Technical data, Technical data 8.1 measuring principle – KROHNE BM 702 A EN User Manual
Page 48
8
TECHNICAL DATA
48
BM 702 A
www.krohne.com
09/2009 - 4000643301 - MA BM 702 A R01 en
Technical data
8.1 Measuring principle
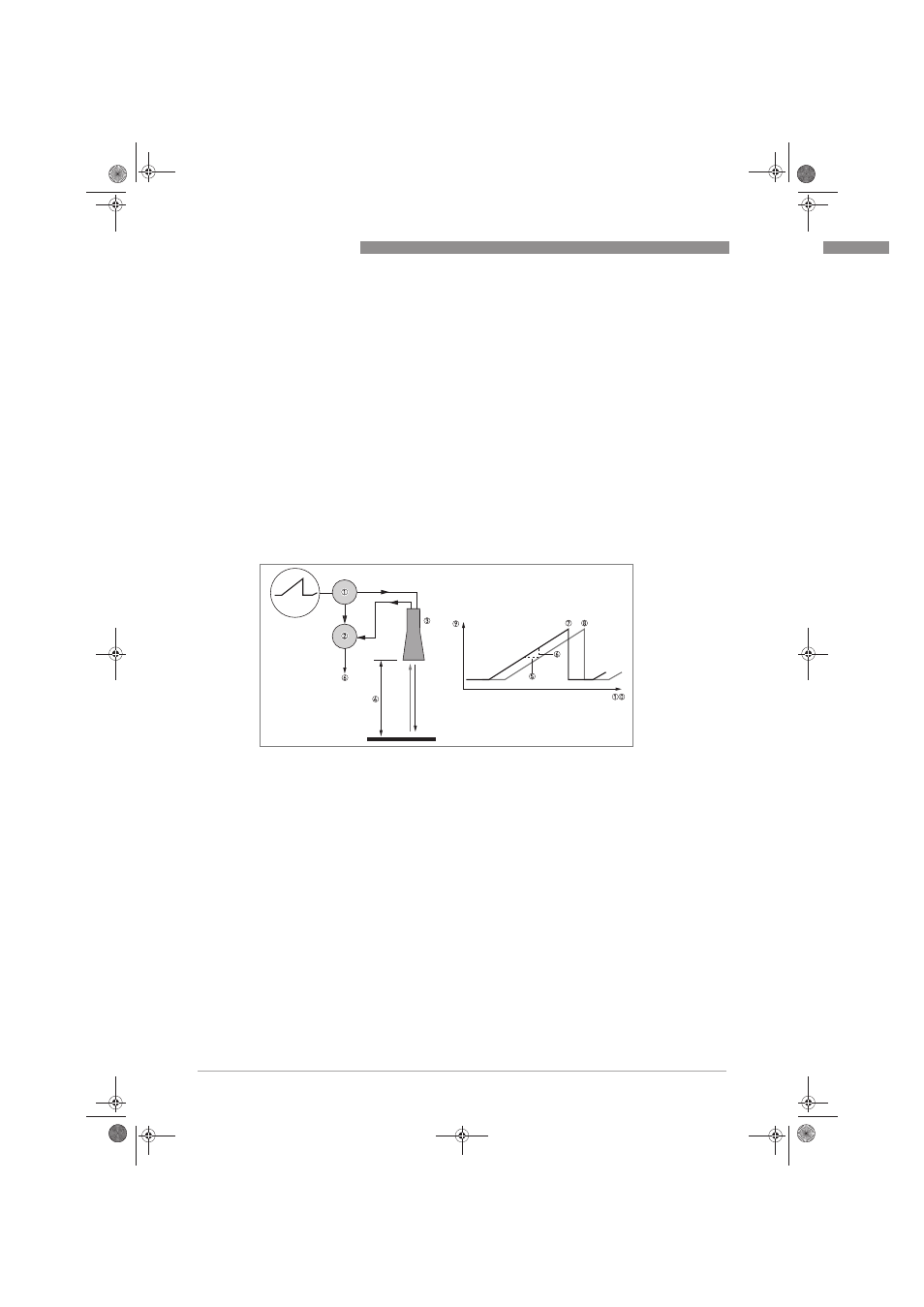
A radar signal is emitted via an antenna, reflected on the product surface and received after a
time t. The radar principle used is FMCW (Frequency Modulated Continuous Wave).
The FMCW-radar transmits a high frequency signal whose frequency increases linearly during
the measurement phase (called the frequency sweep). The signal is emitted, reflected on the
measuring surface and received with a time delay, t. Delay time, t=2d/c, where d is the distance
to the product surface and c is the speed of light in the gas above the product.
For further signal processing the difference Δf is calculated from the actual transmit frequency
and the receive frequency. The difference is directly proportional to the distance. A large
frequency difference corresponds to a large distance and vice versa. The frequency difference Δf
is transformed via a Fourier transformation (FFT) into a frequency spectrum and then the
distance is calculated from the spectrum. The level results from the difference between tank
height and measuring distance.
Figure 8-1: Measuring principle of FMCW radar
1 Transmitter
2 Mixer
3 Antenna
4 Distance to product surface, where change in frequency is proportional to distance
5 Differential time delay, Δt
6 Differential frequency, Δf
7 Frequency transmitted
8 Frequency received
9 Frequency
10 Time
.book Page 48 Thursday, September 3, 2009 2:53 PM
