Guralp Systems CMG-6TD User Manual
Page 67
Configuration with Scream!
If you expect breaks in communication between the instrument and its client
to last more than 256 blocks, or if you want the instrument to handle breaks
in transmission (rather than relying on the client to request missed blocks),
you should use:
•
ADAPTIVE mode, if you want data to stay as near to real time as
possible (but do not mind if blocks are received out of order); or
•
FIFO mode, if you need blocks to be received in strict order (but do not
mind if the instrument takes a while to catch up to real time).
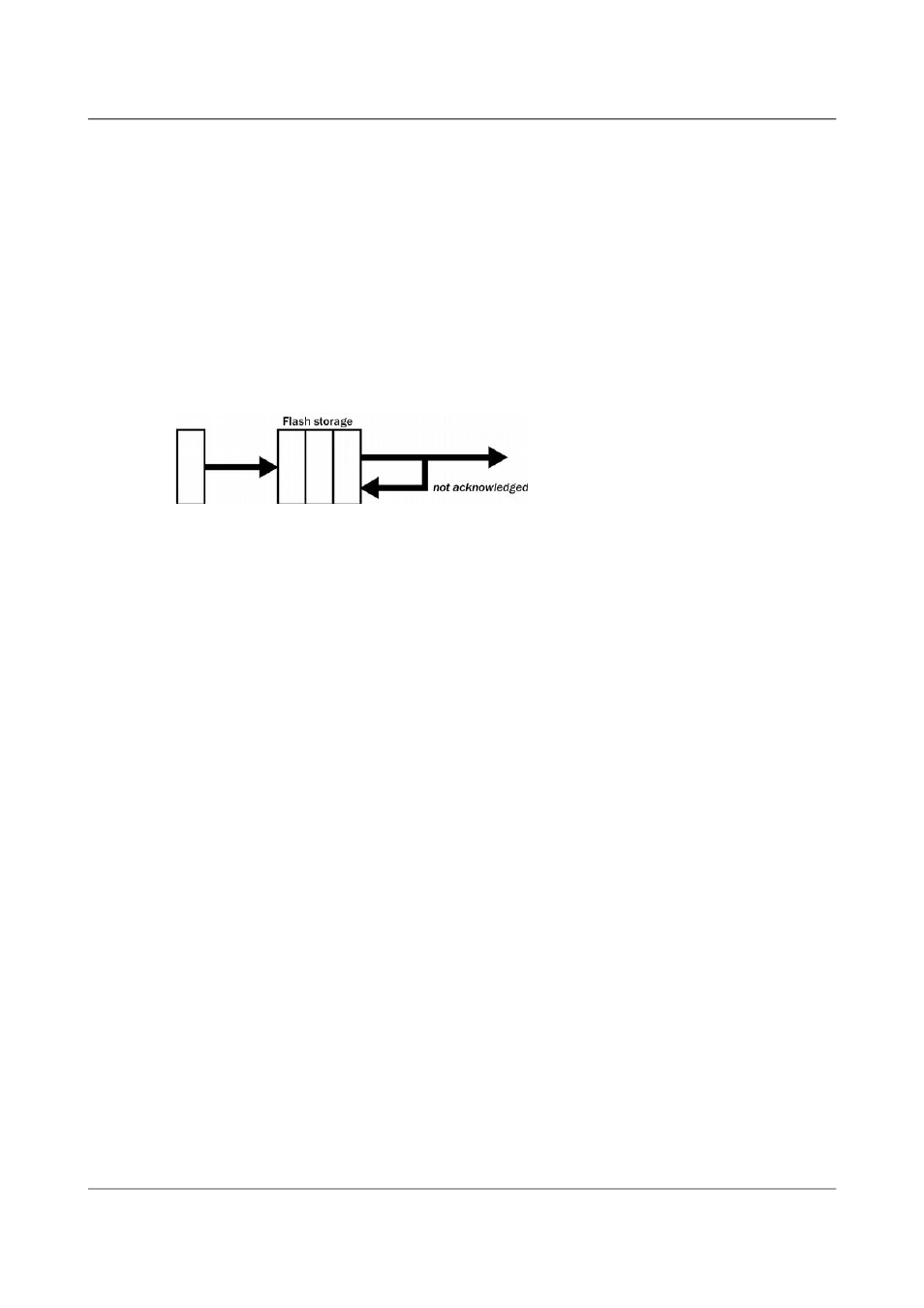
5.2.5.4 FIFO (First In First Out)
Syntax: FIFO
Instructs the 6TD to begin writing blocks to Flash memory as for FILING
mode, but also to transmit data to clients. Data are transmitted in strict order,
oldest first; the 6TD will only transmit the next block when it receives an
explicit acknowledgement of the previous block.
If the communications link is only marginally faster than the data rate, it will
take some time to catch up with the real-time data after an outage. If you
want data to be transmitted in real-time where possible, but are worried about
possible breaks in communication, you should use ADAPTIVE mode instead.
FIFO mode will consider a data block successfully transmitted once it has
received an acknowledgement from the next device in the chain. If there are
several devices between you and the instrument, you will need to set up the
filing mode for each device (if applicable) to ensure that data flow works the
way you expect.
Like all the filing modes, FIFO mode does not delete data once it has been
transmitted. You can still request anything in the Flash memory using
Scream! or over the command line. The only way data can be deleted is if
they are overwritten (in the RECYCLE buffering mode, see below) or if you
delete it manually.
67
Issue F - February 2014
