Rainbow Electronics MAX5961 User Manual
Page 20
MAX5961
0 to 16V, Quad, Hot-Swap Controller
with 10-Bit Current and Voltage Monitor
20
______________________________________________________________________________________
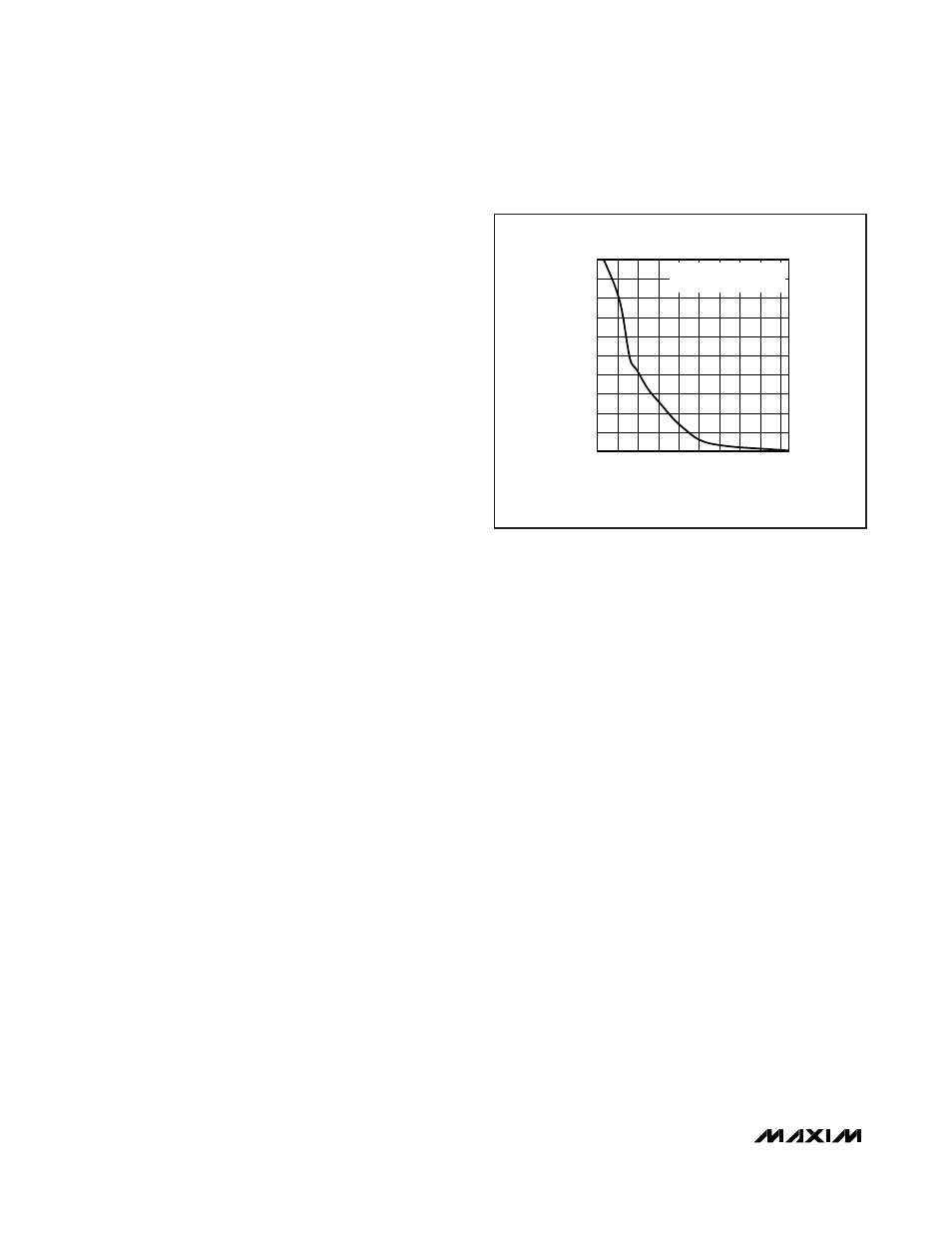
The fast-trip threshold is always higher than the slow-trip
threshold, and the fast-trip comparator responds very
quickly to protect the system against sudden, severe
overcurrent events. The slower response of the slow-trip
comparator varies depending upon the amount of over-
drive beyond the slow-trip threshold. If the overdrive is
small and short-lived, the comparator will not shut down
the affected channel. As the overcurrent event increas-
es in magnitude, the response time of the slow-trip com-
parator decreases. This scheme provides good
rejection of noise and spurious overcurrent transients
near the slow-trip threshold while aggressively protect-
ing the system against larger overcurrent events that
occur as a result of a load fault (see Figure 2).
Setting Circuit-Breaker Thresholds
To select and set the MAX5961 slow-trip and fast-trip
comparator thresholds, use the following procedure.
1) Select one of four ratios between the fast-trip thresh-
old and the slow-trip threshold: 200%, 175%, 150%,
or 125%. A system that experiences brief but large
transient load currents should use a higher ratio,
whereas a system that operates continuously at
higher average load currents might benefit from a
smaller ratio to ensure adequate protection. The
ratio is set by writing to the ifast2slow register. (The
default setting on power-up is 200%.)
2) Determine the slow-trip threshold V
TH,ST
based on
the anticipated maximum continuous load current
during normal operation, and the value of the cur-
rent-sense resistor. The slow-trip threshold should
include some margin (possibly 20%) above the max-
imum load current to prevent spurious circuit-break-
er shutdown and to accommodate passive
component tolerances:
V
TH,ST
= R
SENSE_
x I
LOAD,MAX
x 120%
3) Calculate the necessary fast-trip threshold V
TH,FT
based on the ratio set in step 1:
V
TH,FT
= V
TH,ST
x (ifast2slow ratio)
4) Select one of the three maximum current-sense
ranges: 25mV, 50mV, or 100mV. The current-sense
range is initially set upon power-up by the state of
the associated ILIM_ input, but can be altered at any
time by writing to the status2 register. For maximum
accuracy and best measurement resolution, select
the lowest current-sense range that is larger than the
V
TH,FT
value calculated in step 3.
5) Program the fast-trip and slow-trip thresholds by
writing an 8-bit value to the
dac_chx
register. This 8-
bit value is determined from the desired V
TH,ST
value that was calculated in step 2, the threshold
ratio from step 1, and the current-sense range from
step 4:
DAC = V
TH,ST
x 255 x (ifast2slow ratio)/(ILIM_ current
sense range)
The MAX5961 provides a great deal of system flexibility
because the current-sense range, DAC setting, and
threshold ratio can be changed “on the fly” for systems
that must protect a wide range of interchangeable load
devices, or for systems that control the allocation of
power to smart loads. Table 6 shows the specified
ranges for the fast-trip and slow-trip thresholds for all
combinations of current-sense range and threshold
ratio. The fast-trip DAC can be programmed to values
below 0x66 (40% of the current-sense range), but
accuracy is not specified for operation below 40%.
MAX5961 fig02
[(V
SENSE_
- V
MON_
) - V
TH,ST
] (V)
TURN-OFF TIME (ms)
9
8
6
7
2
3
4
5
1
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
1.2
1.4
1.6
1.8
2.0
0
0
25mV SENSE RANGE;
DAC = 191, V
TH,ST
= 9.36mV
Figure 2. Slow-Comparator Turn-Off Time vs. Overdrive
