Figure 21. 8xc196lx block diagram, 2 block diagram, 3 internal timing – Intel 8XC196Lx User Manual
Page 16: Block diagram -2, Internal timing -2, 8xc196l
8XC196L
X SUPPLEMENT
2-2
2.2
BLOCK DIAGRAM
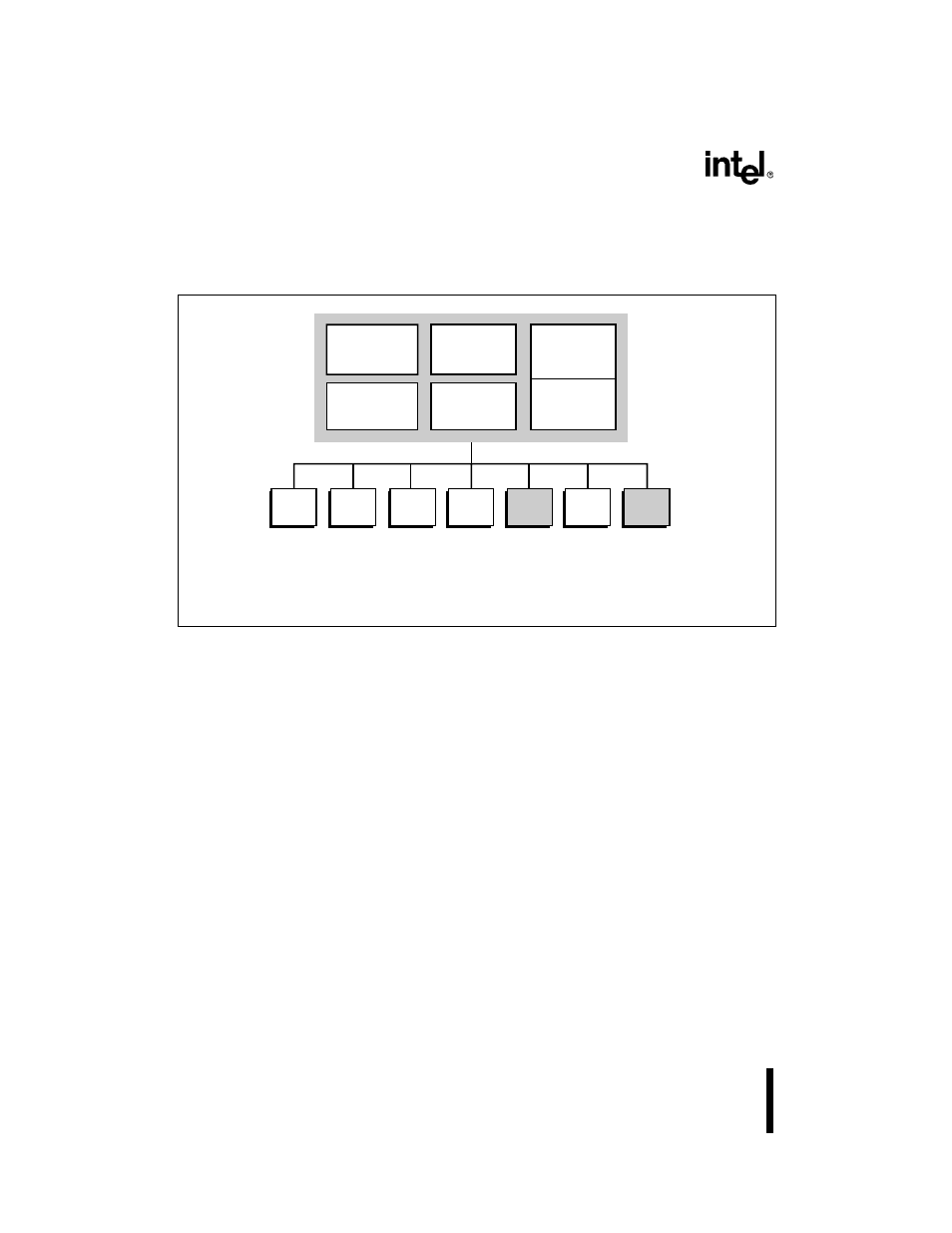
Figure 2-1 is a simplified block diagram that shows the major blocks within the microcontroller.
Observe that the slave port peripheral does not exist on the 8XC196Lx.
Figure 2-1. 8XC196L
x Block Diagram
2.3
INTERNAL TIMING
The 87C196LA, LB clock circuitry (Figure 2-2) implements a phase-locked loop and clock mul-
tiplier circuitry, which can substantially increase the CPU clock rate while using a lower-frequen-
cy input clock. The clock circuitry accepts an input clock signal on XTAL1 provided by an
external crystal or oscillator. Depending on the value of the PLLEN pin, this frequency is routed
either through the phase-locked loop and multiplier or directly to the divide-by-two circuit. The
multiplier circuitry can double the input frequency (F
XTAL
1
) before the frequency (f) reaches the
divide-by-two circuitry. The clock generators accept the divided input frequency (f/2) from the
divide-by-two circuit and produce two nonoverlapping internal timing signals, PH1 and PH2.
These signals are active when high.
NOTE
This manual uses lowercase “f” to represent the internal clock frequency. For
the 87C196LA and LB, f is equal to either F
XTAL
1
or 2F
XTAL
1
, depending on the
clock multiplier mode, which is controlled by the PLLEN input pin.
A5253-01
Optional
ROM/
OTPROM
Core
(CPU, Memory
Controller)
Optional
Code/Data
RAM
Clock and
Power Mgmt.
Peripheral
Transaction
Server
EPA
A/D
SSIO
I/O
WDT
SIO
J1850
Interrupt
Controller
Note:
The J1850 peripheral is unique to the 87C196LB device.
The A/D peripheral is unique to the 87C196LA, LB devices.
