1 step 1, 2 step 2, 3 step 3 – Karcher IV 100 - 55 M B1 User Manual
Page 18: 4 step 4, 1 step, 2 step, 3 step, 4 step
18
English 5.906-587.0 Rev. 00 (05/14)
In this example calculation, a suction unit for a shop with 3
work stations is to be designed. The system is to be de-
signed in a way that 2 vacuuming points can be operated
in parallel respectively.
Plastic granules are to be vacuumed up.
A Section: DN 80, 25 m, 3x Y-pieces, 2x 90° bends
B Section: DN 60, 5 m
C Section: DN 50, 5 m suction hose
Note
If they are not in operation, all branch lines are shut off by
means of a slide or a flap. At the end of the collecting pipe
(section A) a false air valve (see setting false air valve)
must be installed as the volume flow is pending there.
The total volume flow of all simultaneously operated vacu-
uming points is calculated for the calculation of the air
speed first.
Note
The air speed results from the available power of the vac-
uum cleaner (technical data), the number of vacuuming
points that are to be operated in parallel and the inner pipe
diameter of the line.
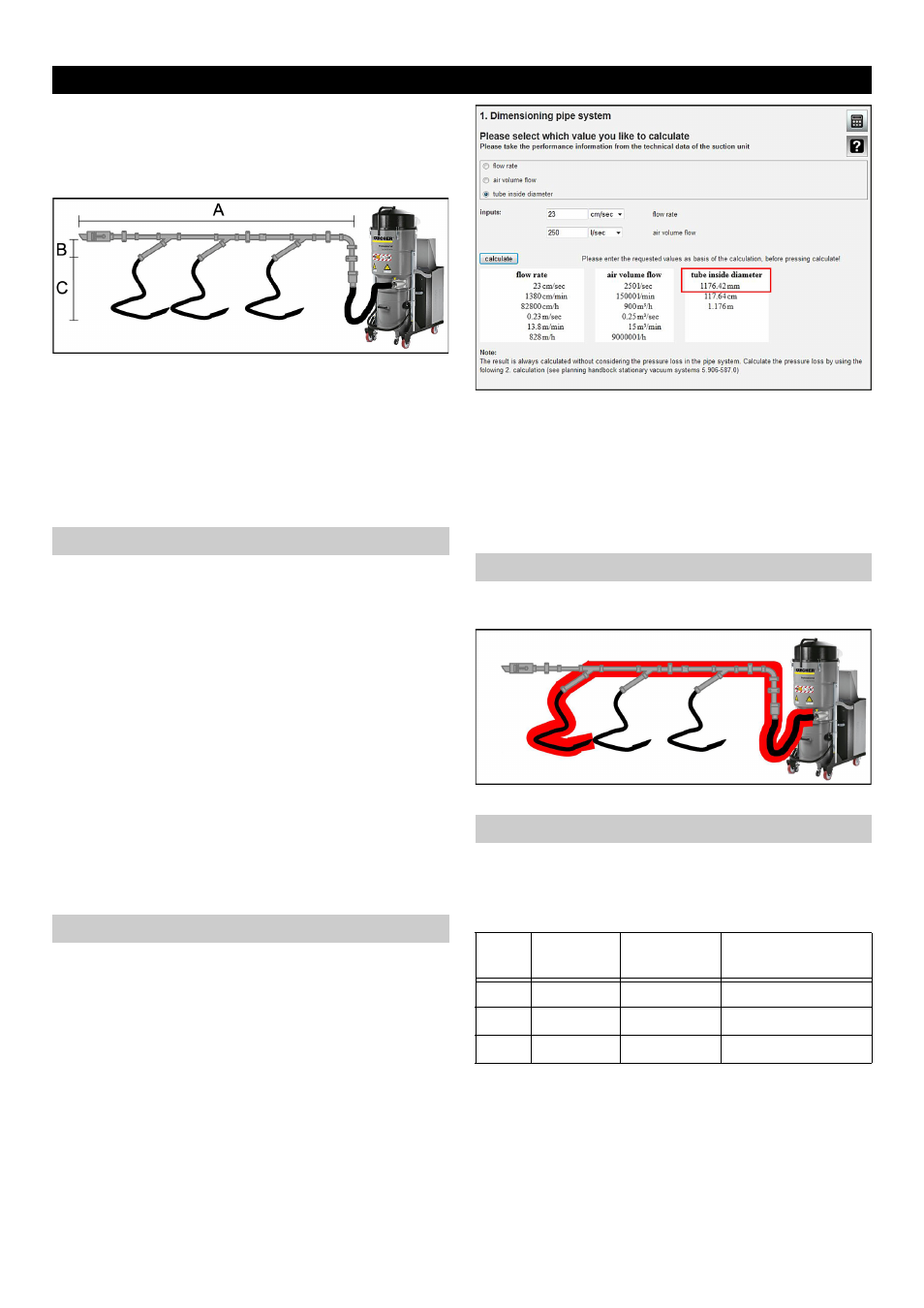
Example:
IV 100/55 as per technical data sheet 139l/s, that equals
500 m³/h (calculated with the calculation tool).
With 2 vacuuming points the following applies:
Volume flow per vacuuming point:
500 m³/h / 2 vacuuming points = 250 m³/h per vacuuming
point.
Available volume flow per vacuuming point = 250 m³/h.
Now the maximum pipe diameter is calculated under con-
sideration of the air speed.
Note
Determination of the pipe diameter by matching the avail-
able pipe sizes with the air speed required for the material.
As per the table in Chapter "Air speed", plastic granules Ø
2-3 mm require an air speed of 20-23 m/s.
By means of the calculation tool a max. pipe diameter of
62 mm in the side arm is calculated from the volume flow
250 m³/h and the speed 23 m/s.
The closest diameter in the pipeline programme is DN 60.
As two vacuuming points are operated in parallel, there is
a max. volume flow of 2 x 250 m³/h in the collecting pipe.
For this the calculated pipe diameter with 87.68 mm (with
23 m/s and 500 m3/h) is DN 80.
Identification of the main run in the pipeline system: Main
run is the way that causes the greatest pressure loss.
Main run shaded in red.
Calculation of the air speed in the individual sections of the
main run by means of the calculation tool.
Example:
11 Sample calculation for the dimensioning of the vacuum cleaner
11.1 Step 1
11.2 Step 2
11.3 Step 3
11.4 Step 4
Sec-
tion
Suction
hose
Volume
flow rate
Flow speed
1
DN 80
500m³/h
27.63 m/s
2
DN 60
250m³/h
24.56 m/s
3
DN 50
250m³/h
35.37 m/s
