2t.03 introduction to plasma, Cutmaster 42 introduction – Tweco 42 CutMaster Service Manual User Manual
Page 20
CUTMASTER 42 INTRODUCTION
Introduction 2T-2 Manual 0-5171
2T.03 Introduction to Plasma
A. Plasma Gas Flow
Plasma is a gas which has been heated to an ex-
tremely high temperature and ionized so that it be-
comes electrically conductive. The plasma arc cutting
and gouging processes use this plasma to transfer
an electrical arc to the workpiece. The metal to be
cut or removed is melted by the heat of the arc and
then blown away.
While the goal of plasma arc cutting is separation of
the material, plasma arc gouging is used to remove
metals to a controlled depth and width.
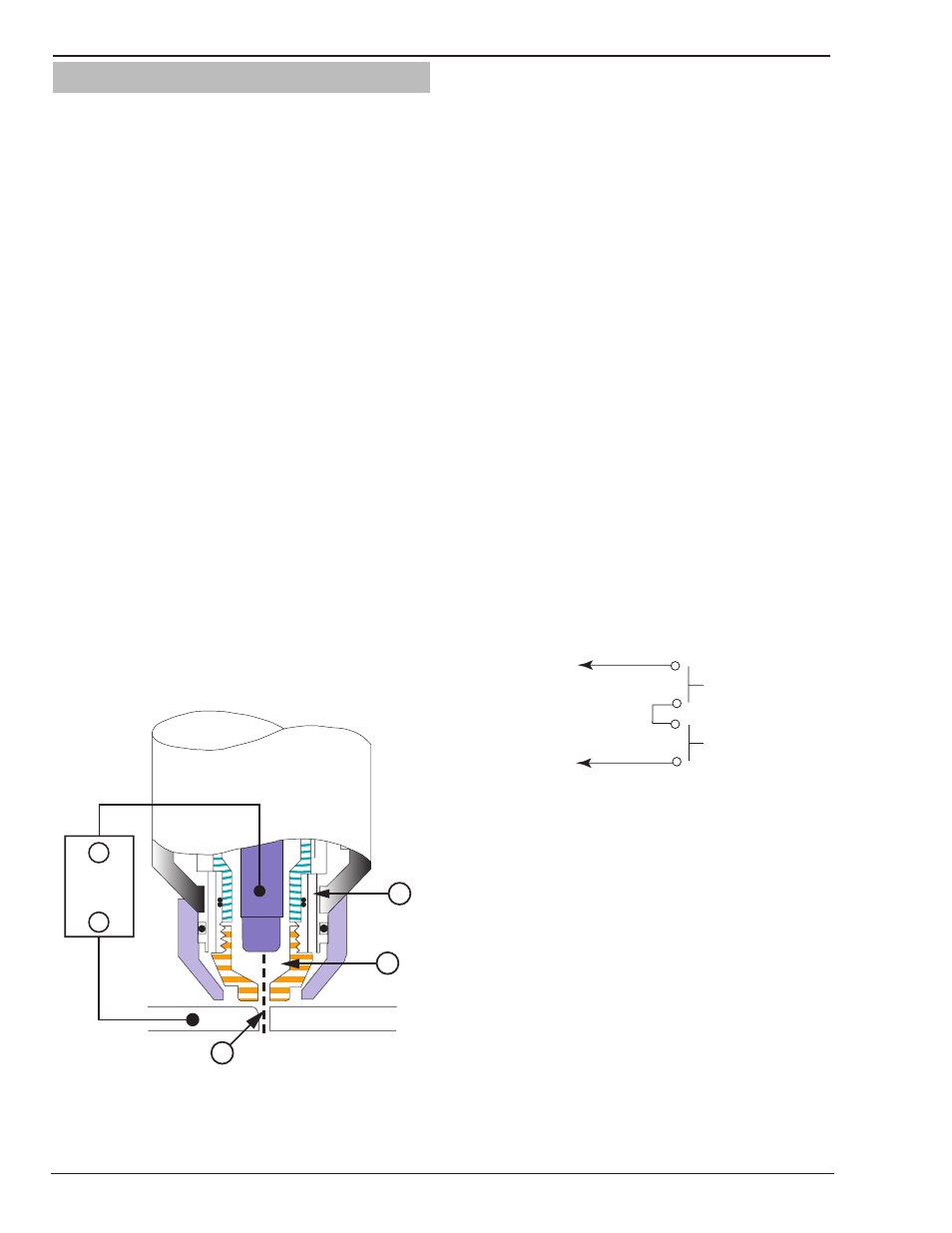
In a Plasma Cutting Torch a cool gas enters Zone B,
where a arc between the electrode and the torch tip
heats and ionizes the gas. The main cutting arc then
transfers to the workpiece through the column of
plasma gas in Zone C.
By forcing the plasma gas and electric arc through a
small orifice, the torch delivers a high concentration
of heat to a small area. The stiff, constricted plasma
arc is shown in Zone C. Direct current (DC) straight
polarity is used for plasma cutting, as shown in the
illustration.
Zone A channels a secondary gas that cools the torch.
This gas also assists the high velocity plasma gas in
blowing the molten metal out of the cut allowing for
a fast, slag - free cut.
A-00002
Workpiece
Power
Supply
+
_
C
B
A
Typical Torch Head Detail
B. Gas Distribution
The single gas used is internally split into plasma and
secondary gases.
The plasma gas flows into the torch through the
negative lead, through the starter cartridge, around
the electrode, and out through the tip orifice.
The secondary gas flows down around the outside
of the torch starter cartridge, and out between the tip
and shield cup around the plasma arc.
C. Pilot Arc
When the torch is started a pilot arc is established
between the electrode and cutting tip. This pilot arc
creates a path for the main arc to transfer to the work.
D. Main Cutting Arc
DC power is also used for the main cutting arc. The
negative output is connected to the torch electrode
through the torch lead. The positive output is con-
nected to the workpiece via the work cable and to the
torch through a pilot wire.
E. Parts - In - Place (PIP)
The torch includes a 'Parts - In - Place' (PIP) circuit.
When the shield cup is properly installed, it closes
a switch. The torch will not operate if this switch is
open.
Torch Trigger
PIP Switch
Shield Cup
To Control
Cable Wiring
Torch Switch
A-09595
Parts - In - Place Circuit Diagram for Hand Torch
