Deployment scenarios, Point to point bridge connection, Point to multi-point bridge connection – H3C Technologies H3C WA2600 Series WLAN Access Points User Manual
Page 62: Mesh bridge connection
9-2
z
Easy to deploy in scenarios of metro, company, office, large warehouses, manufacturing, ports and
waterfronts and so on
Deployment Scenarios
The WDS feature provides the following three topologies as required by actual applications.
Point to point bridge connection
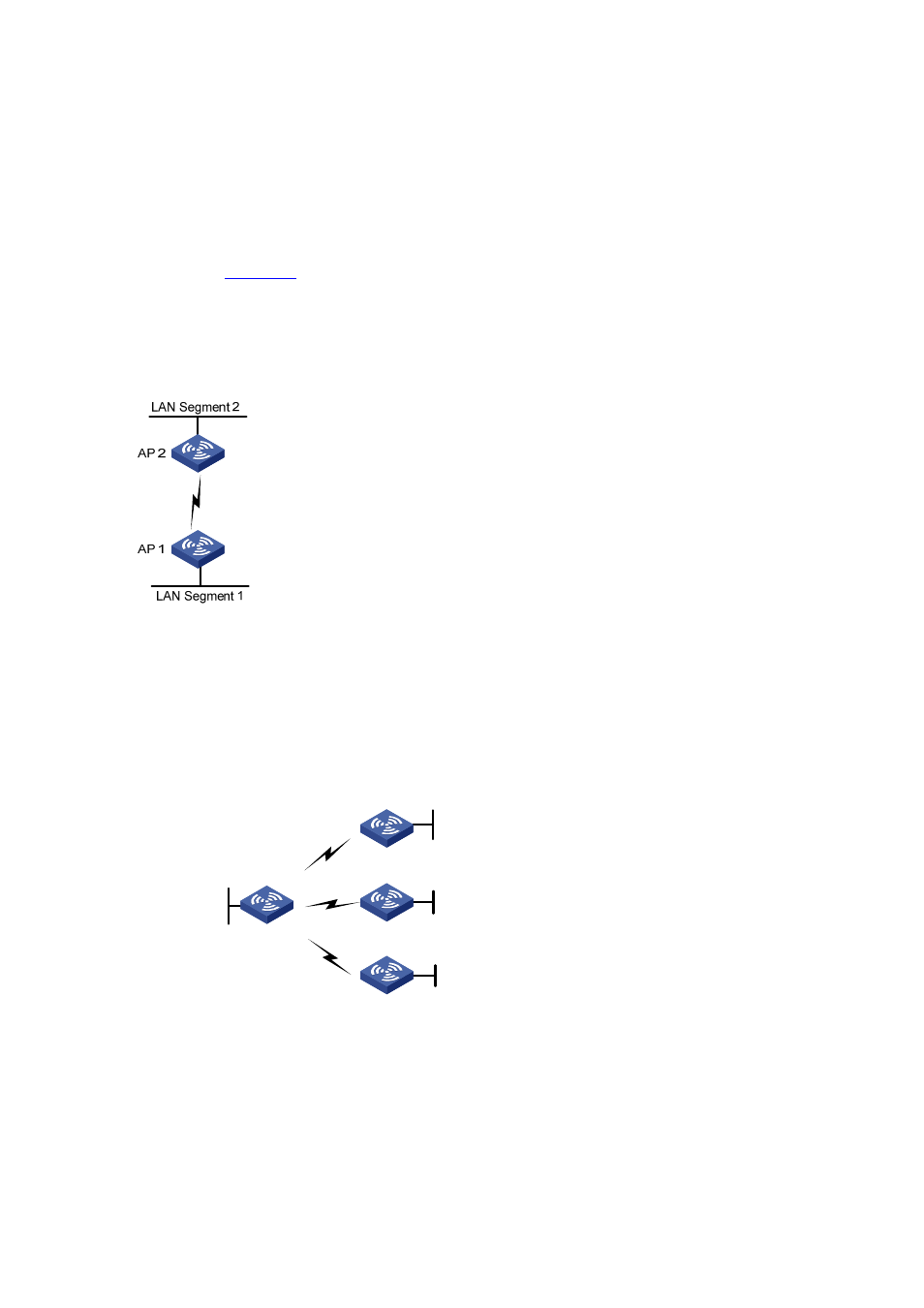
As shown in
, AP 1 and AP 2 create a WDS bridge link to connect LAN segment 1 and LAN
segment 2 to form a unified LAN. When users in LAN segment 1 are to access resources of LAN
segment 2, all packets will be transformed into wireless packets by AP 1, sent to AP 2 through the
wireless bridge link, restored on AP 2, and then sent to the destination, and vice versa.
Figure 9-1 WDS point to point topology
Point to multi-point bridge connection
In this topology, a device acts as the centralized device, and all the other devices set up wireless bridge
connections with only the centralized device, to interconnect multiple networks. This method
conveniently connects multiple network islands to existing networks. However, all data exchanged
between any two branch networks is forwarded by the centralized device.
Figure 9-2 WDS point to multi-point topology
LAN Segment 1
AP 2
AP 4
LAN Segment 2
LAN Segment 4
AP 1
AP 3
LAN Segment 3
Mesh bridge connection
In this topology, multiple bridging devices form mesh wireless bridge connections and interconnect
multiple LANs through manual configuration or self detection. In a mesh bridge network, when a WDS
link fails, a backup link can take over. However, you need to use STP to eliminate loops in actual
applications.
