Brookfield DV-I Prime User Manual
Page 37
Brookfield Engineering Laboratories, Inc.
Page 37
Manual No. M/07-022-D0613
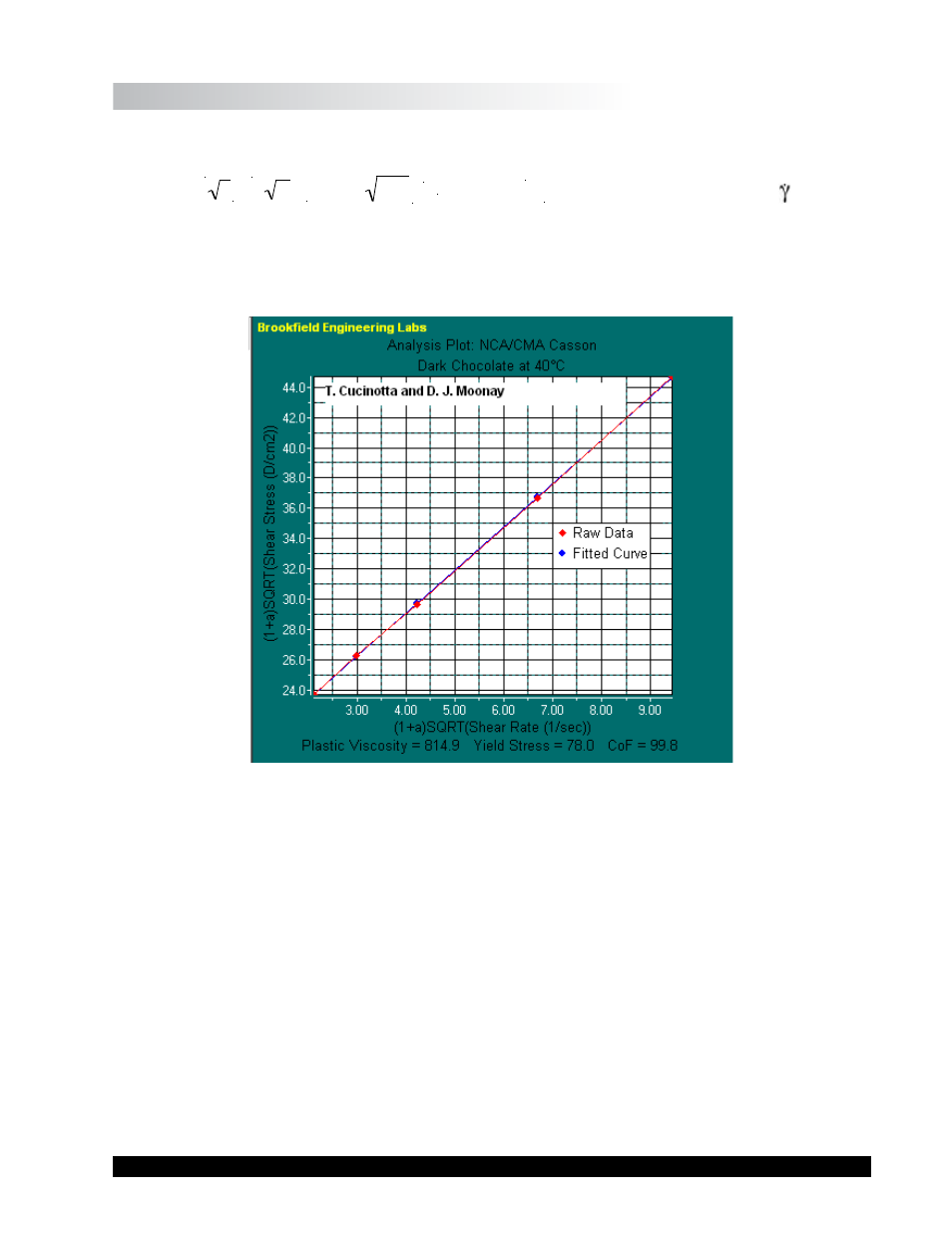
II.12.5 Other Common Rheological Models
The NCA/CMA Casson Model
(1 + a)
€
t
=
€
2
t
o
+
(1 + a)
€
hg
(
€
t
= shear stress
,
€
t
o
= yield stress,
h
= plastic viscosity, and
= shear rate)
The NCA/CMA Casson model is designed by the National Confectioners Association and the
Chocolate Manufacturers Association as the standard rheological model for the industry. This
model determines yield and flow properties under specified conditions and closely approximates
the plastic behavior of chocolate before final processing.
Figure II-47
When chocolate is used for enrobing, it must have a yield stress high enough to stay in place once
it enrobes the filling. In the case of decorating chocolate, the yield stress must be high enough so it
can keep its shape once it has been squeezed into place through a nozzle. For molding chocolate,
the plastic viscosity must be low enough to completely fill the mold.
(The NCA/CMA lists Brookfield’s HA-spring range viscometer with a Small Sample Adapter,
SC4-27 spindle and SC4-13R sample chamber as the approved apparatus.)
The IPC Paste Model
h
=kR
n
(
h =
viscosity
,
k
= consistency index, R = rotational speed, n = shear sensitivity factor)
The IPC Paste Model was developed for solder pastes. It calculates the viscosity of solder pastes
at 10rpm. The IPC Paste Model requires that the product be tested with a Brookfield Spiral
Adapter at multiple speeds. More details can be found in the IPC-TM-650 Test Methods Manual
(methods 2.4.34.2 and 2.4.3).
