Hardware identification glossary of modeling terms – Carl Goldberg GPMA1968 Tiger 60 ARF User Manual
Page 6
6
HARDWARE IDENTIFICATION
GLOSSARY OF MODELING TERMS
ARF: Almost Ready to Fly
AILERON: the control surface on the wing that rolls the
plane
AIRFOIL: the shape of the wing as seen from the end
ANGLE OF ATTACK: the angle at which the wing meets
the air flow
BEVEL: to sand to an angle shape
BURR: the rough edges on a piece of wood or metal after
it is cut
CAP STRIP: a thin strip glued to the edges of the ribs to
shape the wing
CONTROL HORN: a device attached to each control sur-
face to provide an attachment point for the pushrod
COWL (COWLING): the nose section of the fuselage that
encloses the engine
DECALAGE: the difference between the incidence of the
wing and stabilizer
DIHEDRAL: the upward angle of the wings, as seen from
the front
ELEVATOR: the moveable part of the horizontal tail,
which controls pitch
EMPENNAGE: the tail of the plan
FIN: the fixed vertical part of the tail
FIREWALL: the hard wooden former at the front of the
fuselage, to which the engine is mounted
FORMER: a piece which shapes the fuselage; and to
which the sides of the fuselage are attached.
GUSSET: a small triangular piece glued into a corner to
strengthen it
INCIDENCE: the angle of the wing or the tail in relation
to the thrustline
LAMINATE: to glue two thin sheets of material together
to form a thick sheet
LEADING EDGE (L.E.): the edge of the wing that first
meets the airflow
LONGERON: a stringer that runs the length of the fuse-
lage
OUTPUT ARM: the piece that attaches to the servo and
connects it to the pushrod
PITCH: an up and down movement of the nose of the
plane, which is controlled by the elevator
PROTOTYPE: the full scale airplane from which the
model design was taken
PUSHROD: the long, stiff dowel, plastic or wire piece that
connects the servo with the control horn
RTF: Ready to Fly
RIB: the airfoil-shaped piece that connects the leading
edge, spars and trailing edge of the wing together
and holds them in shape
RETRACTS: devices for extending and retracting the
wheels on command
ROLL: tilting of the plane as viewed from the front, con-
trolled by the ailerons
RUDDER: the moveable vertical tail of the plane, which
controls yaw
SERVO: the part of the airborne radio system that
moves the control surfaces
SHEAR WEB: wood sheeting that connects the top and
bottom spars to stiffen the wing
SHIM: a thin piece of wood inserted between two other
pieces to improve their fit
SPAR: a wooden stick running lengthwise through the
wing that serves as its backbone
SPINNER: the rounded cone that fits over the propeller
hub
STABILIZER (STAB): the fixed horizontal part of the tail
STALL: a situation in which the plane is flying too slow-
ly to move sufficient air across the wing to produce
lift
STRINGER: a long piece of wood attached to the form-
ers to shape the fuselage
THRUSTLINE: a line drawn from the center of the pro-
peller hub straight through the airplane
TORQUE: a rolling tendency caused by the spinning
propeller
TRAILING EDGE (T.E.): the edge of the wing that faces
the rear of the plane
TRIM: small adjustments made to the control surfaces
to cause the plane to fly straight and level by itself
WASHIN: a twist in the wing that makes the trailing
edge lower than normal
WASHOUT: a twist in the wing that makes the trailing
edge higher than normal
WING SADDLE: the shaped part of the fuselage in
which the wing rests
WHEEL COLLAR: a metal ring that holds the wheel on
the axle
YAW: a right-to-left movement of the nose, controlled by
the rudder
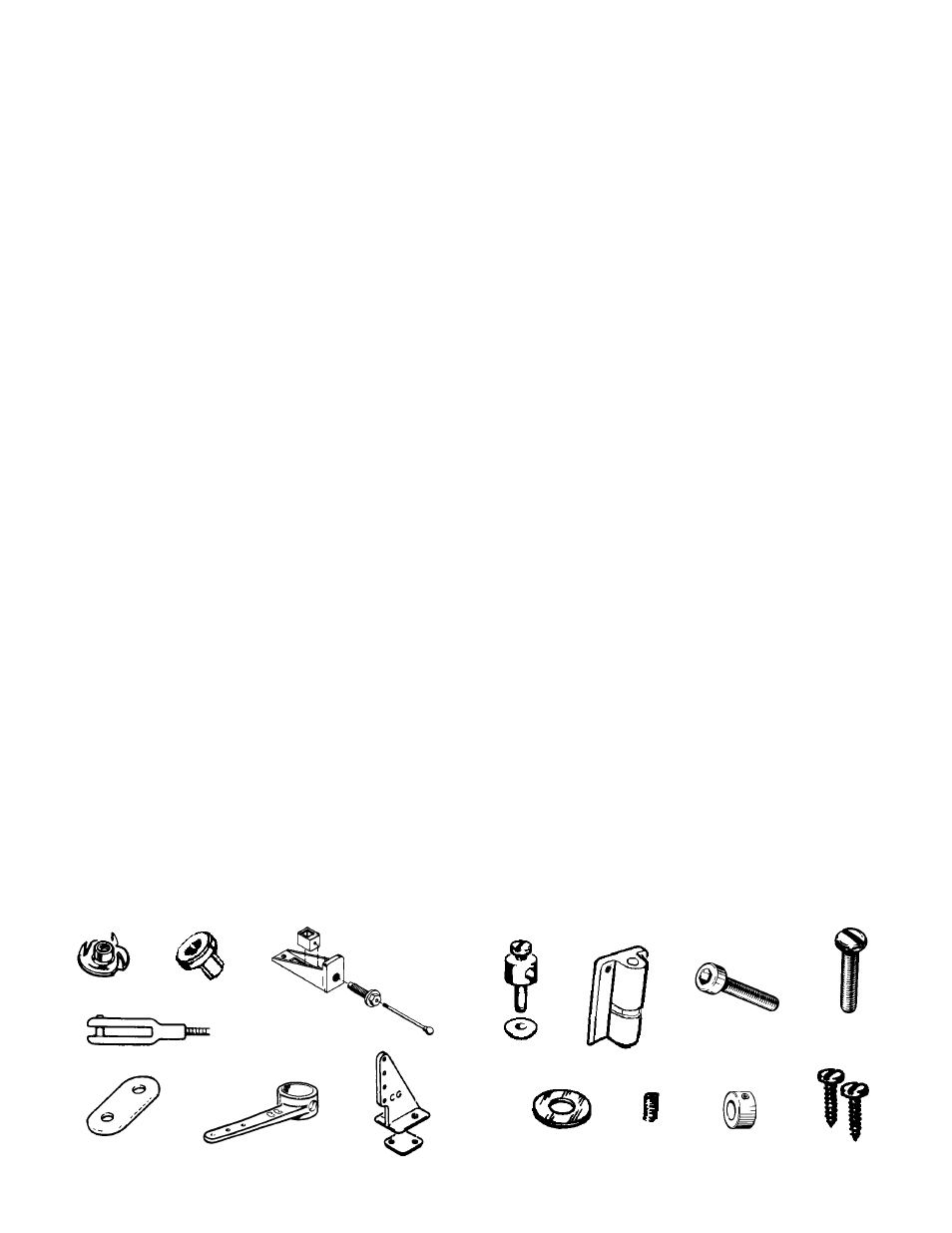
BLIND NUT
EYELET
PUSHROD CONNEC-
TOR WITH SNAP NUT.
NOSE GEAR BLOCK
SNAP LINK
LANDING GEAR
STRAP
STEERING ARM
CONTROL HORN
ON/OFF SWITCH
SOCKET HEAD
SCREW
WHEEL COLLAR
PAN HEAD
SCREW
SHEET METAL
SCREW
SET SCREW
WASHER
