equinux VPN Tracker 8.1.1 User Manual
Page 40
Make sure the host you are trying to reach knows where to
send replies
This one is a little more complex to check. Start with checking if your local
address is part of the remote network:
‣ Connect the VPN
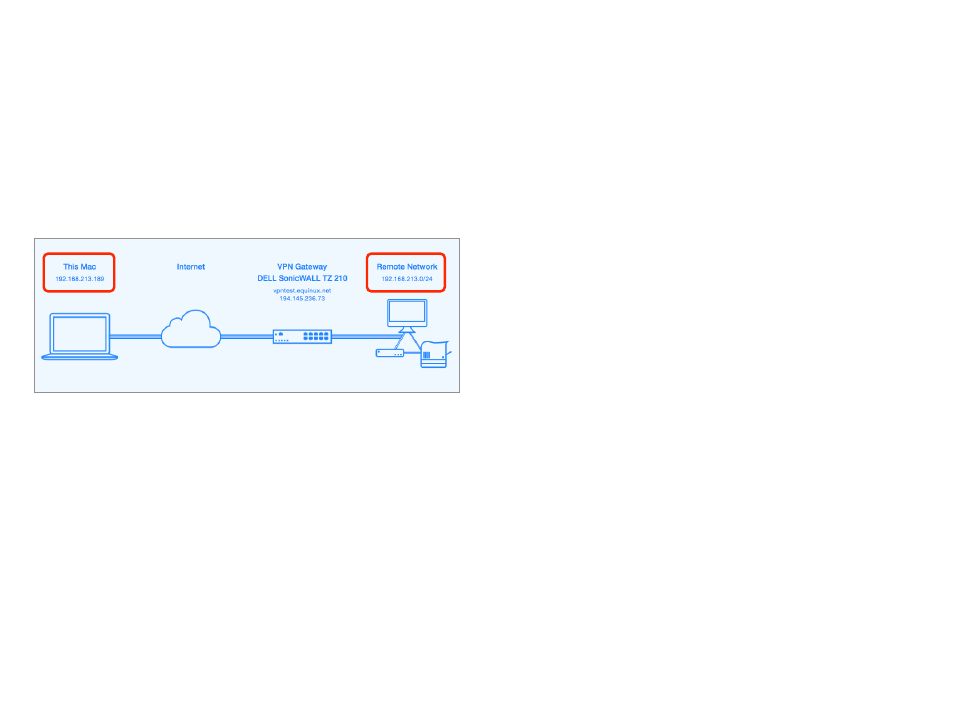
‣ Go to the Status tab
‣ Compare the IP address listed under “This Mac” (local address) and the
networks listed under “Remote Network”. Is the local address part of the
remote network(s)?
In this example, the local address 192.168.213.189 is part of the remote network
192.168.213.0/24
If the local address is part of the remote network(s):
There are exactly three setups where the local IP address may be part of the
remote network(s). If your setup is not one of these, you must choose a local
address that is
not part of the remote network(s).
1. When connecting to a SonicWALL using SonicWALL Simple Client Provision-
ing or DHCP over VPN.
2. When connecting to a Cisco VPN gateway using Cisco EasyVPN.
3. When connecting to a VPN gateway that can act as an ARP proxy for IP ad-
dresses assigned through Mode Config, and/or for fixed local addresses.
That third one is a bit tricky to figure out. If you find a reference to ARP Proxy
(or Proxy ARP) in the device’s documentation, or if the manual specifically in-
structs to choose the local address or the Mode Config address pool to be
part of the remote network, then it’s ok for the IP address to be part of the
remote network.
In all other cases you must choose an IP address as the local address (or a
Mode Config address pool) that is not part of the remote network(s). If
you are using Mode Config, you need to change the Mode Config address
pool on the VPN gateway. Otherwise, simply change the local address in VPN
Tracker (Basic > Local Address).
If the local IP is not part of the remote network(s):
Check if your VPN gateway is the default gateway (router) of its network.
If your VPN gateway is not the default gateway of the remote network, you
will have to ensure that responses to all IP addresses used by VPN clients are
routed to the VPN gateway. You can do so either by adding a general route on
the network’s actual default gateway, or by adding individual routes on each
host that VPN clients need to communicate with.
40
