Link: vlan, Overview, Vlan overview – Motorola Netopia 3342N User Manual
Page 107: Oups. see
107
Link:
VLAN
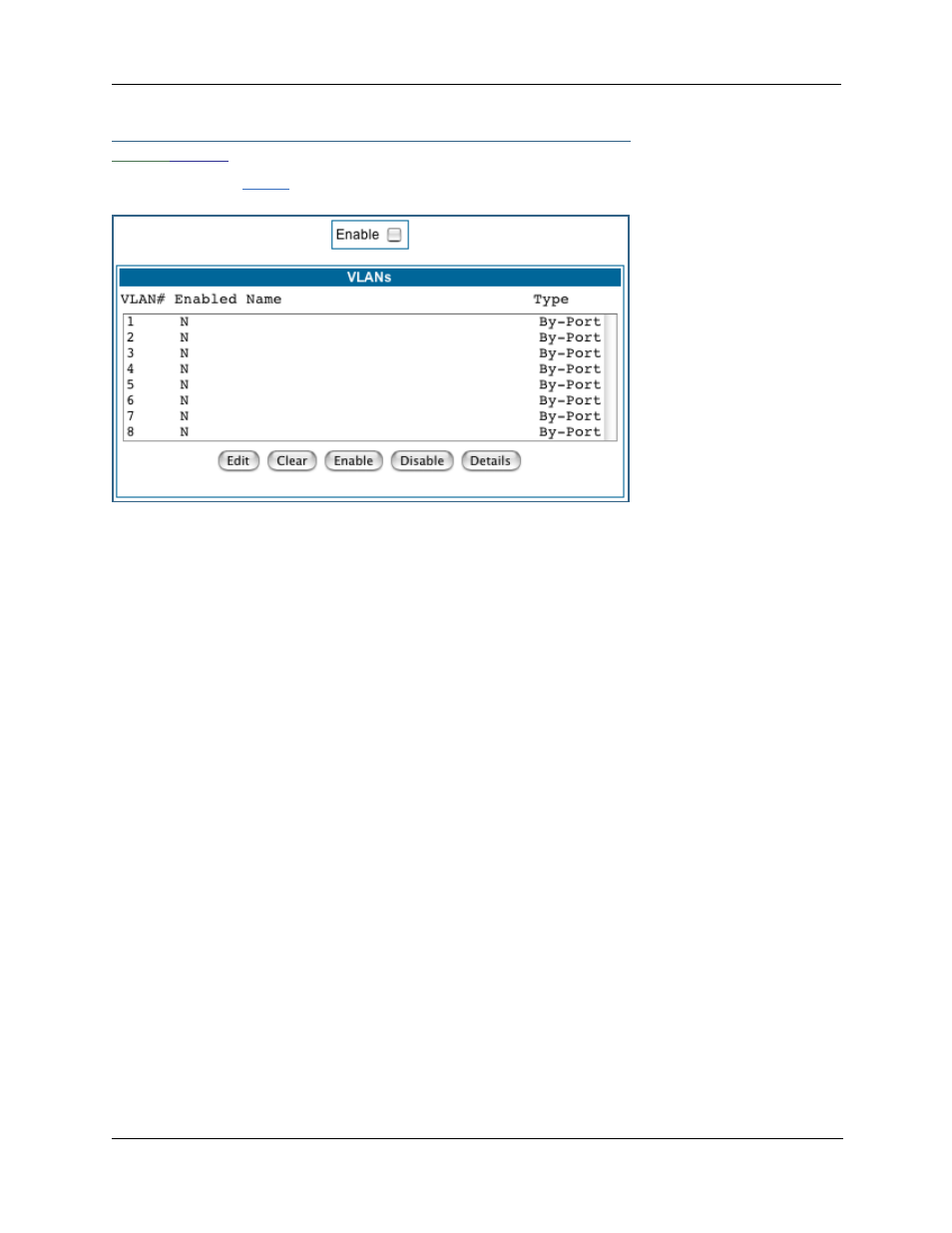
When you click the
VLAN
link the
VLANs page appears.
Overview
A Vir tual Local Area Network (VLAN) is a network of computers or other devices that behave as if they are
connected to the same wire even though they may be physically located on different segments of a LAN.
You set up VLANs by configuring the Gateway software rather than hardware. This makes VLANs ver y flexi-
ble. VLANs behave like separate and independent networks.
Beginning with Version 7.7.4, VLANs are now strictly layer 2 entities. They can be thought of as vir tual
Ethernet switches, into which can be added: Ethernet por ts, router IP inter faces, ATM PVC/VCC inter faces,
SSIDs, and any other physical por t such as USB, HPNA, or MOCA. This allows great flexibility on how the
components of a system are connected to each other.
VLANs are par t of Motorola’s VGx Vir tual Gateway technology which allows individual por t-based VLANs to
be treated as separate and distinct “channels.” When data is passed to a Motorola Netopia VGx-enabled
broadband gateway, specific policies, routing, and prioritization parameters can be applied to each individ-
ual ser vice, delivering that ser vice to the appropriate peripheral device with the required level of quality of
ser vice (QoS). In effect, a single Motorola gateway acts as separate vir tual gateways for each distinct ser-
vice being delivered.
Motorola’s VGx technology maps multiple local VLANs to one or more specific permanent vir tual circuits
(PVCs) for DSL, or wide area network VLANs for a fiber network. VGx provides ser vice segmentation and
QoS controls, ser vice management, and suppor ts deliver y of triple play applications: voice for IP Telephony,
video for IPTV, and data.
Your Gateway suppor ts the following:
•
Por t-based VLANs - these can be used when no trunking is required
•
Global VLANs - these are used when trunking is required on any por t member of the VLAN
- Suppor ts 802.1q and 802.1p; both are configurable
•
Routed VLANs
