Robustel R3000 User Guide User Manual
Page 72
Robustel GoRugged R3000 User Guide
RT_UG_R3000_v.2.0.0 17.01.2014 71 / 131
Confidential
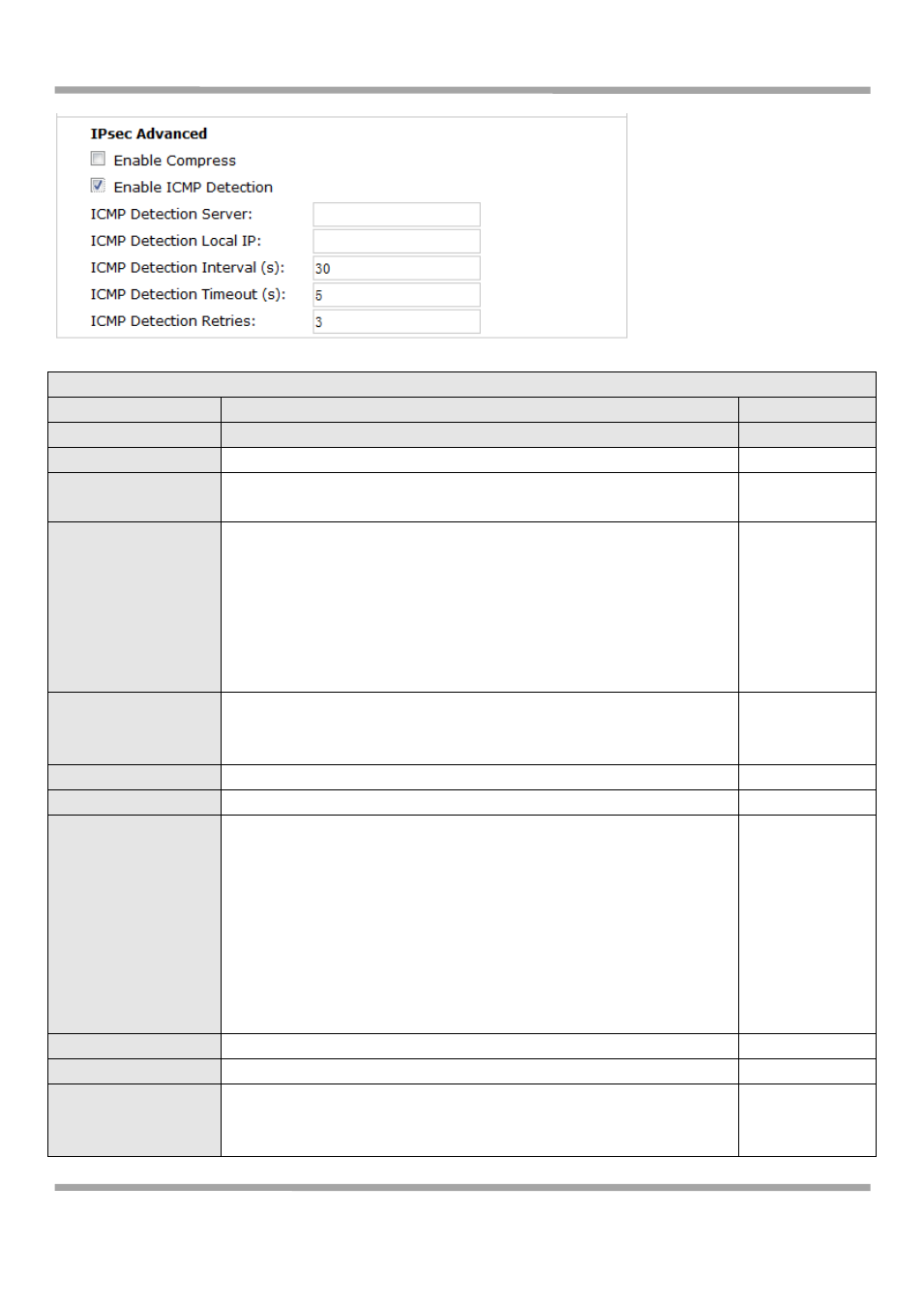
IPSec Tunnel @ IPSec
Item
Description
Default
Add
Click Add to add new IPSec Tunnel
Null
Enable
Enable IPSec Tunnel, the max tunnel account is 3
Null
IPSec Gateway
Address
Enter the address of remote side IPSec VPN server.
Null
IPSec Mode
Select from “Tunnel” and “Transport”.
Tunnel: Commonly used between gateways, or at an end-station to a
gateway, the gateway acting as a proxy for the hosts behind it.
Transport: Used between end-stations or between an end-station and a
gateway, if the gateway is being treated as a host—for example, an
encrypted Telnet session from a workstation to a router, in which the
router is the actual destination.
Tunnel
IPSec Protocol
Select the security protocols from “ESP” and “AH”.
ESP: Uses the ESP protocol.
AH: Uses the AH protocol.
ESP
Local Subnet
Enter IPSec Local Protected subnet’s address.
0.0.0.0
Local Subnet Mask
Enter IPSec Local Protected subnet’s mask.
0.0.0.0
Local ID Type
Select from “IP Address”, “FQDN” and “User FQDN” for IKE negotiation.
“Default” stands for “IP Address”.
IP Address: Uses an IP address as the ID in IKE negotiation.
FQDN: Uses an FQDN type as the ID in IKE negotiation. If this option is
selected, type a name without any at sign (@) for the local security
gateway, e.g., test.robustel.com.
User FQDN: Uses a user FQDN type as the ID in IKE negotiation. If this
option is selected, type a name string with an sign “@” for the local
security gateway, e.g., [email protected].
Default
Remote Subnet
Enter IPSec Remote Protected subnet’s address.
0.0.0.0
Remote Subnet Mask
Enter IPSec Remote Protected subnet’s mask.
0.0.0.0
Remote ID Type
Select from “IP Address”, “FQDN” and “User FQDN” for IKE negotiation.
IP Address: Uses an IP address as the ID in IKE negotiation.
FQDN: Uses an FQDN type as the ID in IKE negotiation. If this option is
Default
