1 - power analysis, Step 1 - identify system components, Step 2 - create system layout – HID EDGE EVO EHR40-EHRP40 Reader-Controller Installation Guide User Manual
Page 2: Power analysis, Hi-o networked controller & reader
Hi-O Networked Controller & Reader
EHR40 AND EHRP40
82000-922 D.0
INSTALLATION GUIDE
2
©2009 - 2012 HID Global Corporation. All rights reserved.
Before starting installation, determine which components will be used in the system and analyze the power requirements to
avoid over-loading the EDGE EVO Hi-O Networked Controller & Reader (EHR40/EHRP40).
The steps that follow illustrate sizing power requirements for the system.
Step 1 - Identify System Components
Installation components include the following examples.
•
Door Position Switch – Detects when the door is open or closed.
•
Magnetic Lock – Holds the door locked.
•
Request to Exit (REX) Switch – Unlocks the door when exiting the secured area.
•
EDGE EVO Hi-O Edge Door Module (EDM-M) – Connects peripheral devices to the Hi-O bus.
•
EDGE EVO Hi-O Networked Controller & Reader – Provides entry into the protected area and manages all peripherals
around the door.
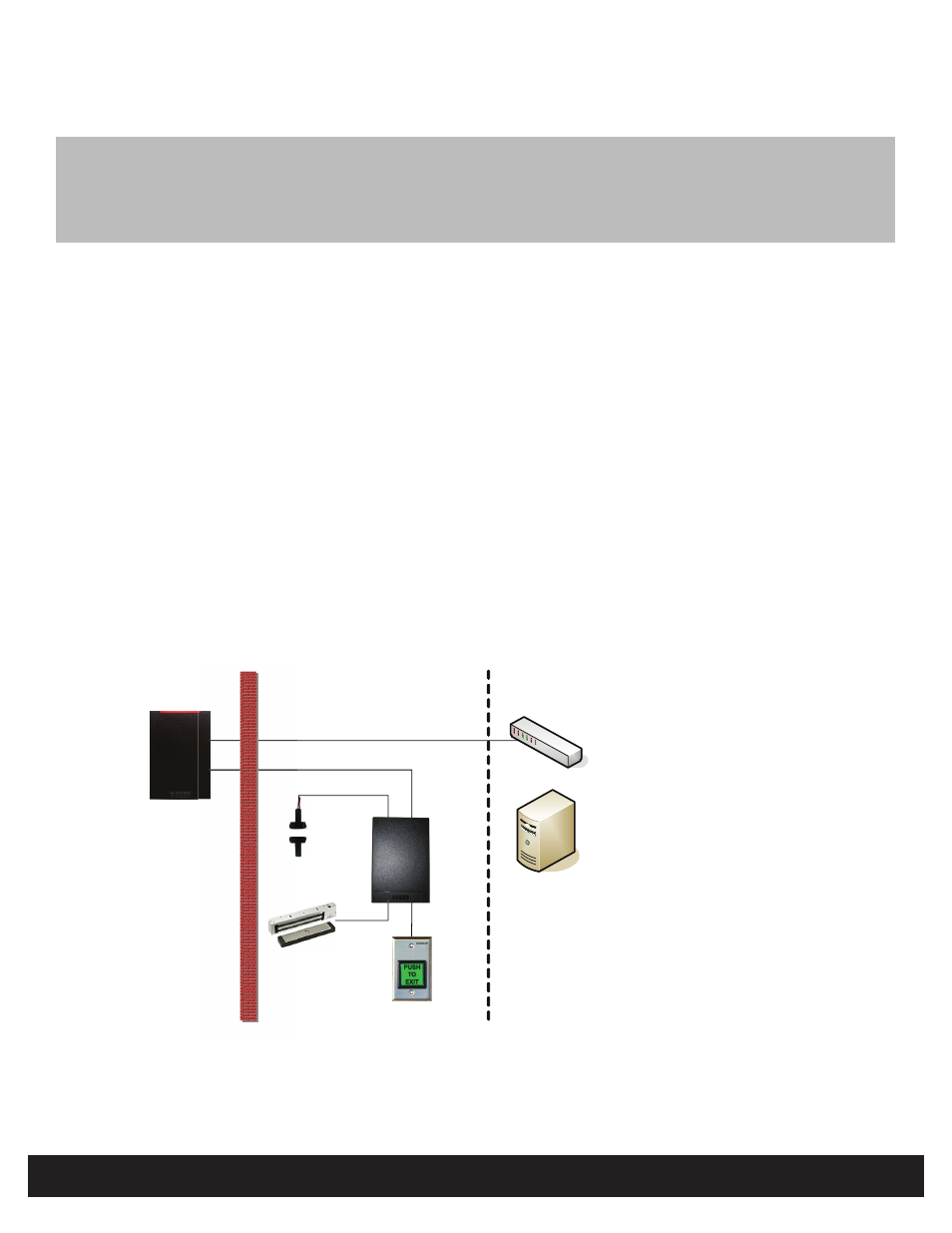
Step 2 - Create System Layout
Using the components identified in “Step 1 - Identify System Components” on page 2, create the overall system layout.
This example illustrates connecting the EH40/EHRP40 to the remote server through an Ethernet connection and manages
door peripherals over the Hi-O bus. The EDM-M receives inputs from the Door Position Switch and REX Switch to drive the
Magnetic Lock output.
Unprotected
Area
Protected Area
Physical Access
Control Server
(real-time functions
not required )
Remote Area
CANbus Data
Ethernet Switch
Ethernet Data
Door Position
Switch
Magnetic Lock
REX Switch
CANbu
Door P
Swi
Magne
Etherne
cted
Hi-O Networked
Controller and Reader
Door
Monitor
Figure 1 - System Layout Example
1
Power Analysis
