Status register – sreg, Stack pointer – sp – Rainbow Electronics AT90C8534 User Manual
Page 17
AT90C8534
17
Status Register – SREG
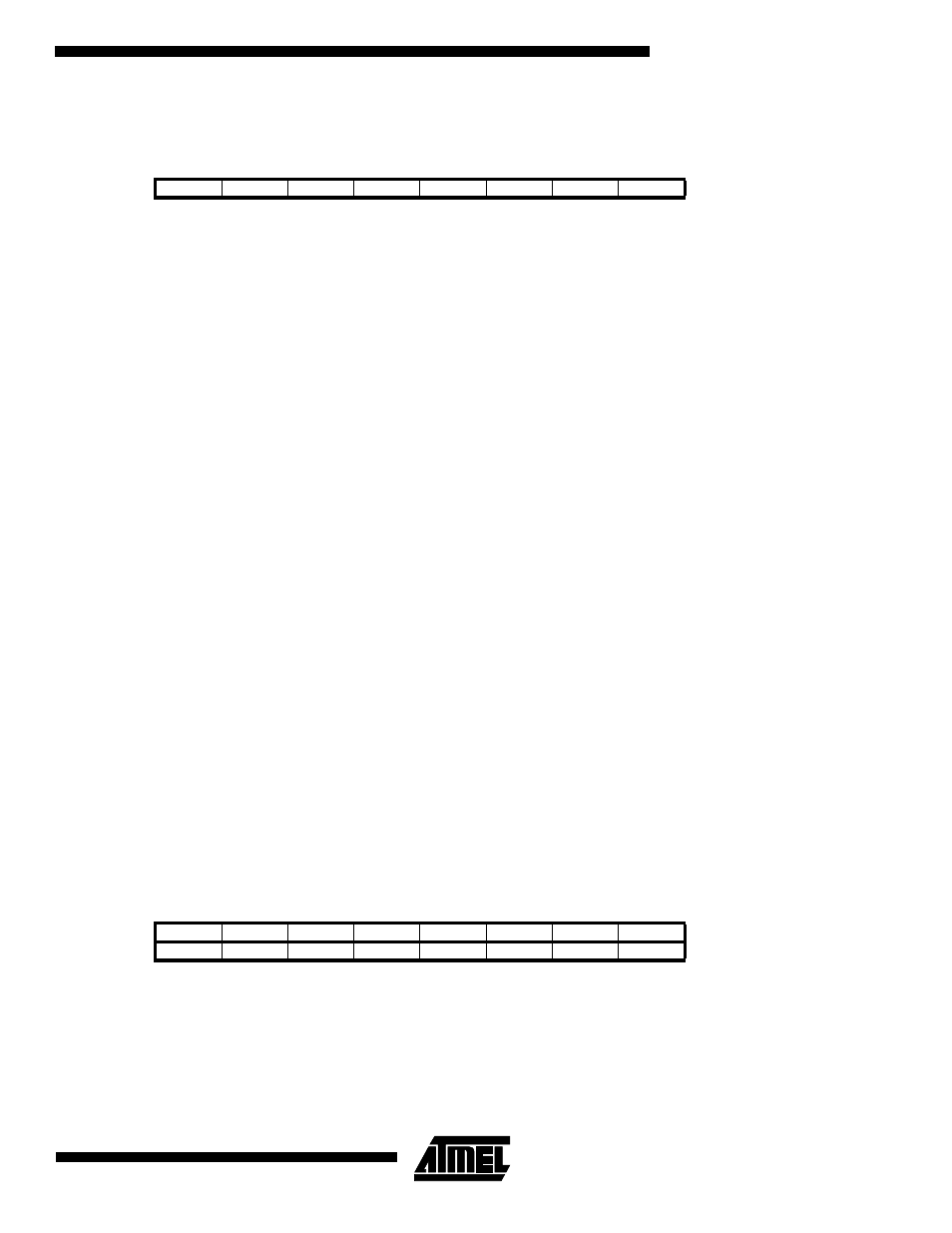
The AVR status register (SREG) at I/O space location $3F ($5F) is defined as:
•
Bit 7 – I: Global Interrupt Enable
The global interrupt enable bit must be set (one) for the interrupts to be enabled. The individual interrupt enable control is
then performed in separate control registers. If the global interrupt enable bit is cleared (zero), none of the interrupts are
enabled independent of the individual interrupt enable settings. The I-bit is cleared by hardware when an interrupt routine is
entered and is set by the RETI instruction to enable subsequent interrupts.
•
Bit 6 – T: Bit Copy Storage
The bit copy instructions BLD (Bit LoaD) and BST (Bit STore) use the T-bit as source and destination for the operated bit. A
bit from a register in the register file can be copied into T by the BST instruction and a bit in T can be copied into a bit in a
register in the register file by the BLD instruction.
•
Bit 5 – H: Half-carry Flag
The half-carry flag H indicates a half-carry in some arithmetical operations. See the Instruction Set description for detailed
information.
•
Bit 4 – S: Sign Bit, S = N
⊄⊕
V
The S-bit is always an exclusive or between the negative flag N and the two’s complement overflow flag V. See the Instruc-
tion Set description for detailed information.
•
Bit 3 – V: Two’s Complement Overflow Flag
The two’s complement overflow flag V supports two’s complement arithmetics. See the Instruction Set description for
detailed information.
•
Bit 2 – N: Negative Flag
The negative flag N indicates a negative result from an arithmetical or logical operations. See the Instruction Set descrip-
tion for detailed information.
•
Bit 1 – Z: Zero Flag
The zero flag Z indicates a zero result from an arithmetical or logical operations. See the Instruction Set description for
detailed information.
•
Bit 0 – C: Carry Flag
The carry flag C indicates a carry in an arithmetical or logic operation. See the Instruction Set description for detailed
information.
Note that the status register is not automatically stored when entering an interrupt routine or restored when returning from
an interrupt routine. This must be handled by software.
Stack Pointer – SP
The AT90C8534 Stack Pointer is implemented as two 8-bit registers in the I/O space locations $3E ($5E) and $3D ($5D).
As the AT90C8534 data memory has $15F locations, nine bits are used.
The Stack Pointer points to the data SRAM stack area where the Subroutine and Interrupt Stacks are located. This stack
space in the data SRAM must be defined by the program before any subroutine calls are executed or interrupts are
enabled. The Stack Pointer is decremented by 1 when data is pushed onto the stack with the PUSH instruction and it is
Bit
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
$3F ($5F)
I
T
H
S
V
N
Z
C
SREG
Read/Write
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
Initial value
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
Bit
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
$3E ($5E)
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
SP8
SPH
$3D ($5D)
SP7
SP6
SP5
SP4
SP3
SP2
SP1
SP0
SPL
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
Read/Write
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
Initial value
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
