tekmar 263 Boiler Control User Manual
Page 9
9
of
36
©
2009 D
263
-
03/09
Example 1:
A boiler requires a 1.8 V (dc) signal to fire the boiler at low fire. The boiler can be modulated to 10 V (dc) where it reaches high fire.
This means the boiler’s input signal range is 1.8 to 10 V (dc). The 263 control has an output signal range of 0 to 20 mA which can be
externally converted to 0 to 10 V (dc) using a 500 Ω resistor (Refer to Modulation Output section in Step 4 of the Installation section).
To make the two signal ranges the same, the Minimum Modulation required is:
Minimum Modulation =
0 V – 1.8 V
0 V – 10 V
x 100% = 18%
Example 2:
If the boiler’s input signal range is 6 to 20 mA the required Minimum Modulation is:
Minimum Modulation =
4 mA – 6 mA
4 mA – 20 mA
x 100% = 13%
MAXIMUM MODULATION
The maximum modulation defines the maximum output signal from the control to the boiler burner. It is based on a percentage of
the control’s output signal range.
The Maximum Modulation setting for boilers with power burners is typically set to 100%.
For boilers with electronic operators, the boiler’s input signal range may not match the output signal range of the 263 control. The
Maximum Modulation
setting limits the control output range in order to match the boiler’s input range.
To calculate the Maximum Modulation, use the following formulae:
For 4 to 20 mA:
Maximum Modulation =
4 mA – Boiler’s Maximum Input Signal
4 – 20 mA
x 100%
For 0 to 10 V (dc):
Maximum Modulation =
0 V (dc) – Boiler’s Maximum Input Signal
0 – 10 V (dc)
x 100%
For 2 to 10 V (dc):
Maximum Modulation =
2 V (dc) – Boiler’s Maximum Input Signal
2 – 10 V (dc)
x 100%
Example 1:
A boiler’s input signal range is 2 to 9 V (dc). The 263 control has an output signal range of 2 to 10 V (dc).
To make the two signal ranges the same, the Maximum Modulation required is:
Maximum Modulation =
2 V – 9 V
2 V – 10 V
x 100% = 88%
Example 2:
If the boiler’s input signal range is 6 to 19 mA the required Maximum Modulation is:
Maximum Modulation =
4 mA – 19 mA
4 mA – 20 mA
x 100% = 94%
BOILER MASS
The Boiler Mass setting allows the installer to adjust the control to the thermal mass of the type of heat sources used in the
application. The modulation of the boiler can become unstable if the incorrect Boiler Mass setting is chosen. A key sign of the boiler
modulation being unstable is the flame will continue to increase and then decrease in short periods of time. By choosing a lower
Boiler Mass
setting, the boiler response will become more stable.
Lo (1)
The Lo setting is selected if the boiler that is used has a low thermal mass. This means that the boiler has a very small water
content and has very little metal in the heat exchanger. A boiler that has a low thermal mass comes up to temperature quite rapidly
when fired. This is typical of many copper fin-tube boilers. The Lo Mass setting provides a fast response to the heating system.
Med (2)
The Med setting is selected if the boiler that is used has a medium thermal mass. This means that the boiler either has a large
water content and a low metal content or a low water content and a high metal content. This is typical of many modern residential
cast iron boilers or steel tube boilers. The Med Mass setting provides a moderate response to the heating system.
Hi (3)
The Hi setting is selected if the boiler that is used has a high thermal mass. This means that the boiler has both a large water
content and a large metal content. A boiler that has a high thermal mass is relatively slow in coming up to temperature. This is
typical of many commercial cast iron and steel tube boilers. The Hi Mass setting provides a slow response to the heating system.
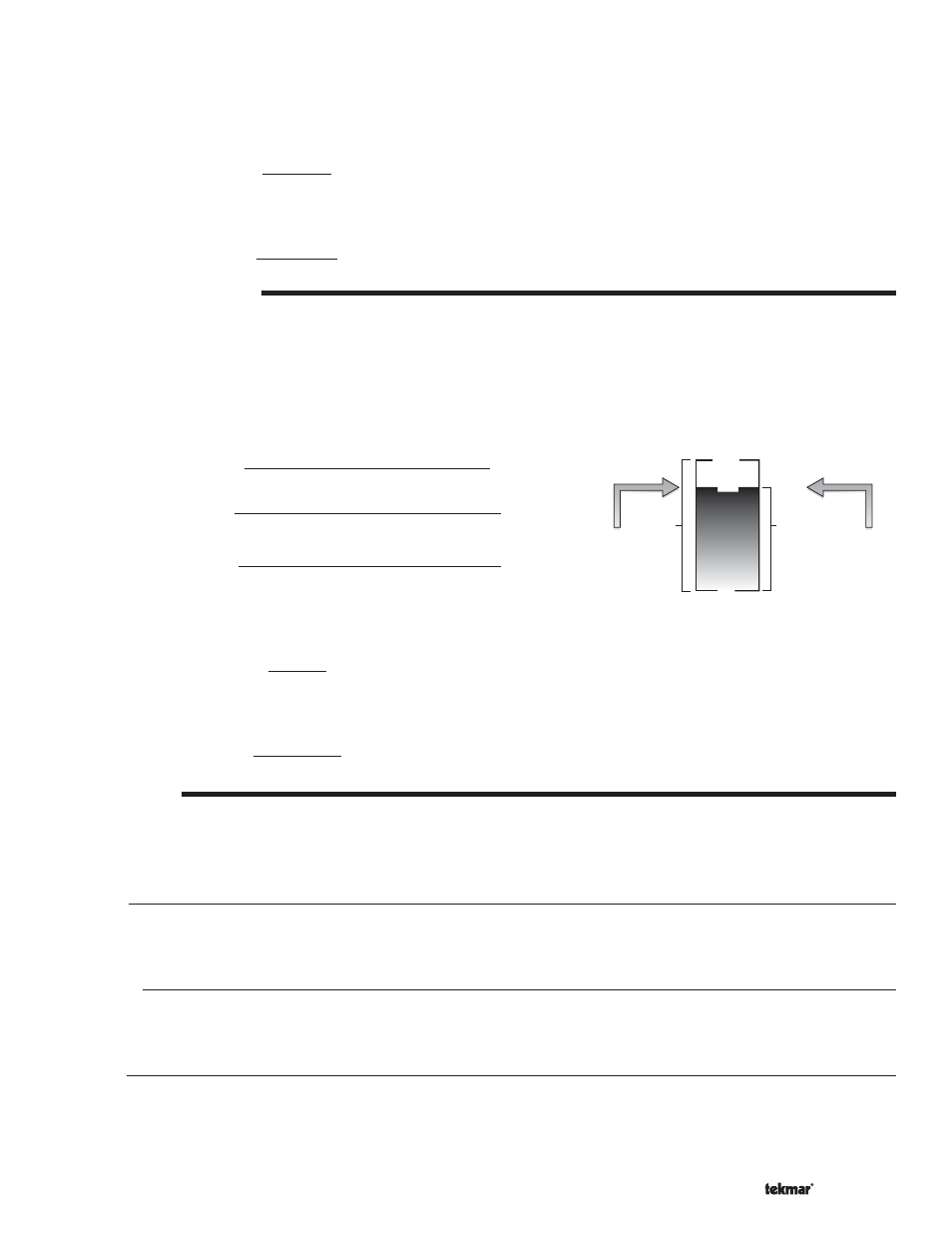
MAXIMUM MODULATION
88%
0%
2 V (dc)
2 V (dc)
100%
10 V (dc)
9 V (dc)
Control's
Output
Signal
Range
Maximum
Modulation
Boiler's
Maximum
Input Signal
Boiler's
Input
Signal
Range
