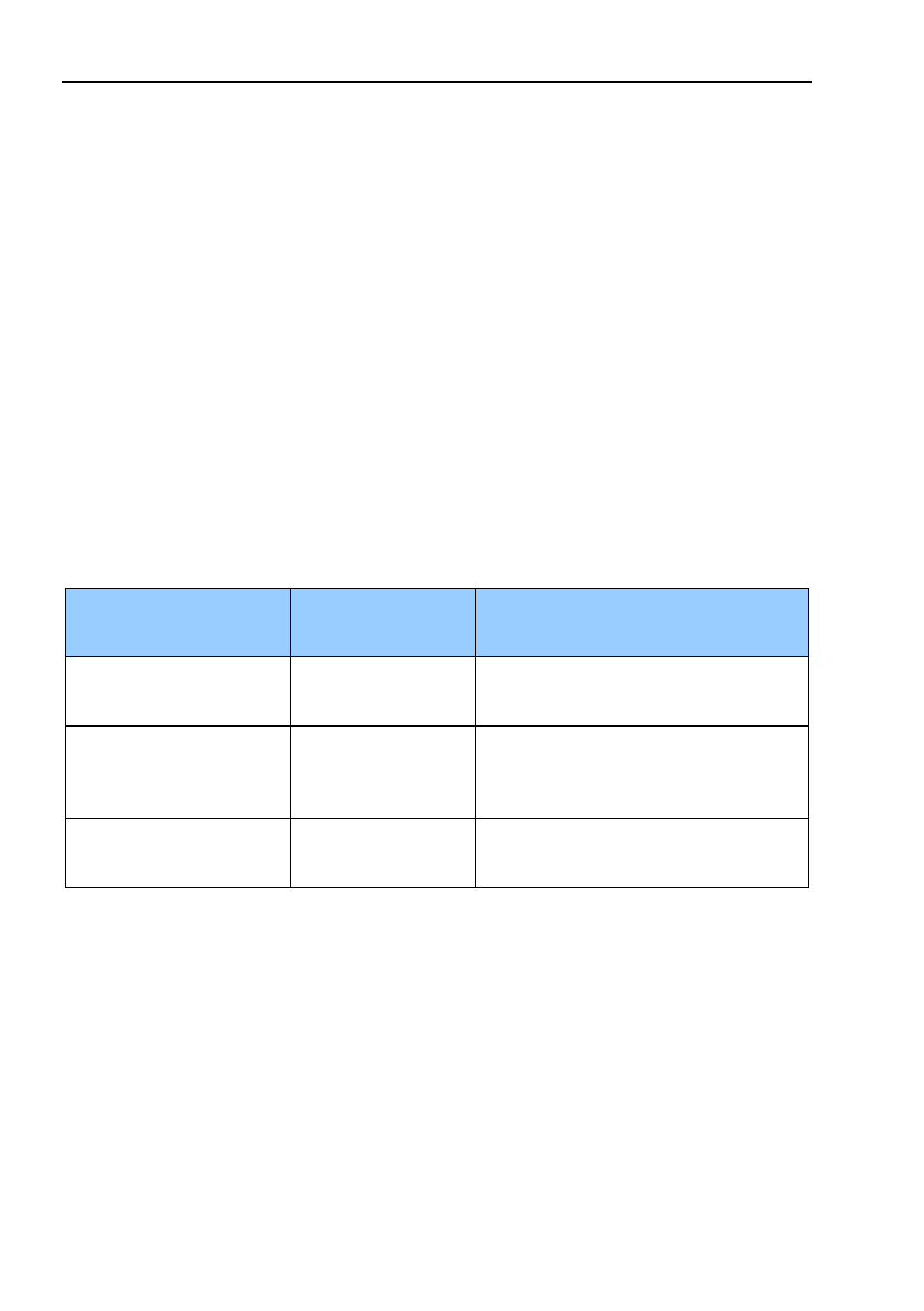
Table 21 channel diagnostics, Alarms and warnings, Diagnostics and alarms – HEIDENHAIN PROFINET User Manual
Page 50: Channel diagnostics, Table 21, 5alarms and warnings
Alarms and warnings
50
5
Alarms and warnings
5.1
Diagnostic data is always transferred acyclically using Record Data
communications over the non real time channel. An IO Supervisor
must specifically request the diagnostic or status data from the IO
device using RDO (Record Data Object) services.
Alarm data is transmitted from the IO device to the IO controller
Alarm is generated by the encoder when failure occurs which ef-
fects the position value. Alarms can be reset (deleted) when all
encoder parameters are within the specified value ranges and the
5.2
The encoder outputs a diagnostic interrupt to the CPU when it de-
tects one of the supported channel diagnostics.
Position error
The encoder fails to read the correct
The encoder fails to read stored
offset or preset values from the non
diagnostics
User parameter data assignment
Table 23
In a SIMATIC STEP 7 system the operation system responds by
calling a diagnostic OB. The OB number and start information pro-
vides the cause and location of the error. The error information can
be read by calling a system Function block (SFB54 RALRM for
STEP 7). Then the user can decide how the system should handle
Note: If the called OB is not included in the program the CPU
will go to stop.
