3 introduction, 1 synchronisation of the drives via a master angle, Introduction – Lenze E94AxHE Technology Application Synchronism User Manual
Page 11: 3introduction
EDS94TA10040xxxx EN 1.1 - 10/2008
L
11
9400 Technology applications | Synchronism with mark synchronisation
Introduction
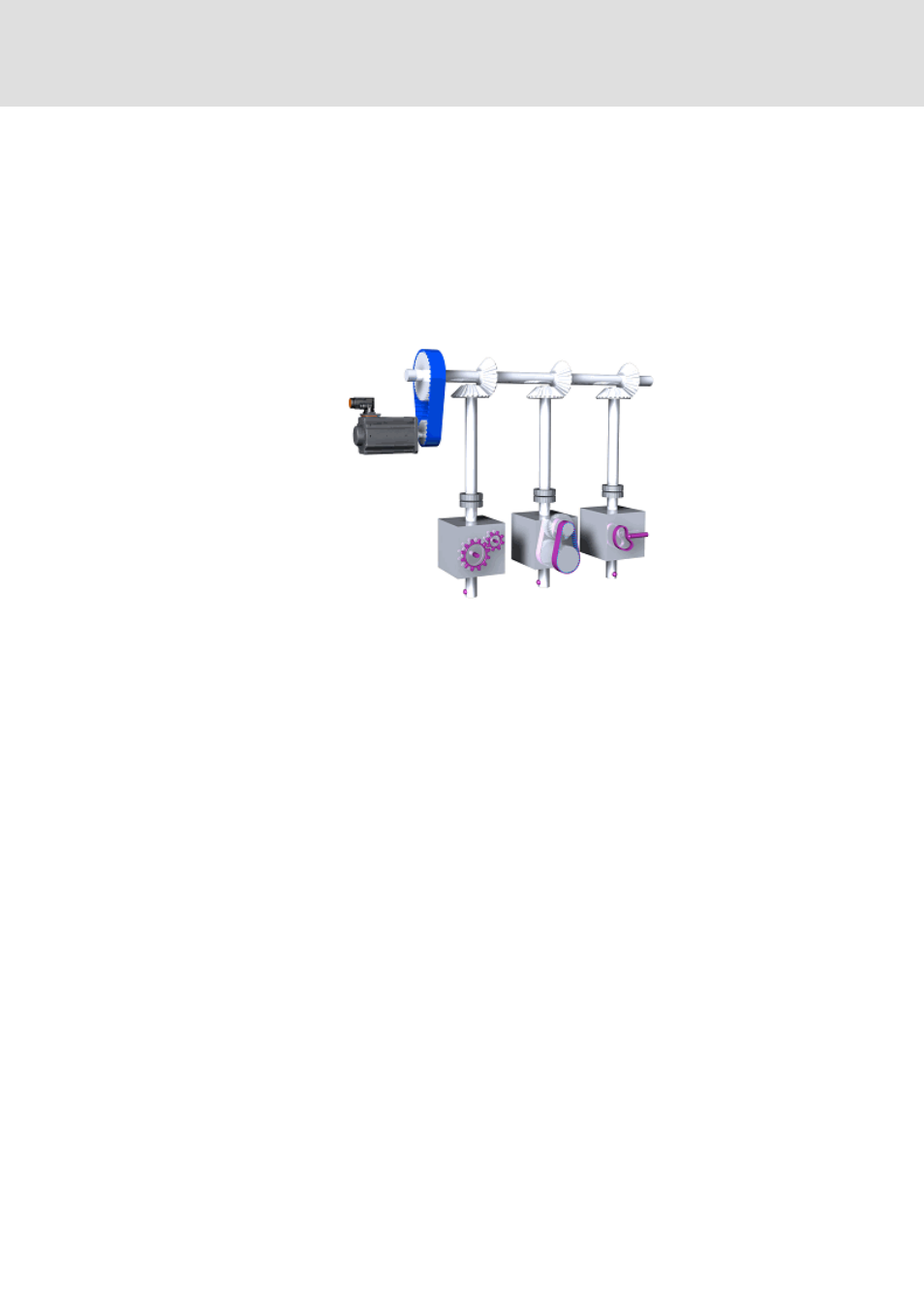
Synchronisation of the drives via a master angle
3
Introduction
The following subchapters provide information on the electrical shaft.
3.1
Synchronisation of the drives via a master angle
By coupling the drives via a master angle the positions are firmly allocated to each other
like a mechanical shaft.
r
A drive with a virtual master or a real master (encoder) is able to create the master
angle and transmit this to the other drives which follow this master angle.
Advantages of this type of synchronisation
r
The communication between the drives is very simple. A time-consuming evaluation of
the status signals of each drive and the control signals to be generated from it for each
single drive is not required.
r
Due to the flexible electronics trimming functions can be carried out very easily. Thus,
motion sequences in machines can be easily synchronised and optimised.
r
A variation of the master angle speed changes the number of cycles of the machine.
The drives keep the position allocation.
