Assignment command – Rockwell Automation 1775-KA PLC-3 Communication Adapter Module User Manual User Manual
Page 80
Message Procedure Commands
Chapter 6
6Ć2
Blanks may be inserted anywhere to improve the readability of a message
procedure. However, blanks should be kept to a minimum because they
use memory space and slow execution of the message procedure.
The assignment command is the most fundamental yet versatile of all the
commands. Its primary purpose is to copy data from the source location to
the destination location. Table 6.B lists the various types of sources and
destinations. Any type of source in Table 6.B may be used with any type
of destination listed.
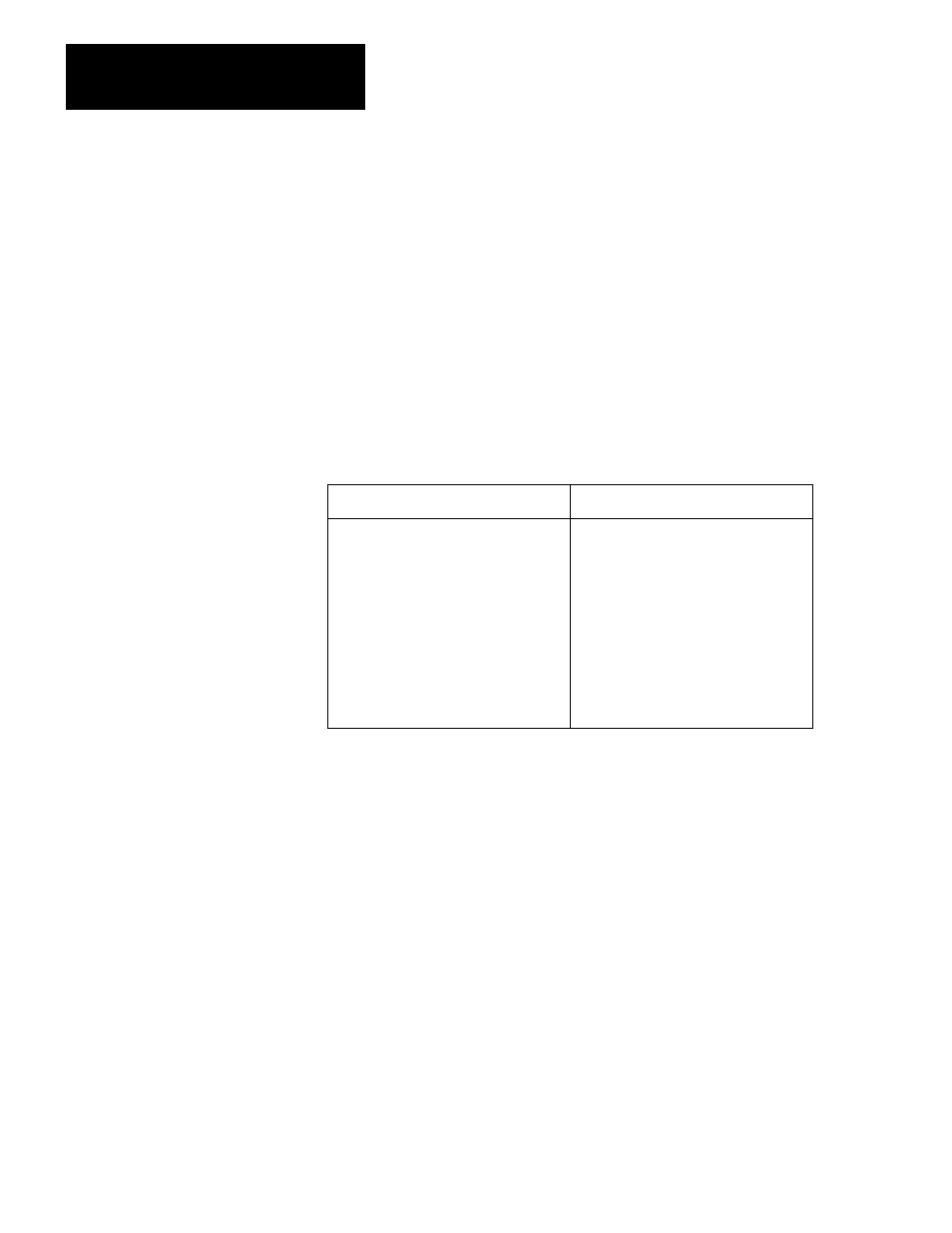
Table 6.B
Data Source and Destination Types
Source
Destination
Direct Value
Procedural user symbol
Procedural user symbol (except when
source is remote)
Interprocedural user symbol
Interprocedural user symbol (except
when source is remote)
Logical address
Logical address
Local symbolic address
Local symbolic address
Global symbolic address
Global symbolic address
Expression
Of special interest is the case where a user symbol is the destination of the
assignment. In such a case, if the user symbol was not previously defined
in the message procedure, a new symbol is generated. If the symbol has
already been defined, using it again as a destination causes its value to be
changed to the value given it by the latest assignment command.
Note that you can not transfer data from another station and place it into a
user symbol defined at your local PLC–3.
Format
The equals sign (=) is the assignment command. As Table 6.A shows, the
destination for the assignment is on the left of the equal sign, and the
source or the numeric value is on the right. In all cases, the source value is
assigned to (or copied to) the destination location. Thus, the assignment
is from right to left on the command line. For example, the statement
$I12:024–US_5
Assignment Command
