4 output enable and disable, Output enable and disable -4, R. 3.4) – KEPCO MST Series User Manual
Page 36
3-4
MST SERIES 061813
3.4
OUTPUT ENABLE AND DISABLE
Enabling or disabling the output of an MST Power Module differs, depending upon whether it is
operating as a voltage source or current source. The difference is determined by the opposite
impedance characteristics of an ideal voltage vs. ideal current source. This section defines the
“disable” function in terms of ideal voltage or current source characteristics, and details the
exact method by which MST Power Modules provides the disable function.
For both voltage and current sources the “disable” condition is always represented by a “no-
load” (zero load power) impedance. Regardless of whether the MST is operating in voltage or
current mode (see PAR. 3.2), the “disable” condition must ensure that the MST provides zero
power to the load, while ensuring full compliance to the load when subsequently enabled. The
correct implementation of the disable function, whether for voltage mode or current mode, is
automatic.
The definition of an ideal voltage source is a source which will supply stable voltage (Vo) into
any load impedance within the limits of its compliance current range (RL = Vo/IMAX). For an
ideal voltage source a no-load condition is then defined as infinite impedance, since this is the
only load condition at which the delivered power (Vo x Io) is zero. MST Power Modules provide
this function by opening all power relays, thus providing an open circuit to the load from the sta-
bilizer output. Enabling the voltage source is accomplished by closing the appropriate relay con-
tacts, depending upon selected output polarity, thus connecting the stabilizer output to the load.
The definition of an ideal current source is a source which will supply stable current (Io) into any
load conductance within the limits of its compliance voltage range (GL = Io/VMAX). For an ideal
current source a no-load condition is then defined as infinite conductance (zero impedance)
since this is the only load condition at which the delivered power is zero. MST Power Modules
provide this function by closing all four power relays, thus placing a short circuit (RL=0) at the
output of the load stabilizer. While “disabled,” output current from the MST load regulator contin-
ues to circulate within the power module and through the shorted power relays. Enabling the
current source is accomplished by opening the appropriate relays contacts, depending upon the
selected output polarity, thus allowing the output current to flow through the load.
As with the output polarity reversal function described in PAR. 3.3, a “dry switching” scheme is
employed during the disable and enable functions. For both voltage and current modes of oper-
ation, the CIIL command to enable the output at the load is Close (CLS), and to disable the out-
put at the load is Open (OPN); the corresponding SCPI commands are OUTP ON and OUTP
OFF, respectively.
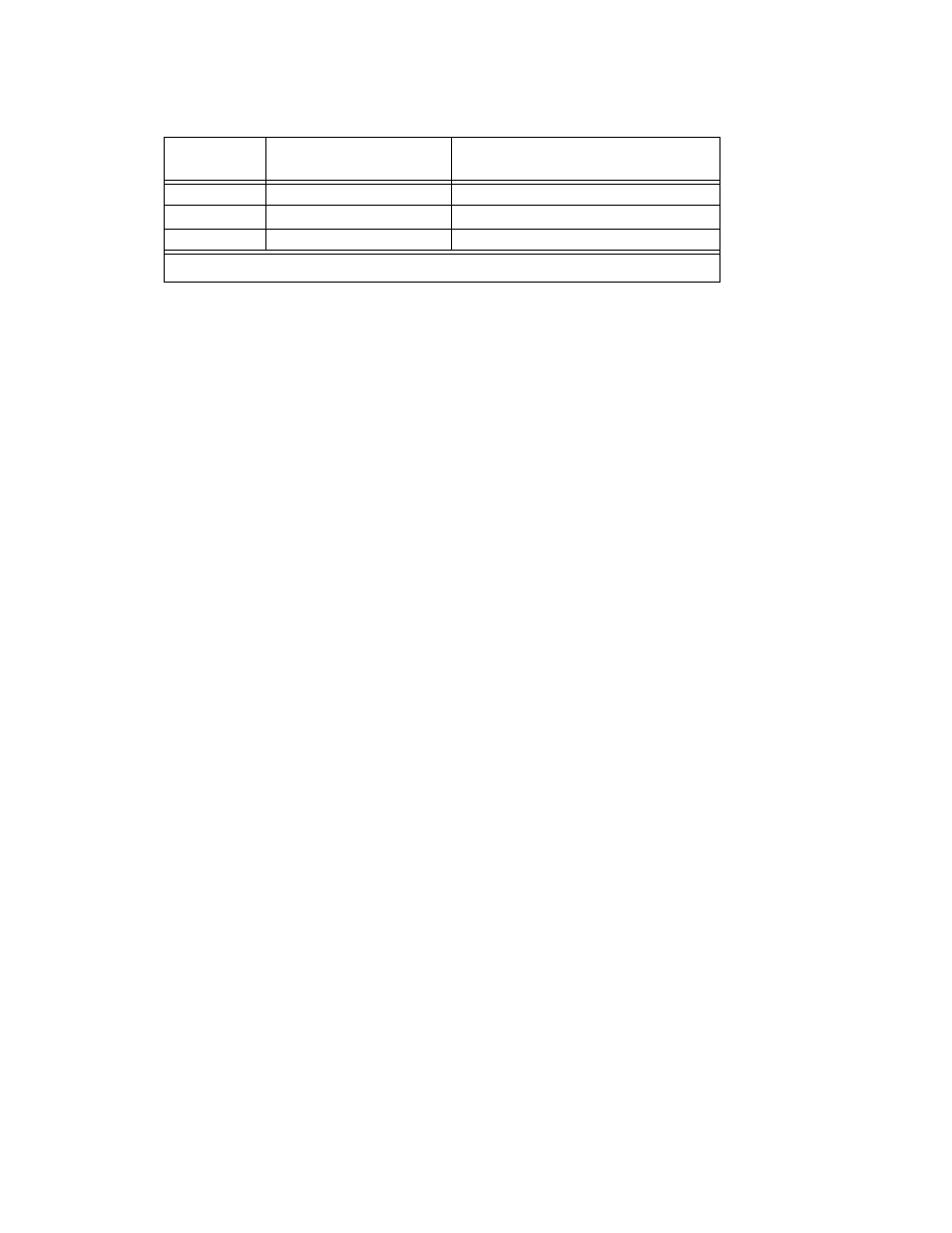
MST 75-2.5
60
1,600
MST 100-2
44
880
MST 150-1.2
30
400
TABLE 3-2. MAXIMUM EXTERNAL CAPACITANCE VALUES TO ENSURE DRY SWITCHING
MODEL
RETURN SUPPLY CURRENT
(MILLIAMPS)
MAXIMUM EXTERNAL CAPACITANCE *
(
µF)
* Values shown for worst case: T = 2 seconds and
∆
V = maximum voltage.
