Resolution – Milestone Analytics 2.2 Dacolian LPR User Manual
Page 41
Milestone XProtect Analytics 2.2 – Dacolian LPR; Administrator’s Manual
www.milestonesys.com
Page 41
Camera Tips & Tricks
Blocking objects: Avoid possible blocking objects in the view path of the camera, such as
pillars, barriers, fences, gates, etc. Remember that barriers, gates, etc. are likely to be
moveable between different positions.
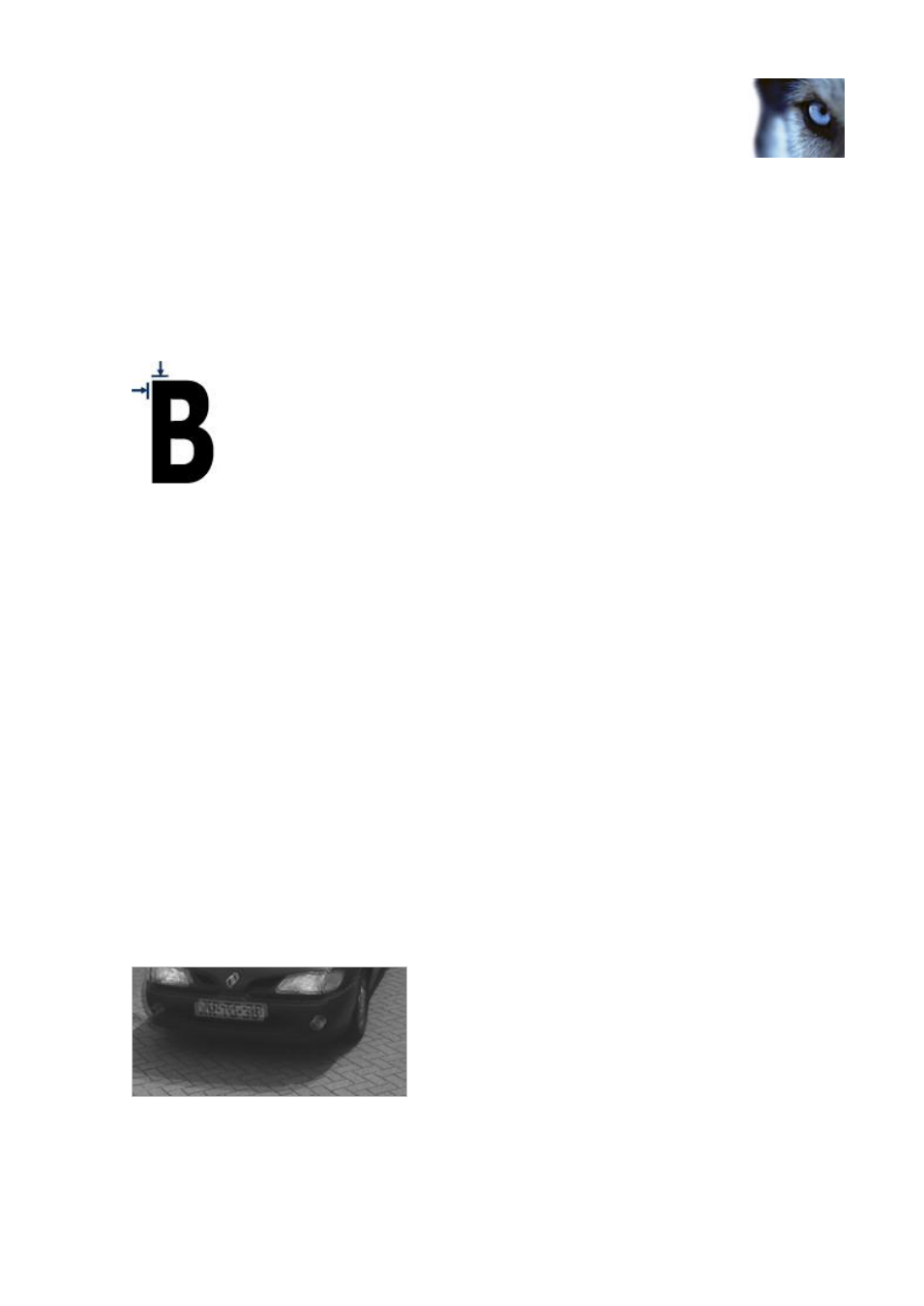
Resolution
The term pixels per stroke is used to define a minimum requirement for license place recognition.
The following illustration outlines what is meant by stroke:
Because the thickness of strokes depends on country and plate style, measurements like pixels/cm
or pixels/inch are not used.
The resolution for best license plate recognition performance should be at least 2.7 pixels/stroke.
For single line US plates (plate width 30.5 cm; stroke width around 0.7 cm) this typically
means that the plate width in the image must be at least 130 pixels.
For single line European style plates (plate width 52 cm; stroke width around 1 cm) this
typically means that the plate width in the image must be at least 170 pixels.
When vehicles are moving when recorded, and an interlaced camera is used, only a half of image
can be used (only the even lines). This means that the resolution requirements almost must be
doubled.
For single line US plates (plate width 30.5 cm; stroke width around 0.7 cm) this typically
means that the plate width in the image must be at least 215 pixels.
For single line European style plates (plate width 52 cm; stroke width around 1 cm) this
typically means that the plate width in the image must be at least 280 pixels.
FAQ: What is interlacing? Interlacing is a method determining how an image is refreshed when
shown on a screen. With interlacing, the image is refreshed by first scanning every other line in the
image, then scanning every opposite line, and so forth. This allows for a faster refresh rate because
less information must be processed during each scan. However, in some situations, interlacing may
cause flickering, or the changes in only half of the image’s lines for each scan may be noticeable.
Interlaced image of a moving car
