Displaying terrain-svs data, Hazard avoidance – Garmin G1000 Socata TBM 850 User Manual
Page 380
Garmin G1000 Pilot’s Guide for the Socata TBM 850
190-00709-02 Rev. B
366
HAZARD AVOIDANCE
SY
STEM
O
VER
VIEW
FLIGHT
INSTRUMENTS
EAS
AUDIO P
ANEL
& CNS
FLIGHT
MANA
GEMENT
HAZARD
AV
OID
ANCE
AFCS
ADDITIONAL FEA
TURES
APPENDICES
INDEX
subject to variations in pressure and temperature that normally affect pressure altitude sensors. GPS-MSL altitude
does not require local altimeter settings to determine MSL altitude. It is a widely-used MSL altitude source.
Terrain and obstacle databases are referenced to MSL. Using the GPS position and altitude, the TERRAIN-SVS
feature portrays a 3-D picture of the surrounding terrain and obstacles relative to the position and altitude of the
aircraft. GPS position and GPS-MSL altitude are used to calculate and predict the aircraft’s flight path in relation
to the surrounding terrain and obstacles. In this way, the pilot can view predicted dangerous terrain and obstacle
conditions.
DISPLAYING TERRAIN-SVS DATA
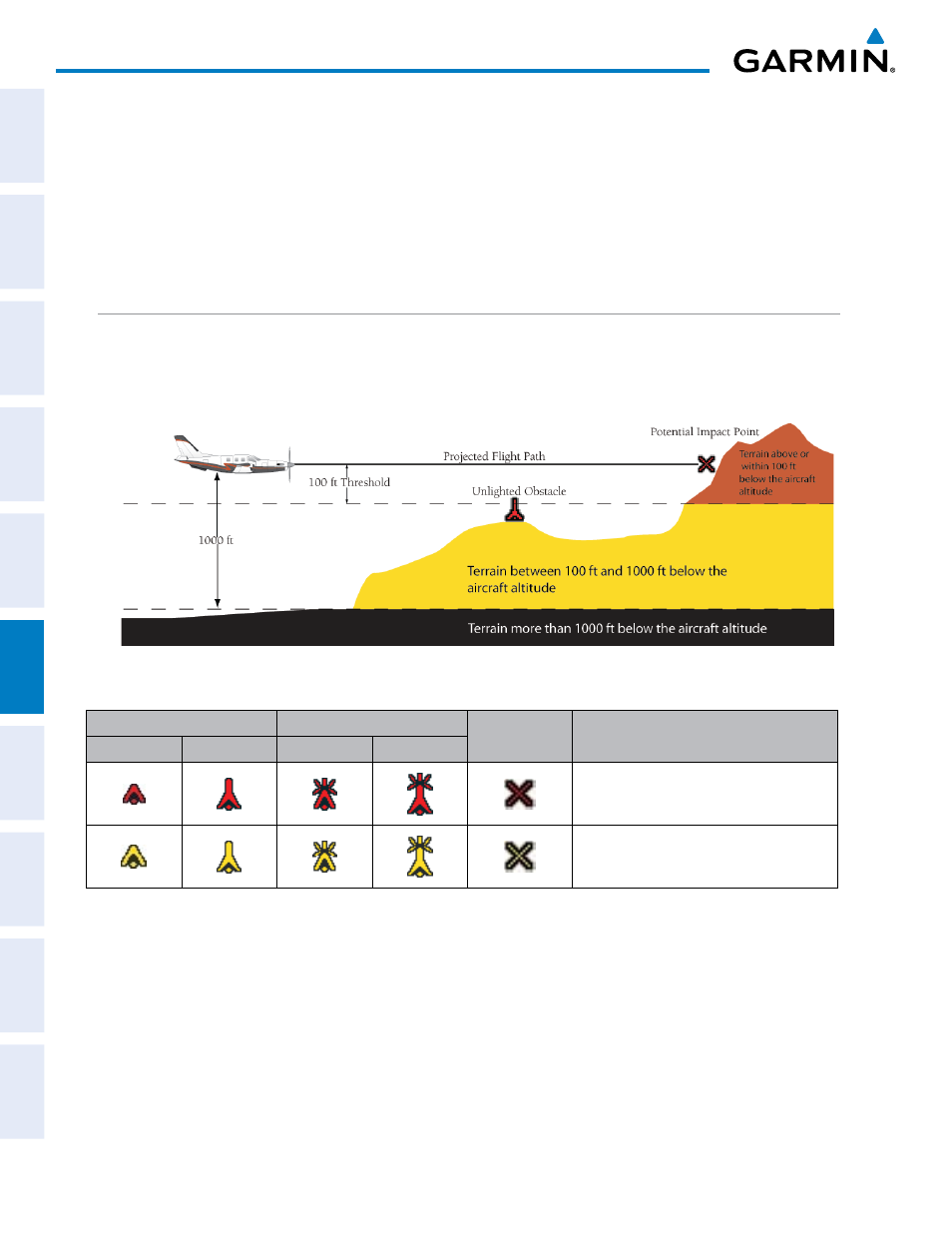
TERRAIN-SVS uses yellow (caution) and red (warning) to depict terrain and obstacles with heights greater
than 200 feet above ground level, AGL. Alerts are given relative to aircraft altitude. Colors are adjusted
automatically as the aircraft altitude changes. The colors and symbols shown in the figure and table below are
used to represent terrain, obstacles, and potential impact points.
Figure 6-78 Terrain Altitude/Color Correlation for TERRAIN-SVS
Unlighted Obstacle
Lighted Obstacle
Potential
Impact Points
Obstacle Location
< 1000’ AGL > 1000’ AGL < 1000’ AGL > 1000’ AGL
WARNING: Red obstacle is above or within
100’ below current aircraft altitude
CAUTION: Yellow obstacle is between 100’
and 1000’ below current aircraft altitude
Table 6-7 TERRAIN-SVS Obstacle Colors and Symbology
