5 general considerations, 1 spectrum planning, General considerations – Motorola PTP 400 Series User Manual
Page 39: Spectrum planning, Table 6 - ptp 400 series bridge frequency variants, 5general considerations
37
5
General Considerations
5.1 Spectrum
Planning
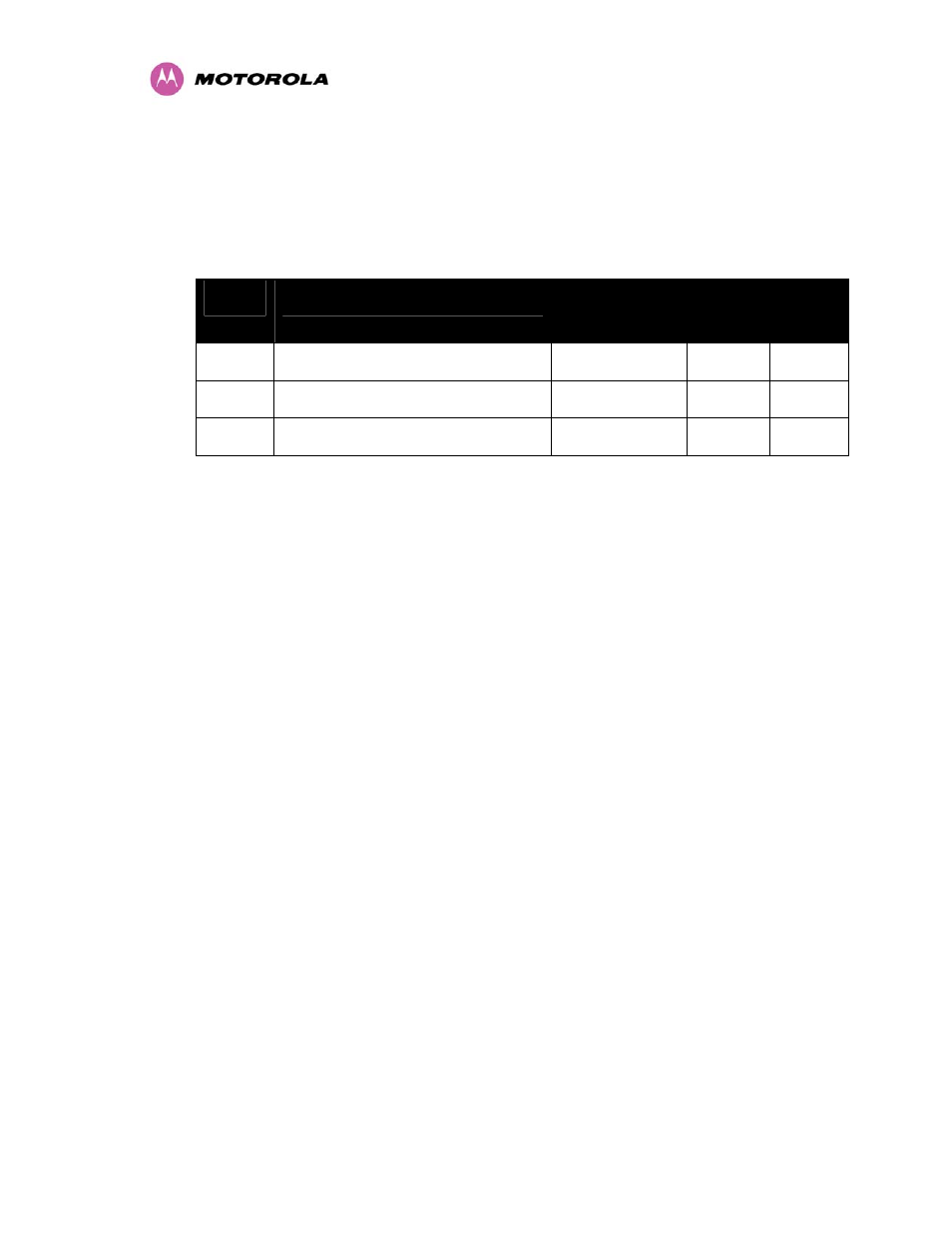
The PTP 400 Series Bridge has three frequency variants in its product range.
Band
Definition
Frequency
Coverage
Channel
Width
Channel
Raster
4.9 GHz USA National Public Safety Band
4940-4990 MHz
10 MHz
5 MHz
5.4 GHz ETSI 5 GHz band B
5470-5725 MHz
11 MHz
12 MHz
5.8 GHz USA ISM Band / ETSI 5 GHz band C
5725-5850 MHz
11 MHz
6 MHz
Table 6 - PTP 400 Series Bridge Frequency Variants
There are two distinct approaches to spectrum planning:
First, an operator can utilize the default spectrum management mode i-DFS (intelligent
Dynamic Frequency Selection). This mode uses the PTP 400 Series Bridge’s ability to
measure the interference levels in all channels to build up a picture of the interference / noise
levels in all channels. The PTP 400 Series Bridge uses statistical techniques to select the
most appropriate transmit and receive channels. I-DFS can be influenced in its channel
decision process by selectively barring channels from use. The use of this functionality is
described in detail in section 8.3.8 “Spectrum Management”.
Second, when detailed control of the spectrum allocation is required it is recommended that
the fixed frequency mode is used to statically allocate transmit and receive channels.
