3 how time-weighted averages are calculated – LumaSense Technologies INNOVA 1412i User Manual
Page 95
Chapter 8
______________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
BE6025-15
1412i Photoacoustic Gas Monitor
LumaSense Technologies A/S
Page 95 of 202
2. “Enter” the period of time required for averaging – this could for
example be 8 hours if you are interested in finding out whether
the 8 hour Time Weighted Average concentration of gases are in
compliance with National Occupational Exposure Limits; or,
alternatively, the averaging period could be 15 minute Time-
Weighted Average if you are interested in finding out whether the
Short Term Exposure Limit (STEL) of the gases complies with
National Occupational Exposure Limits.
3. Press SET-UP and then AVERAGE.
When steps 1 to 3 are complete, scroll through the measurement
results displayed on the screen (Display Memory). Notice that all
measurements have been averaged over the chosen averaging
period. A detailed example is given in
8.1.3
How Time-weighted Averages are Calculated
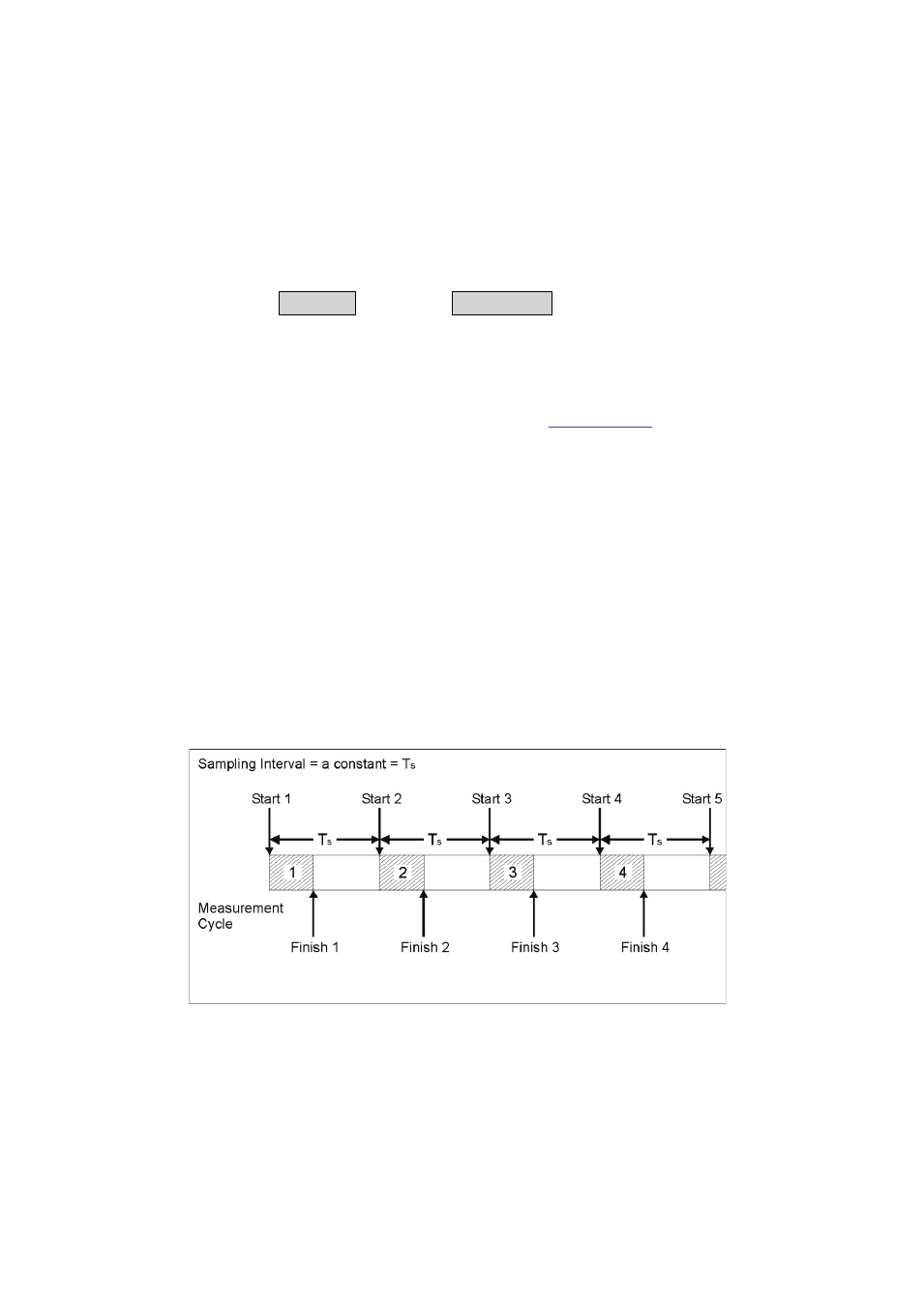
In order to explain how the 1412i averages gas measurements over
a fixed user-defined “averaging period”, let us suppose that a
particular gas has been monitored continuously and that its
measured concentration was C
1
during the first sampling interval T
1
min, C
2
during the second sampling interval T
2
min…. C
n
during the
n
th
sampling interval T
n
min (see Fig.8.2). Suppose that you wished
the 1412i to calculate the Time-weighted average (TWA) over a
period of time = T min.
Fig.8.2 Illustration of a monitoring task
The Time-weighted average of these measurements over the
averaging period of T min is calculated using the following
mathematical equation:
