4 esi command transfer, 1 esi read transfer, 2 esi write transfer – Seagate Fibre Channel Interface User Manual
Page 120: Esi command transfer, Esi read transfer, Esi write transfer, Figure 15, Esi command transfers, Figure 16, Esi reads
106
Fibre Channel Interface Manual, Rev. D
10.4
ESI command transfer
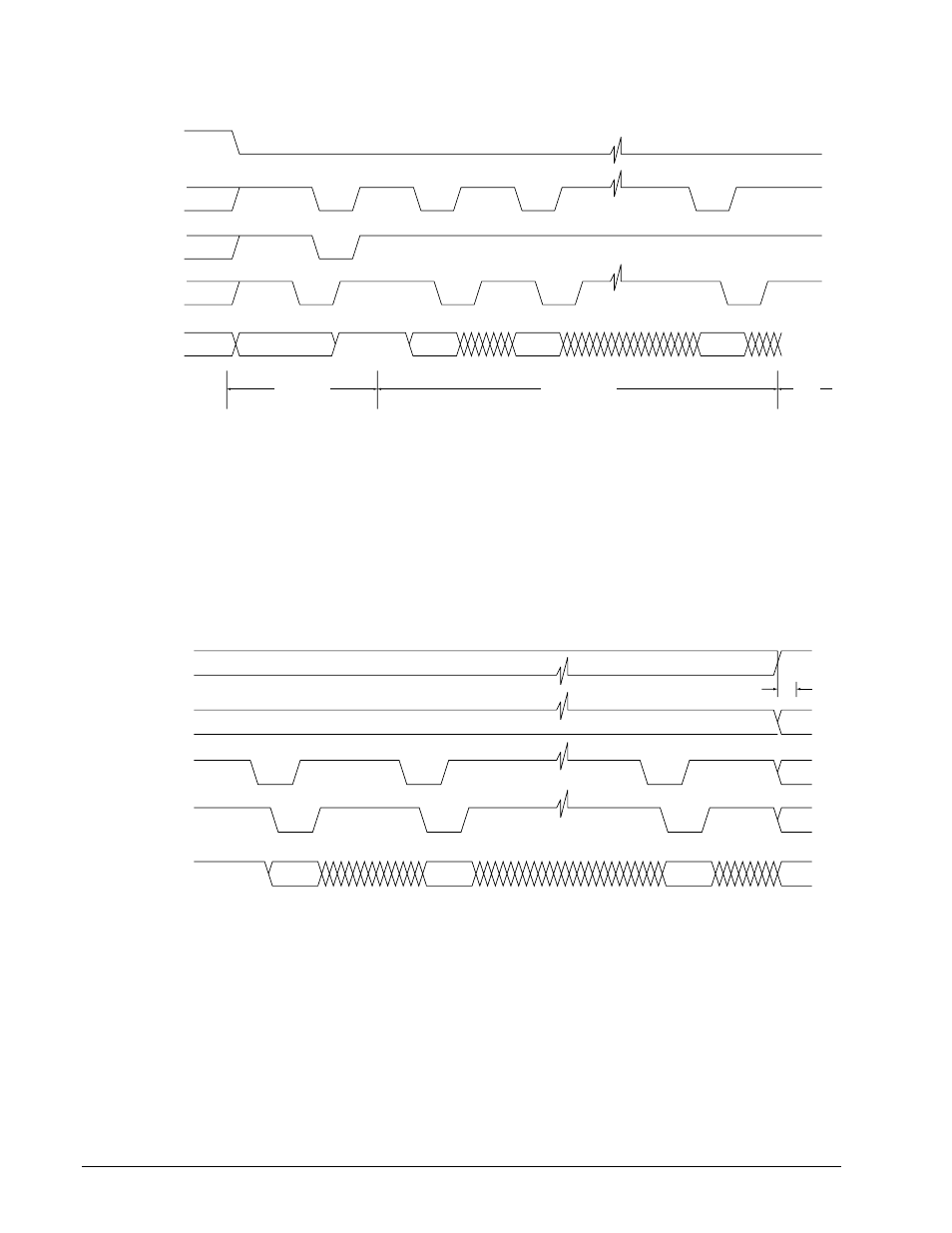
Figure 15.
ESI command transfers
10.4.1
ESI read transfer
To receive data from the enclosure, the drive pulls –DSK_RD pin low to request information from the enclo-
sure. The enclosure responds by driving the Data pins with ESI and pulling –ENCL_ACK low to signal that the
data is valid. The drive strobes the data and allows high –DSK_RD to return high. The enclosure responds
to the –DSK_RD going high by allowing –ENCL_ACK to return to high. This sequence may be repeated for as
many bytes, two nibble each, requested by the host. The drive exits the ESI mode by not pulling –P_ESI low—
the pull up resistor returns –P_ESI to a high level.
Figure 16.
ESI reads
10.4.2
ESI write transfer
To send data to the enclosure, the drive places ESI data on the data pins and pulls –DSK_WR in low. The
enclosure strobes the data and responds by pulling –ENCL_ACK low to signal the drive it has taken the data.
The drive stops pulling –DSK_WR low, allows the pin to return to a high . The enclosure responds to the –
-P_ESI
SEL_6/-DSK_WR
SEL_4/-ENCL_ACK
SEL(3:0)/DATA
-SEL(3:0)
CMD
Nibble 1
CMD
Nibble 2
CMD
Nibble 8
SEL_5/-DSK_RD
Discovery
Data
ESI Command
-P_ESI
SEL_6/-DSK_WR
SEL_6
SEL_4/-ENCL_ACK
SEL(3:0)/DATA
SEL(3:0)
Data
Nibble 1
Data
Nibble 2
Data
Nibble N
SEL_5/-DSK_RD
SEL_5
SEL_4
1
µsec max
