Measurement Computing DaqBook 2000 Series User Manual
Page 66
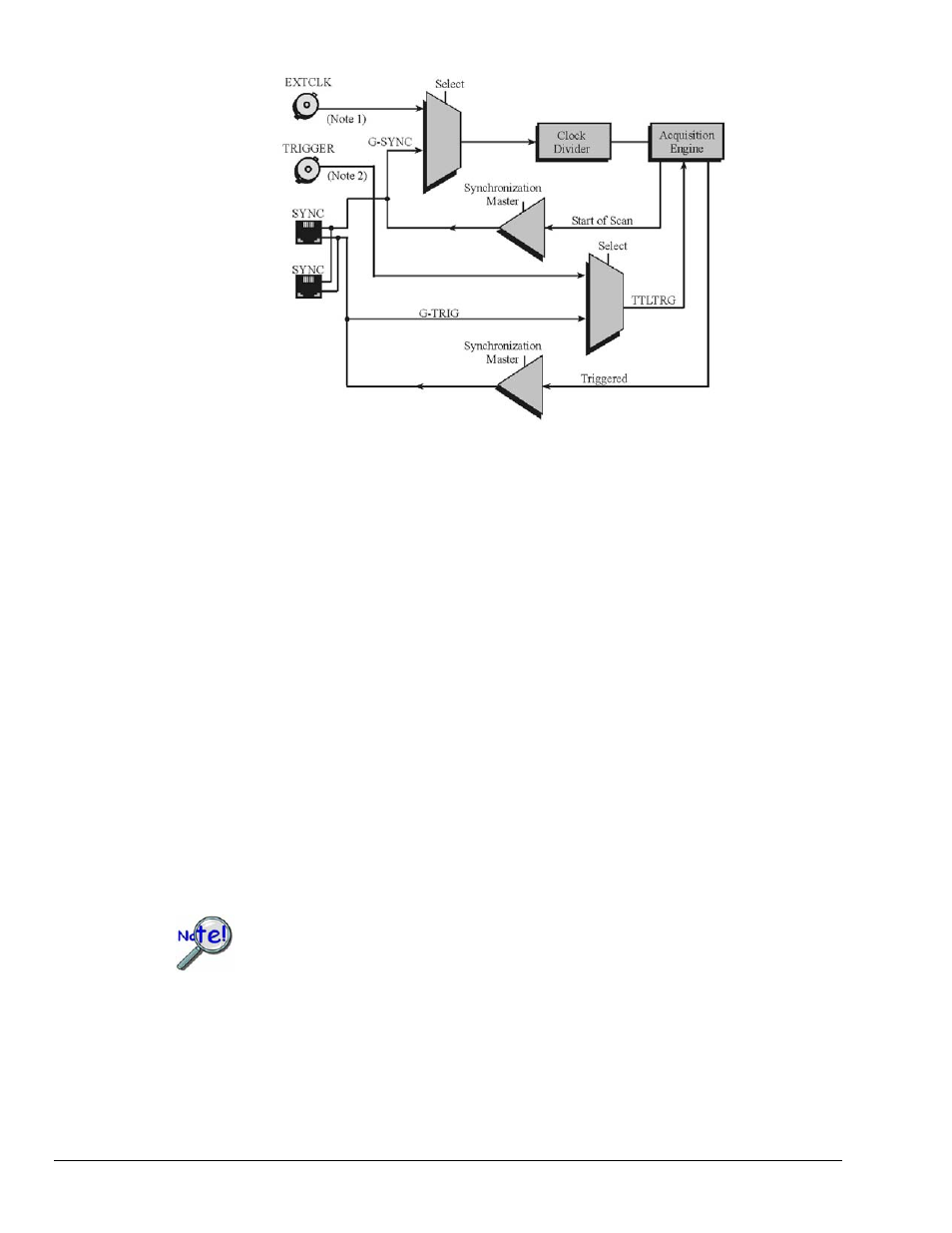
8-4 Taking Measurements
898695
DaqBook/2000 and DaqOEM/2000 Series
Synchronization Model for DaqBook/2000 and DaqOEM/2000 Series Devices,
DaqBook/2020 uses BNC
connectors for EXTCLK
and TRIGGER inputs.
The other devices use
pins as indicated in notes
1 and 2.
Note 1: For DaqBook/2001 and DaqBook/2005, the clock signal is from P1, pin 20.
For DaqOEM/2000 Series devices, the clock signal is from JP1, pin 2.
Note 2: For DaqBook/2001 and DaqBook/2005 the trigger signal is from P1, pin 25.
For DaqOEM/2000 Series devices, the trigger signal is from JP1, pin 12.
In regard to synchronization, the following applies:
•
One of three signals can be used to drive the DaqBook’s acquisition scan rate. These are:
−
the internal acquisition pacer clock
−
an external acquisition pacer clock.
−
the global sync (G-SYNC) input from the SYNC ports
•
Both the SYNC connector input and the external clock input can be divided down.
•
When a DaqBook is in the Master Mode, both the trigger condition and the scan timing are output
on the SYNC port. The global trigger (G-TRIG) is selected instead of the TTL Trigger Input.
Whether the DaqBook is using its internal scan clock, or external clock input, it can be programmed to
output the clock on the SYNC connector. In either case, the unit is behaving like a synchronization
master
. Other DaqBook units [that are connected to the master, via a SYNC port] should be programmed
as synchronization slaves.
When a DaqBook is programmed as a synchronization slave, it will derive its scan period from the SYNC
port. If the slave unit must be triggered at the same time as the master unit, then the slave unit should use
TTL Trigger as its trigger source.
Multi-unit synchronization via the SYNC ports does not support pre-trigger data.
Only post-trigger data can be collected and time correlated between the units.
