Warning, Upply, Iping – Goodman Mfg MVC95 User Manual
Page 34: Irculating, Ilters, Propane gas piping chart i, Propane gas piping chart ii
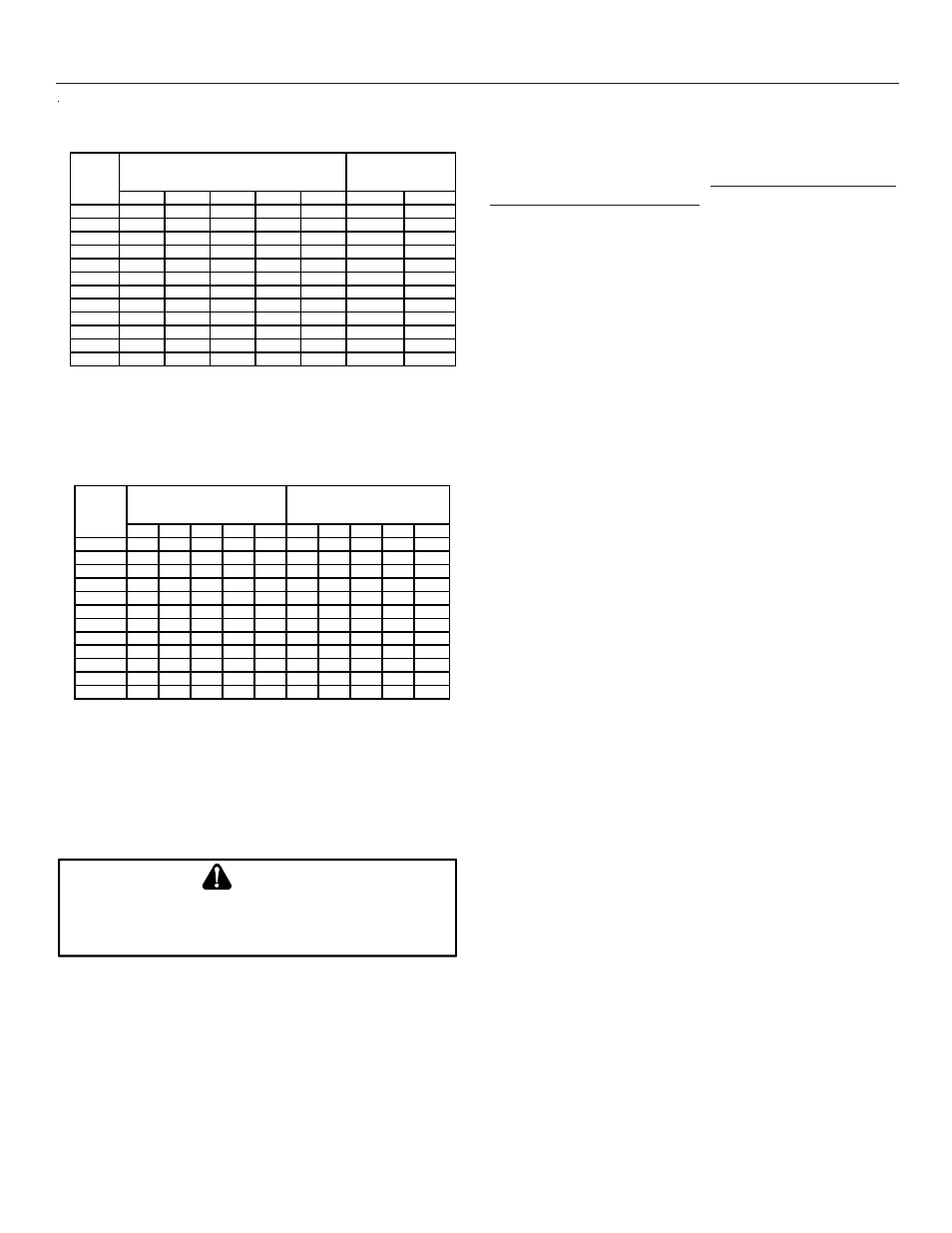
34
G
AS
S
UPPLY
AND
P
IPING
3/8"
1/2"
5/8"
3/4"
7/8"
1/2"
3/4"
10
730
1,700
3,200
5,300
8,300
3,200
7,500
20
500
1,100
220
3,700
5,800
2,200
4,200
30
400
920
2,000
2,900
4,700
1,800
4,000
40
370
850
1,700
2,700
4,100
1,600
3,700
50
330
770
1,500
2,400
3,700
1,500
3,400
60
300
700
1,300
2,200
3,300
1,300
3,100
80
260
610
1,200
1,900
2,900
1,200
2,600
100
220
540
1,000
1,700
2,600
1,000
2,300
125
200
490
900
1,400
2,300
900
2,100
150
190
430
830
1,300
2,100
830
1,900
175
170
400
780
1,200
1,900
770
1,700
200
160
380
730
1,100
1,800
720
1,500
Pipe or
Tubing
Length
Feet
Tubing Size, O.D. Type L
Nominal Pipe Size
Schedule 40
Sizing Between First and Second Stage Regulator*
Maximum Propane Capacities listed are based on 2 psig pressure drop at 10 psig setting.
Capacities in 1,000 BTU/hour.
To convert to capacities at 15 psig settings - multiply by 1.130
To convert to capacities at 5 psig settings - multiply by 0.879
Propane Gas Piping Chart I
3/8"
1/2"
5/8"
3/4"
7/8"
1/2"
3/4"
1"
1-1/4" 1-1/2"
10
39
92
199
329
501
275
567
1,071 2,205 3,307
20
26
62
131
216
346
189
393
732
1,496 2,299
30
21
50
107
181
277
152
315
590
1,212 1,858
40
19
41
90
145
233
129
267
504
1,039 1,559
50
18
37
79
131
198
114
237
448
913
1,417
60
16
35
72
1,211
187
103
217
409
834
1,275
80
13
29
62
104
155
89
185
346
724
1,066
100
11
26
55
90
138
78
162
307
630
976
125
10
24
48
81
122
69
146
275
567
866
150
9
21
43
72
109
63
132
252
511
787
200
8
19
39
66
100
54
112
209
439
665
250
8
17
36
60
93
48
100
185
390
590
Tubing Size, O.D. Type L
Nominal Pipe Size
Schedule 40
Pipe or
Tubing
Length
Feet
*Data in accordance with NFPA pamphlet No. 54
Sizing Between Second or Second Stage Regulator & Appliance*
Maximum Propane Capacities listed are based on 1/2" W.C. pressure drop at 11" W.C. setting.
Capacities in 1,000 BTU/hour.
Propane Gas Piping Chart II
C
IRCULATING
A
IR
& F
ILTERS
D
UCT
WORK
- A
IR
F
LOW
N
EVER
ALLOW
THE
PRODUCTS
OF
COMBUSTION
,
INCLUDING
CARBON
MONOXIDE
,
TO
ENTER
THE
RETURN
DUCT
WORK
OR
CIRCULATION
AIR
SUPPLY
.
WARNING
Duct systems and register sizes must be properly designed for
the CFM and external static pressure rating of the furnace. Design
the ductwork in accordance with the recommended methods of
“Air Conditioning Contractors of America” Manual D.
Install the duct system in accordance with Standards of the Na-
tional Board of Fire Underwriters for the Installation of Air Condition-
ing, Warm Air Heating and Ventilating Systems. Pamphlets No.
90A and 90B.
A closed return duct system must be used, with the return duct
connected to the furnace. NOTE: Ductwork must never be at-
tached to the back of the furnace. For upflow installations requir-
ing 1800 CFM or more, use either two side returns or bottom
return or a combination of side /bottom. Flexible joints may be
used for supply and return connections to reduce noise transmis-
sion. To prevent the blower from interfering with combustion air or
draft when a central return is used, a connecting duct must be
installed between the unit and the utility room wall. Never use a
room, closet, or alcove as a return air chamber.
C
HECKING
D
UCT
S
TATIC
Refer to your furnace rating plate for the maximum ESP (ex-
ternal duct static) rating.
Total external static refers to everything external to the fur-
nace cabinet. Cooling coils, filters, ducts, grilles, registers
must all be considered when reading your total external static
pressure. The supply duct pressure must be read between
the furnace and the cooling coil. This reading is usually taken
by removing the “A” shaped block off plate from the end on the
coil; drilling a test hole in it and reinstalling the block off plate.
Take a duct static reading at the test hole. Tape up the test
hole after your test is complete. The negative pressure must
be read between the filter and the furnace blower.
Too much external static pressure will result in insufficient air
that can cause excessive temperature rise. This can cause
limit switch tripping and heat exchanger failure.
To determine total external duct static pressure, proceed as
follows;
1. With clean filters in the furnace, use a draft gauge (in-
clined manometer) to measure the static pressure of the
return duct at the inlet of the furnace. (Negative Pressure)
2. Measure the static pressure of the supply duct. (Positive
Pressure)
3. The difference between the two numbers is .4” w.c.
Example:
static reading from return duct = -.1" w.c.
static reading from supply duct = .3" w.c.
total external static pressure on this system = .4" w.c.
NOTE: Both readings may be taken simultaneously and read
directly on the manometer if so desired. If an air conditioner
coil or Electronic Air Cleaner is used in conjunction with the
furnace, the readings must also include theses components,
as shown in the following drawing.
