into smaller network by extending network
prefix from 16 bits to, say 24 bits, that’s using its third byte to subnet this class B
network. Now it has a subnet mask 255.255.255.0, in which each bit of the first
three bytes is 1. It’s now clear that the first two bytes is used to identify the class B
network, the third byte is used to identify the subnet within this class B network and,
of course, the last byte is the host number.
Not all IP address is available in the sub-netted network. Two special
addresses are reserved. They are the addresses with all zero’s and all one’s host
number. For example, an IP address 128.1.2.128, what IP address reserved will be
looked like? All 0s mean the network itself, and all 1s mean IP broadcast.
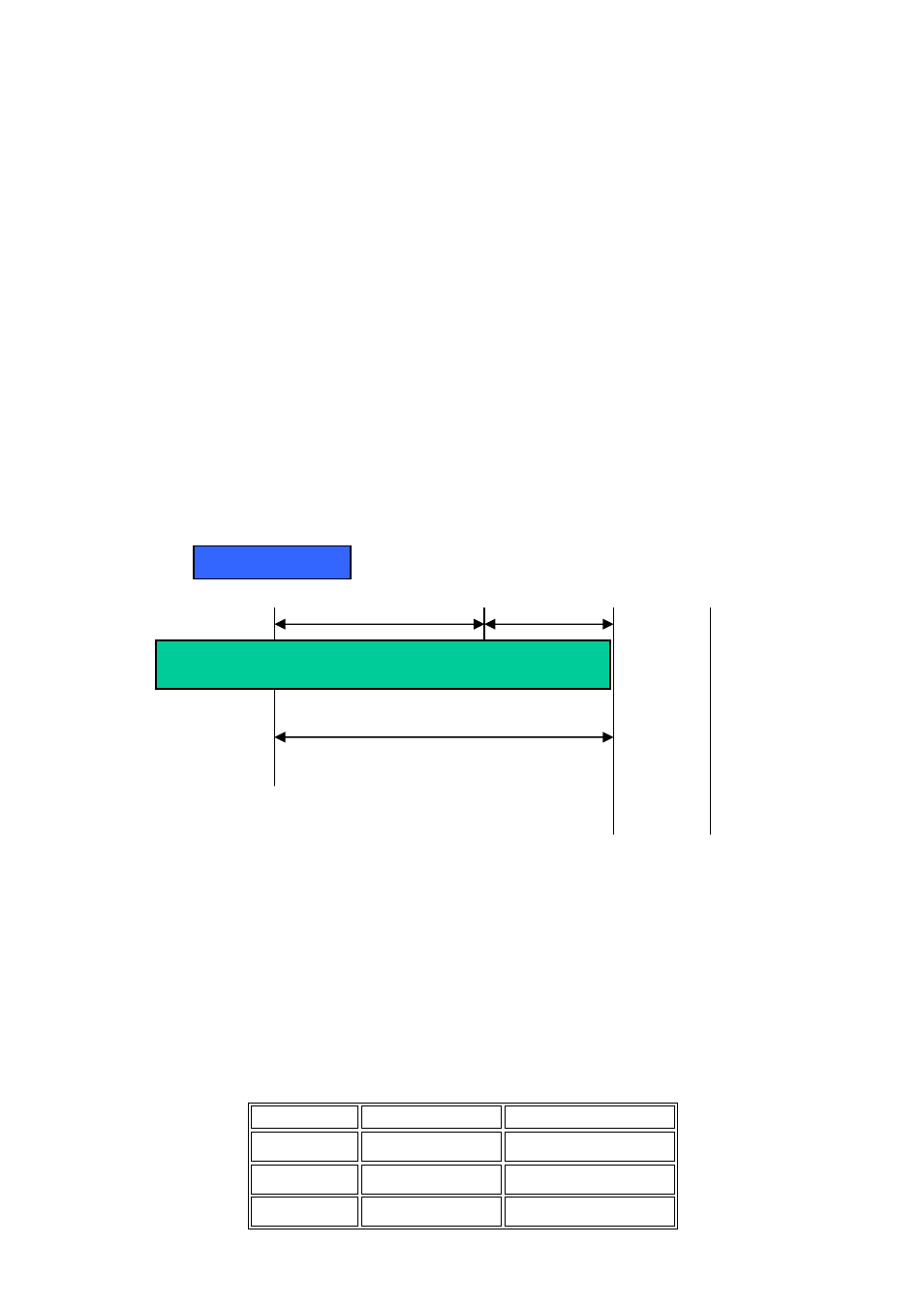
In this diagram, you can see the subnet mask with 25-bit long,
255.255.255.128, contains 126 members in the sub-netted network. Another is that
the length of network prefix equals the number of the bit with 1s in that subnet mask.
With this, you can easily count the number of IP addresses matched. The following
table shows the result.
Prefix Length No. of IP matched No. of Addressable IP
/32 1
-
/31 2
-
/30 4
2
10000000.00000001.00000010.1 0000000
128.1.2.128/25
25 bits
1 0000000
1 1111111
All 0s = 128.1.2.128
All 1s= 128.1.2.255
Subnet
Network
