Venting as a chase – HTP ELP-199 User Manual
Page 40
40
LP-294 REV. 2.20.14
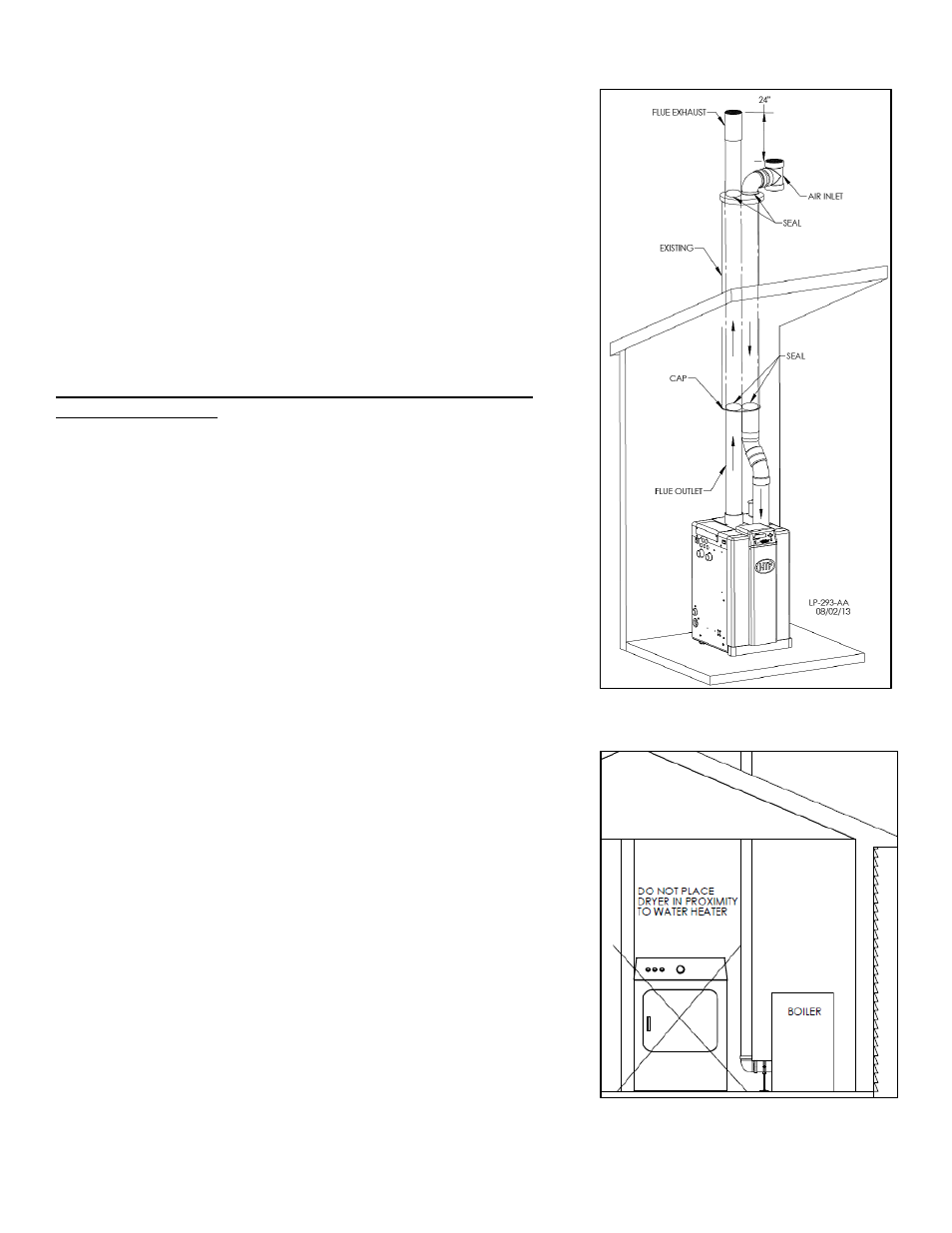
2. VENTING AS A CHASE
When venting as a chase, follow all instructions included in Part 5
– Venting,
Sections A
– G of this manual, as well as the previous Concentric Venting section.
See Figure 19 for chase venting demonstration.
NOTES:
A. For every 1” of overhang, the exhaust vent must be located 1” vertical below
overhang (overhang means top of building structure and not two adjacent walls
[corner of building]).
B. Typical installations require 12” minimum separation between bottom of exhaust
outlet and top of air intake.
C. Maintain 12” minimum clearance above highest anticipated snow level or grade
(whichever is greater).
D. Minimum 12” between vents when installing multiple vents.
E. 12” minimum beyond air intake.
F. Maintain 12” minimum clearance above highest anticipated snow level or grade
(whichever is greater).
M. INDOOR COMBUSTION AIR INSTALLATION IN CONFINED OR
UNCONFINED SPACE
NOTE: This installation is intended for commercial applications. For residential
applications, it is recommended to pipe intake combustion air from the outdoors.
This boiler requires fresh, uncontaminated air for safe operation and must be
installed in a mechanical room where there is adequate combustion and ventilating
air. NOTE: To prevent combustion air contamination, see Table 3.
Combustion air from the indoor space can be used if the space has adequate area or
when air is provided through a duct or louver to supply sufficient combustion air
based on the boiler input. Never obstruct the supply of combustion air to the
boiler. If the boiler is installed in areas where indoor air is contaminated (see Table
3) it is imperative that the boiler be installed as direct vent so that all combustion air
is taken directly from the outdoors into the boiler intake connection.
Unconfined space is space with volume not less than 50 cubic feet per 1,000
Btu/hour (4.8 cubic meters per kW) of the total input rating of all fuel-burning boilers
installed in that space. Rooms connected directly to this space, through openings not
furnished with doors, are considered part of the space.
Confined space is space with volume less than 50 cubic feet per 1,000 Btu/hour (4.8 cubic meters per kW) of the total input rating of
all fuel-burning boilers installed in that space. Rooms connected directly to this
space, through openings not furnished with doors, are considered part of the space.
When drawing combustion air from inside a conventionally constructed building to a
confined space located on the same story, such space should be provided with two
permanent openings: one
located 6” (15 cm) below the space ceiling, the other 6”
(15cm) above the space floor. Each opening should have a free area of one square
inch per 1,000 Btu/hr (22cm
2
/kW) of the total input of all boilers in the space, but not
less than 100 square inches (645cm
2
).
When drawing combustion air from inside a conventionally constructed building to a
confined space located on different stories, such spaces should be considered as
communicating spaces when connected with one or more permanent openings in
doors or floors having a total minimum free area of two square inches per 1,000
Btu/hr (22cm
2
/kW) of the total input of all boilers in the space, but not less than 200
square inches (645cm
2
).
If the confined space is within a building of tight construction, air for combustion must
be obtained from the outdoors as outlined in the Venting section of this manual.
NOTE: It is always recommended to isolate the boiler installation room from the rest
of the building and bring uncontaminated air in from the outside for combustion and
ventilation.
Figure 20
– LP-387-Z
Figure 19
– Venting as a Chase
