2 data access, 3 use of display surfaces, 2 data access 6.1.2.3 use of display surfaces – HP Scalable Visualization Array Software User Manual
Page 49: Using a single sva node from local desktop
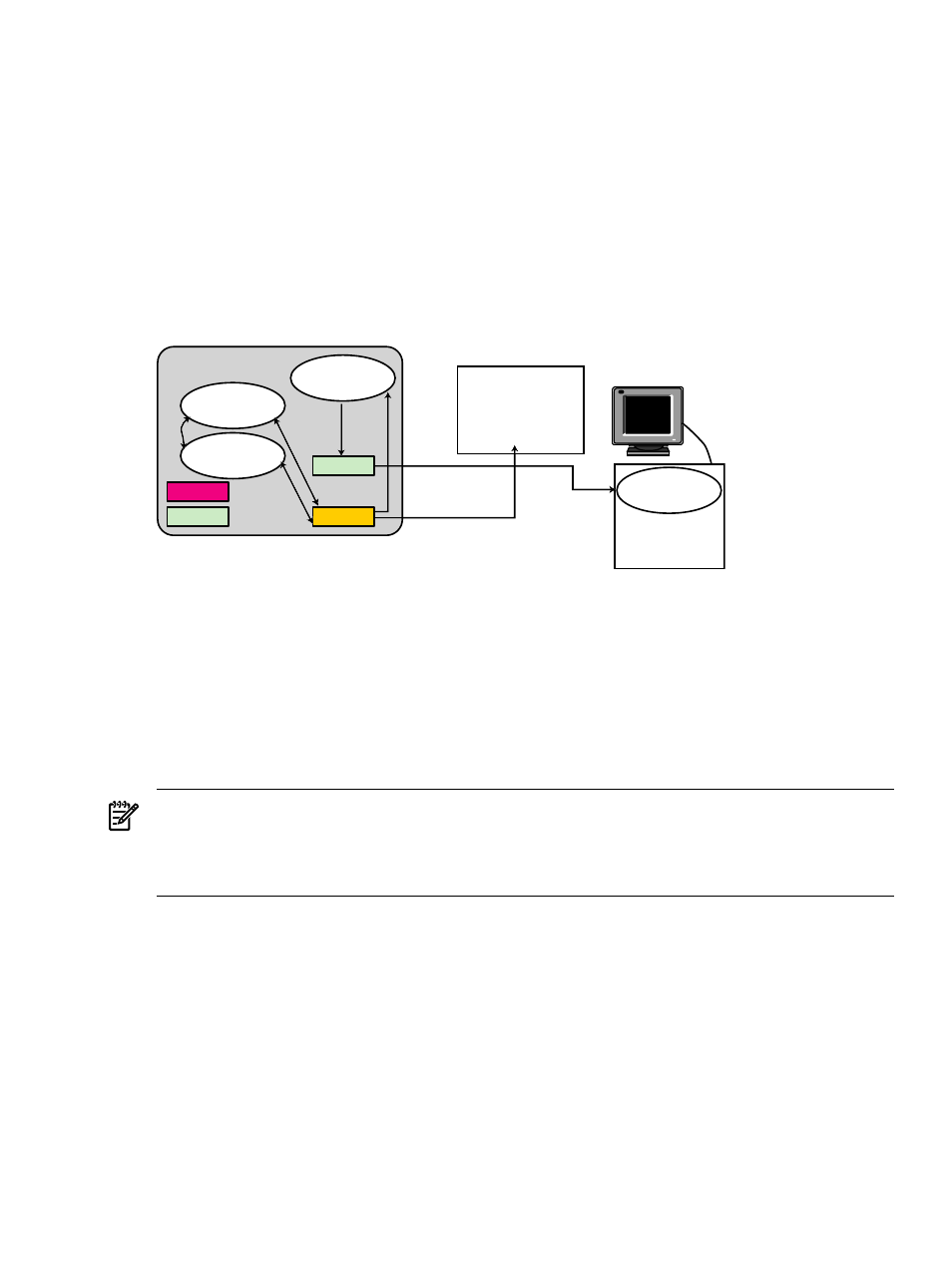
SVA as determined by the cluster node running the RGS Sender if connected to a display
device.
shows the relationships among the various processes that run when you launch
visualization jobs.
There are four processes that must run when a remote visualization session begins.
•
The X Server.
•
RGS Sender on the SVA RGS-capable node.
•
RGS Receiver on your local desktop.
•
Your visualization application.
Figure 6-1 Using a Single SVA Node from Local Desktop
GFX
GigE
GigE
SI
User
Application
X Server
Display Node
RGS
Sender
RGS
Receiver
Local Desktop
Display Device
(attached to SVA)
6.1.2.2 Data Access
If you use a single SVA display node, place the data files in a convenient location given your site
configuration. One location that provides reasonably fast access to the data is on a local disk of
the display node, which is the node running your application. Given that the application in this
scenario runs on a single node, there is little to be gained by distributing the data.
If you choose to store data locally, you can copy the data file to the display node after the
application starts. This ensures that you access a node allocated to your job. You can use the
/tmp
directory to store the data on the local disk.
Tip:
Consider running the launch script interactively if you plan to use local disk access to the data.
When run in interactive mode, the script allocates cluster resources first. You can then copy the
data file to the allocated display node before actually launching your visualization application.
Alternatively, NFS and HP Scalable File Share (SFS) can provide access to the data. Because HP
SFS provides high bandwidth access to data over the SI of SVA, it is the best choice if performance
is a high priority.
See the SVA System Administration Guide for guidelines and alternatives for accessing data files
when running visualization applications on the SVA.
6.1.2.3 Use of Display Surfaces
The SVA provides the infrastructure and utilities to simplify the task of allocating display devices.
The primary mechanism that you use to set up displays is the Display Surface. A Display Surface
is composed of one or more display nodes and their associated display devices; for example, a
simple Display Surface is a specific display node and an attached flat panel display device. Initial
configuration of the SVA sets up a series of default named Display Surfaces, one for each display
node and its directly cabled display device. Any of these default Display Surfaces should work
6.1 Running an Existing Application on a Single SVA Workstation
49
