Hot standby, Terminology, Hot standby mode 1 (true hot standby) – ProSoft Technology PS-QS-1x10-0781 User Manual
Page 60
FieldServer Configuration Manual
Page 60 of 90
FieldServer Technologies 1991 Tarob Court Milpitas, California 95035 USA Web: www.fieldserver.com
Tel: (408) 262-2299 Fax: (408) 262-2269 Toll Free: (888) 509-1970 email: [email protected]
10 HOT STANDBY
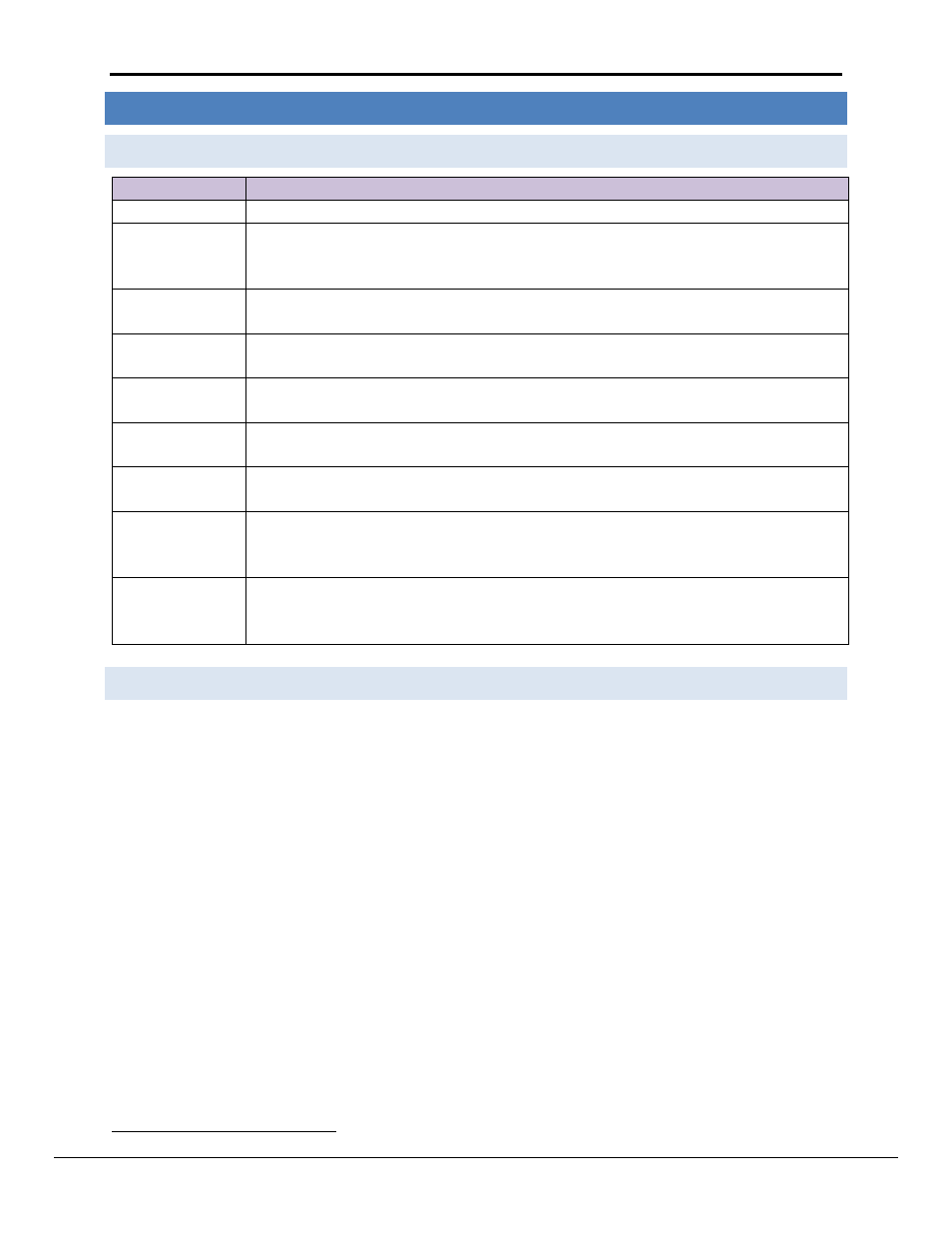
10.1 Terminology
Term
Description
Active FieldServer
The FieldServer actively polling the field Nodes
Standby
FieldServer
A FieldServer which is running, but is not polling field Nodes, nor responding to Client polls.
It will assume active status if the Active FieldServer fails to issue a heartbeat in the
designated time frame.
Failover Timeout
The time interval between the Active FieldServer failing and the Standby FieldServer
preparing to become the Active FieldServer.
Transfer Interval
The total time interval between the Active FieldServer failing and the Standby FieldServer
actually resuming communications as the Active FieldServer
Primary
FieldServer
The FieldServer designated to be the Active FieldServer on system startup
Secondary
FieldServer
The FieldServer designated to be the Standby FieldServer on system startup
Commbit
Data
Array
Bit Data Array that shows all the online Nodes, one bit per Node address. Practical limit is
255 Nodes, the offset corresponds to the Node_ID.
NodeStat
Data
Array
Int Data Array that shows all the status of all Nodes, one integer per Node address. Practical
limit is 255 Nodes, the offset corresponds to the Node_ID. The value of the integer
corresponds to the current Node status.
Hot
Standby
Status Data Array
A Data Array showing the status of all Hot Standby FieldServers in a pair, e.g. which
FieldServer is active, is it the primary or secondary, is the standby FieldServer active, why did
the switchover occur, …
10.2 Hot Standby Mode 1
12
(True Hot Standby)
Two FieldServers are used in this configuration, one designated as Active and the other as Passive. The Active
FieldServer transmits and receives information from the remote Nodes and transmits a constant heartbeat signal
to the Passive unit. On failure of the Active FieldServer, the heartbeat stops and control switches to the Passive
FieldServer which consequently becomes the Active FieldServer. This FieldServer now polls the host for data and
updates its Data Arrays and from this point maintains communication with the host.
The heartbeat can be transferred via 2 Ethernet ports using either 2 hubs (Figure X) or 2 crossover cables (
). Two are used in order to preserve the redundant capability of the entire system.
Hot Standby Mode 1 is ideal for straightforward applications where the objective is simply to prevent a FieldServer
hardware failure from interrupting communications.
12
Only Modbus RTU is supported for Hot Standby at present. Most other drivers could use this function but should refer to FST for assistance.
