How dns works for outbound mail, How private outbound dns works for outbound mail – Google Outbound Services Configuration Guide User Manual
Page 16
Introduction to Outbound Configuration
17
How DNS Works for Outbound Mail
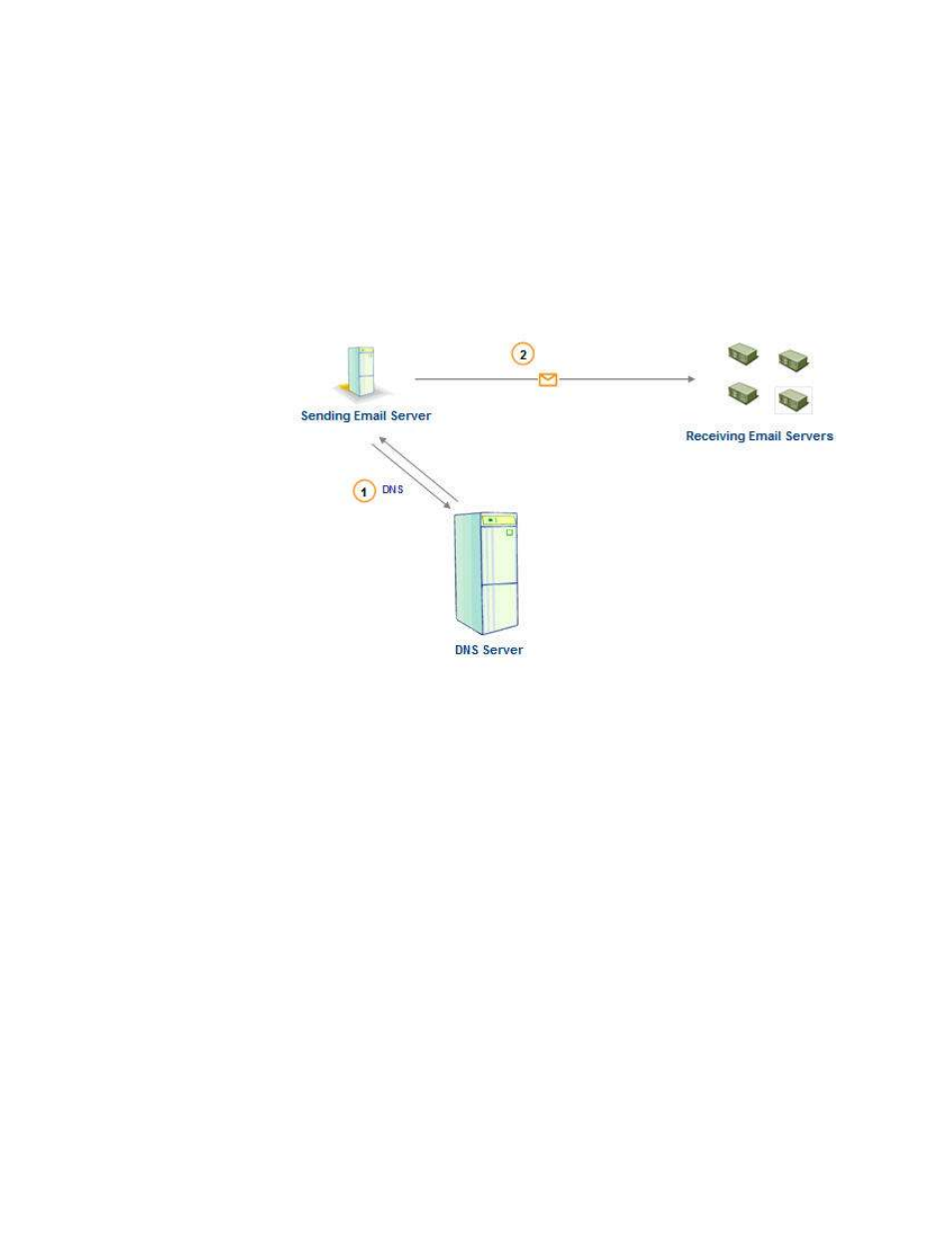
All mail servers use DNS to route outbound mail through the internet. DNS
(Domain Name Service) is a way to translate domain names into IP addresses,
which are used to contact other machines on the Internet. When a message is
sent to another domain, the sending mail server contacts a DNS host to find out
the IP address for the receiving server. The sending mail server submits the
domain name to the DNS host, and the DNS host returns the IP address of the
recipient’s mail server.
This diagram shows how DNS works for outbound mail.
How Private Outbound DNS Works for Outbound Mail
With Private Outbound DNS, you set your mail server to look at specially
configured DNS servers on the message security service. Most DNS servers will
provide the IP address for each domain name separately. The Private Outbound
DNS Service, however, does not return the actual IP address of the recipient.
Instead, when your mail server submits any domain name to the Private
Outbound DNS Service, the DNS Service returns the IP address for the message
security service.
Once you set up Private Outbound DNS, all outgoing mail will be routed through
the message security service. Because your mail server is routing directly to the
internet and not using a smarthost, mail will not be queued. The message security
service then filters outbound mail and routes it to the Internet.
This diagram shows how Private Outbound DNS works for outbound mail.
