Glossary of terms, Powerflex 7000 performance – Rockwell Automation 7000A PowerFlex Medium Voltage AC Drive (A Frame) - ForGe Control (PanelView 550) User Manual
Page 191
Catalog Number Explanation – Drive Selection B-5
7000 “A” Frame
7000A-UM151D-EN-P – March 2013
The PowerFlex 7000 drives have been tested on a dynamometer to
verify performance under locked rotor, accelerating, and low speed-
high torque conditions. Table B-4 below shows the PowerFlex 7000
drive torque capabilities as a percent of motor rated torque, independent
of the drive’s momentary overload conditions.
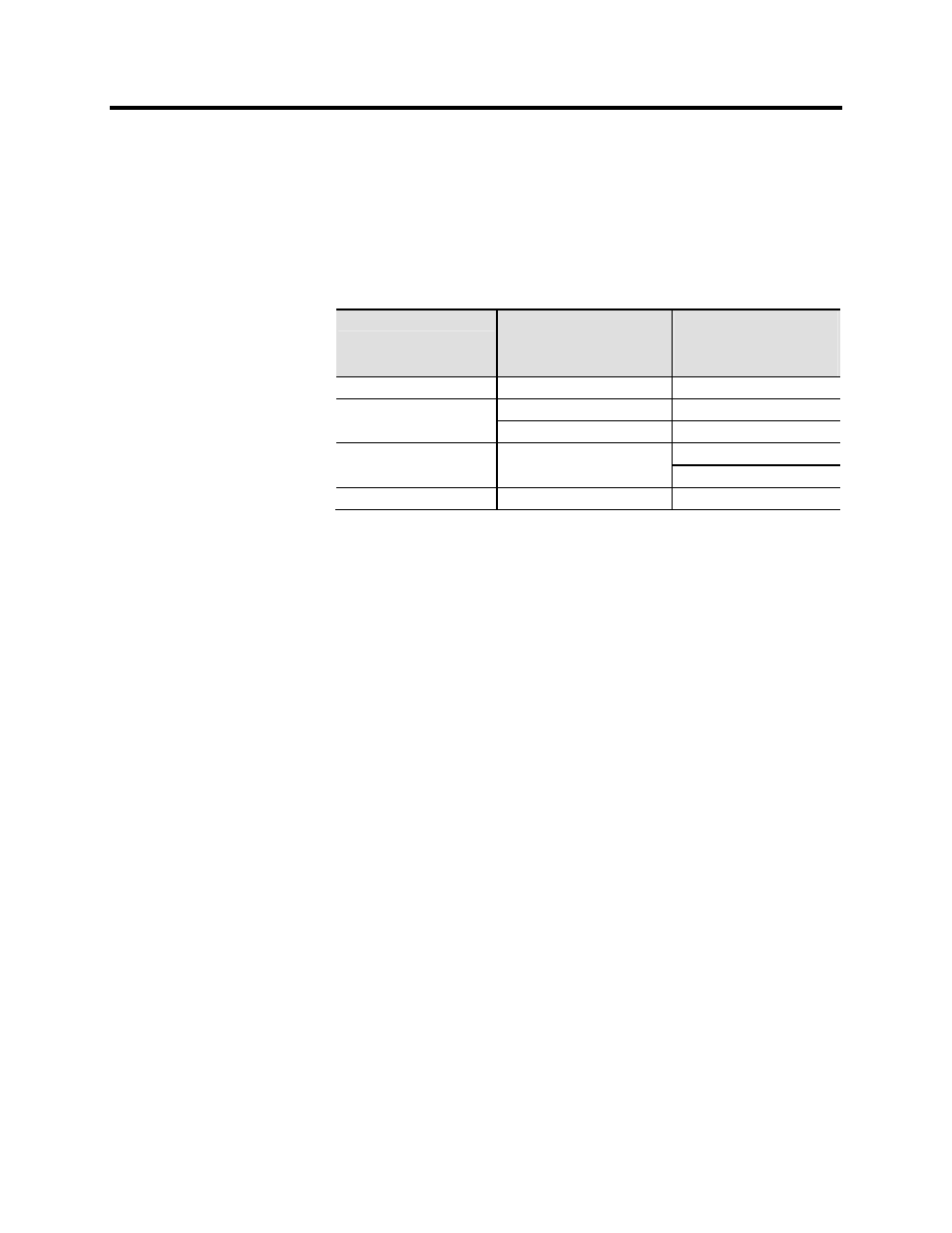
Table B-4 – PowerFlex 7000 Drive Torque Capabilities
Parameter
7000 Torque Capability
Without Tachometer
(% of Motor Rated Torque)
7000 Torque Capability
With Tachometer
(% of Motor Rated Torque)
Breakaway Torque
90%
150%
Accelerating Torque
90% ( 0-8 Hertz )
140% ( 0-8 Hertz )
125% ( 9-75 Hertz )
140% ( 9-75 Hertz )
Steady State Torque
125% ( 9-75 Hertz ) **
100% ( 1-2 Hertz )
140% ( 3-60 Hertz ) **
Maximum Torque Limit
150%
150%
** Drive will require over sizing to achieve greater than 100% continuous torque.
Glossary of Terms
Breakaway Torque:
Torque required to start a machine from standstill.
Accelerating Torque:
Torque required to accelerate a load to a given speed, in a certain
period of time. The following formula may be used to calculate the
average torque to accelerate a known inertia (WK
2
):
T = ( WK
2
× change in RPM) / 308t
where,
T
= acceleration torque in (lb-ft).
WK
2
= total system inertia (lb-ft
2
) that the motor
must accelerate, including motor, gear box, and load.
t
= time (seconds) to accelerate total system load.
Steady State Torque:
Continuous operating torque required to control the load, without
instability.
Torque Limit:
An electronic method of limiting the maximum torque available from
the motor.
The software in a drive typically sets the torque limit to 150% of motor
rated torque.
PowerFlex 7000
Performance
(Torque Capabilities)
