Sun Microsystems eWay JDBC/ODBC Adapter User Manual
Page 11
Chapter 1
Section 1.1
Introducing the JDBC/ODBC eWay
About Java Database Connectivity (JDBC)
JDBC/ODBC eWay Adapter User’s Guide
11
Sun Microsystems, Inc.
different databases. Many mainframe legacy non-relational databases use this kind of
driver.
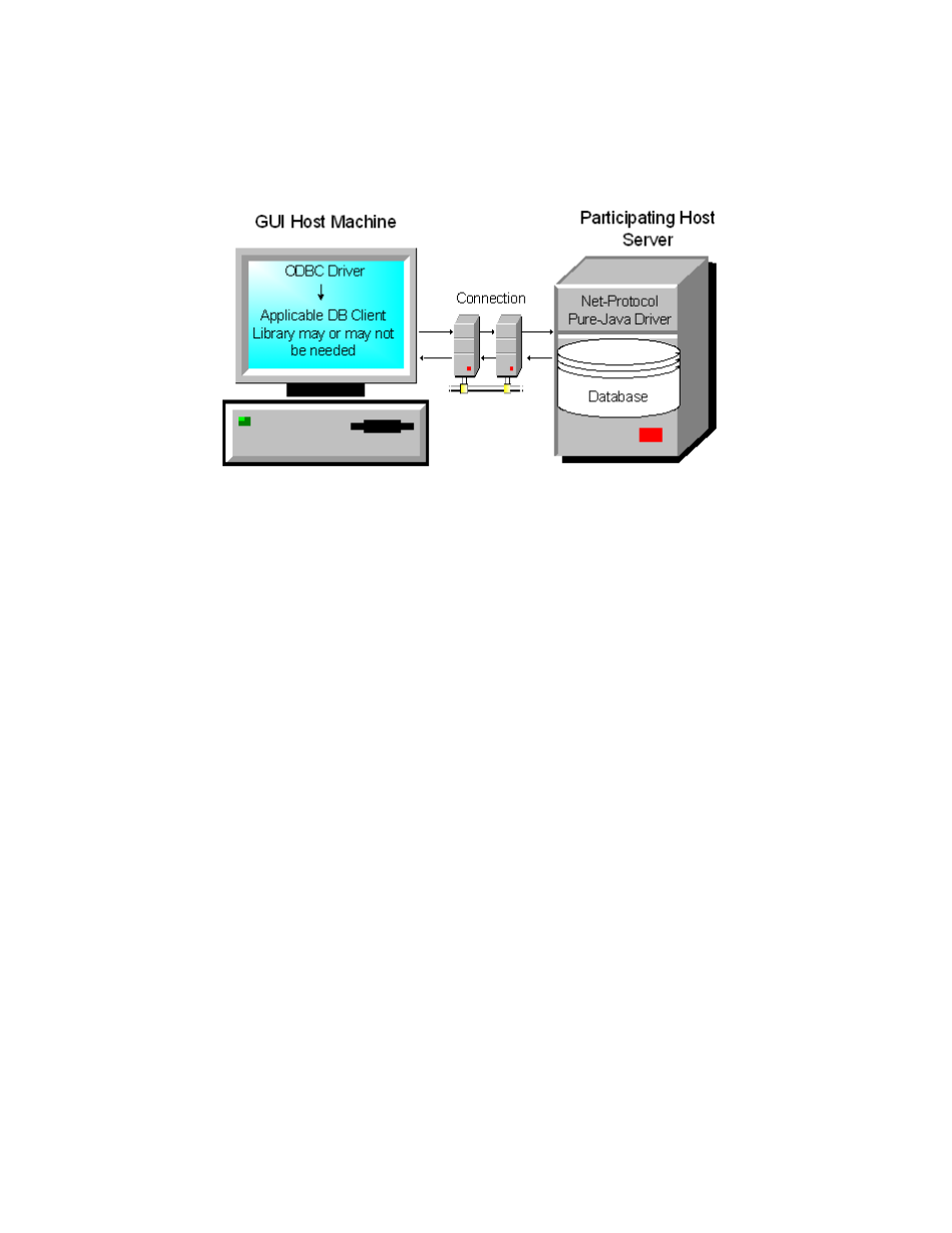
Figure 3 Typical Type 3 Middleware Driver Configuration
The pros and cons for using this type of driver are as follows:
Pros
Allows access to almost any database since the databases ODBC drivers are readily
available
Offers significantly better performance than the JDBC/ODBC Bridge and Type 2
Drivers
Advanced Java feature set
Scalable
Caching
Advanced system administration
Does not require applicable database client libraries
Cons
Requires a separate JDBC middleware server to translate specific native-
connectivity interface.
Type Four Driver: Direct-to-database pure Java driver
This style of driver converts JDBC calls into a network protocol that sends the
converted packets--in a proprietary format--to be used directly by DBMSs, thus
allowing a direct call from the client machine to the DBMS server and providing a
practical solution for intranet access. This type of driver has become very popular
recently and is supported by most database software vendors. All JDBC drivers from
Data Direct Technologies (driver vendor) are Type 4 drivers.
Pros: Better performance than Types 1 and 2. No need to install special software on
client or server.
