Loop detection interval, Loop protection actions, Mstp configuration task list – H3C Technologies H3C S12500-X Series Switches User Manual
Page 114
103
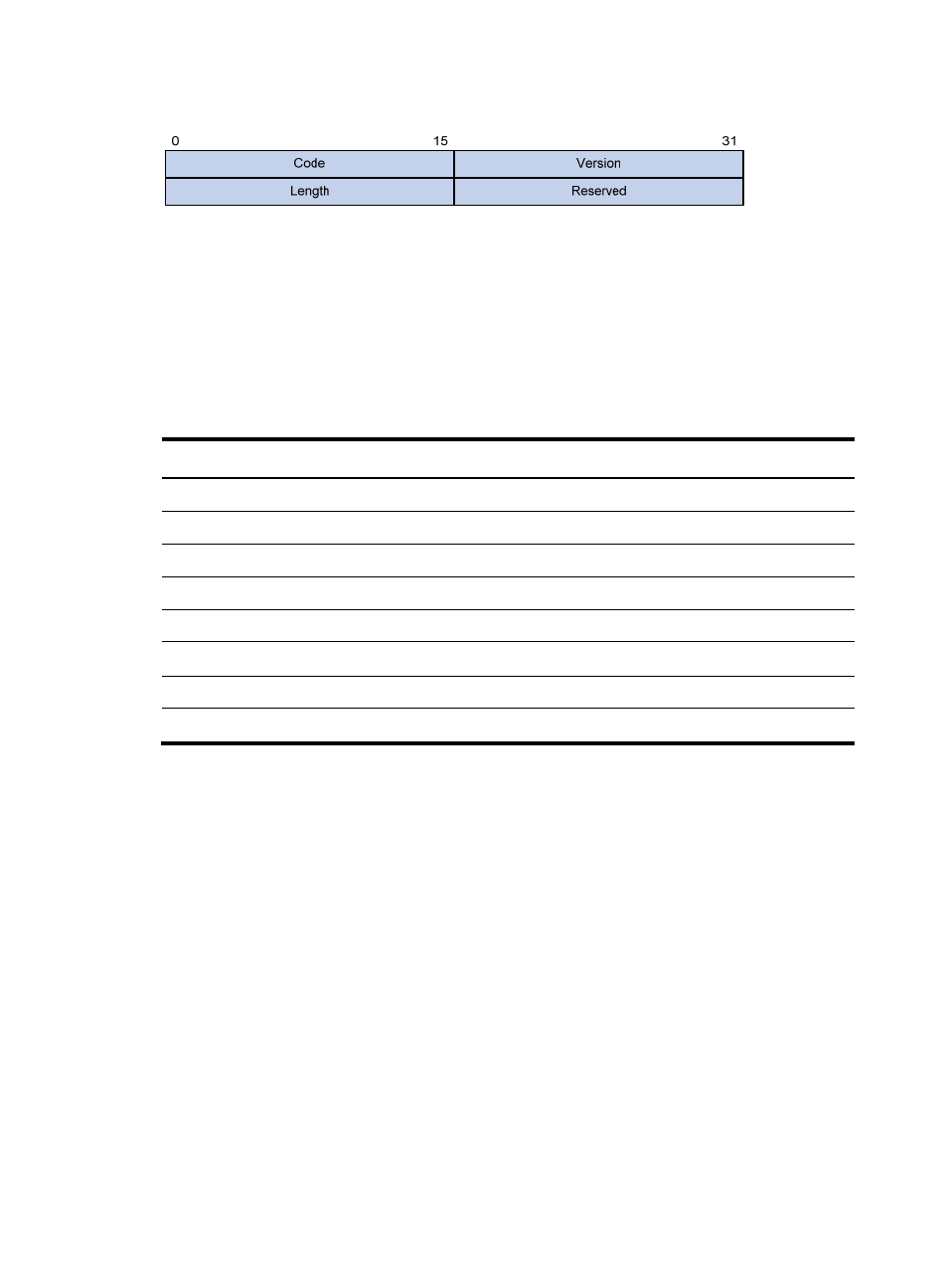
Figure 28 Inner frame header for loop detection
The inner frame header for loop detection contains the following fields:
•
Code—Protocol sub-type, which is 0x0001, indicating the loop detection protocol.
•
Version—Protocol version, which is always 0x0000.
•
Length—Length of the frame. The value includes the inner header, but excludes the Ethernet header.
•
Reserved—This field is reserved.
Frames for loop detection are encapsulated as TLV triplets.
Table 10 TLVs supported by loop detection
TLV
Description
Remarks
End of PDU
End of a PDU.
Optional.
Device ID
Bridge MAC address of the sending device.
Required.
Port ID
ID of the PDU sending port.
Optional.
Port Name
Name of the PDU sending port.
Optional.
System Name
Device name.
Optional.
Chassis ID
Chassis ID of the sending port.
Optional.
Slot ID
Slot ID of the sending port.
Optional.
Sub Slot ID
Sub-slot ID of the sending port.
Optional.
Loop detection uses the following important concepts.
Loop detection interval
Loop detection is a continuous process as the network changes. Loop detection frames are sent at a
specified interval (called a "loop detection interval") to check whether loops occur on ports and whether
loops are removed.
Loop protection actions
When the device detects a loop on a port, it generates a log but performs no action on the port by default.
You can configure the device to take one of the following actions:
•
Block—Disables the port from learning MAC addresses and blocks inbound traffic to the port.
•
No-learning—Disables the port from learning MAC addresses.
•
Shutdown—Shuts down the port to disable it from receiving and sending any frames. The port is
always in the down state until manually brought up with the undo shutdown command.
