Torque and horsepower (cont.) – Rockwell Automation 150 MNL/SMC DIALOG+/APP-PROD GUIDE User Manual
Page 168
10-6
Reference
Torque and Horsepower (cont.)
By manipulating the preceding equation for kVA/HP for three-phas
motors, the following equation can be used for calculating locked-
rotor current:
This equation can then be used to determine the approximate starting
current of any particular motor. For instance, the approximate
starting current for 7-1/2 HP, 230 volt motor with a locked-rotor kVA
code letter of G would be:
Operating a motor in a locked-rotor condition for an extended period
of time will result in insulation failure because of the excessive heat
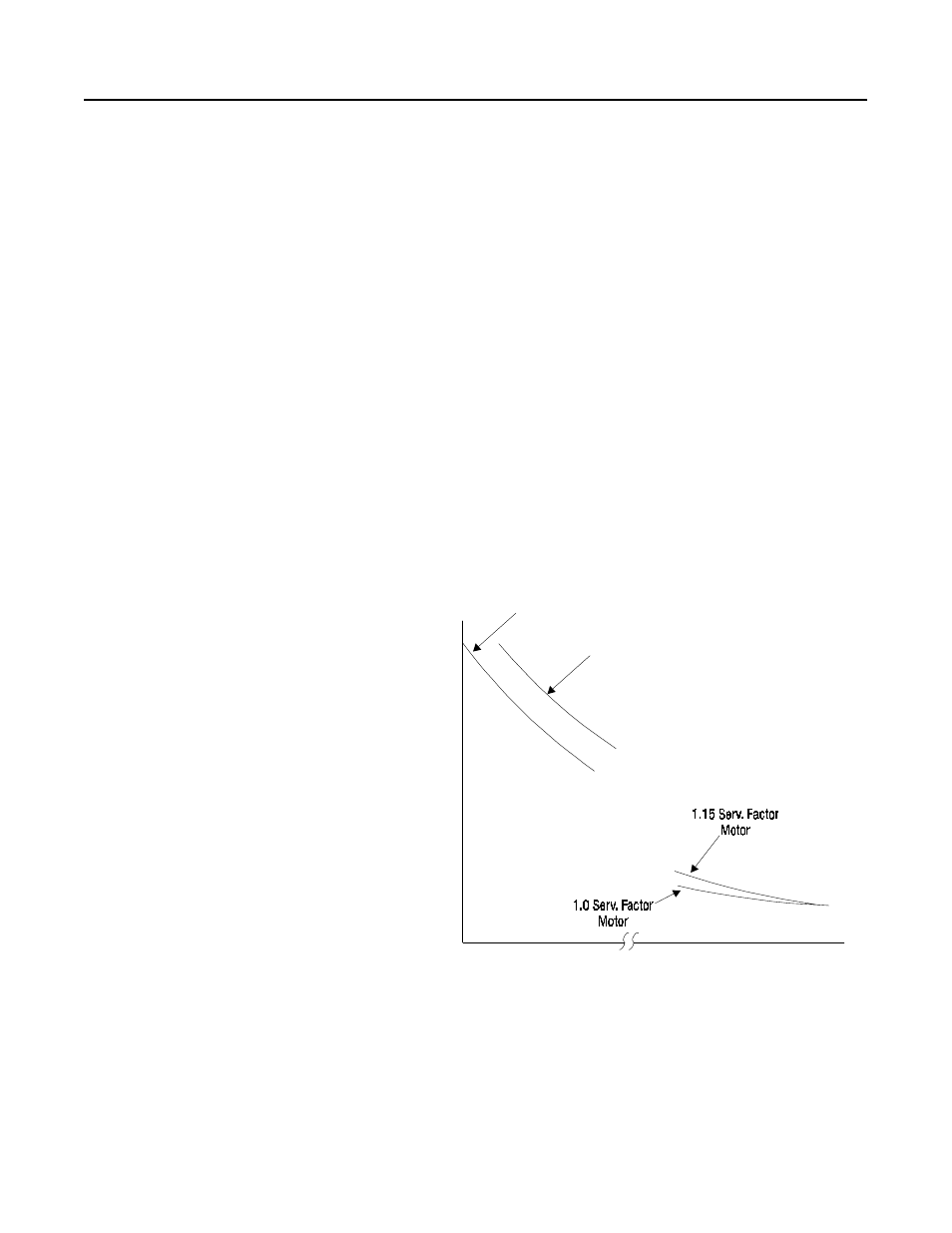
generated in the stator. The following graph illustrates the maximum
time a motor may be operated at locked-rotor without incurring
damage caused by heating. This graph assumes a NEMA Design B
motor with Class B temperature rise.
Figure 10.4 Motor Safe Time vs. Line Current - Standard Induction Motors
➊
Base Amps and Nameplate Amps.
Motor protection, either inherent or in the motor control, should be
selected to limit the stall time of the motor.
LRA
1,00
0H
×
kVA/HP
×
1.73
Volts
×
--------------------------------------------
=
LRA
1,00
07.
Ч
6.0
Ч
1.73
230
Ч
-------------------------------------
113 Amp
=
=
From Operating
Temperature
From Ambient
Motor
Line
Amps
Per
Unit ➀
8
6
4
2
1
0
10 15
20
100
200
700
Motor Running
Motor Stalled
Time in Seconds
