1 output waveform, Time voltage – Magnum Energy MS Series User Manual
Page 15
Page 6
©
2012 Magnum Energy, Inc.
Introduction
1.3 Advantages of a Pure Sine Wave vs a Modifi ed Sine Wave Inverter
Today’s inverters come in three basic output waveforms: square wave, modifi ed sine wave (which
is actually a modifi ed square wave) and pure sine wave (see Figure 1-5). Modifi ed sine wave
inverters approximate a pure sine wave form and will run most appliances and electronics without
any problems. These inverters are less expensive, and therefore, offer a viable alternative to more
expensive pure sine inverters.
The output of the MS Series inverter—which is pure sine wave—is equal to, or in many cases,
better than the utility power used in your home. Virtually any electronic device will operate from a
pure sine wave inverter. Motors run cooler, microwaves usually cook faster, and clocks keep better
time just to name a few examples. Without compromising quality or performance, the MagnaSine
provides you with all the advantages of a pure sine wave inverter at a much lower cost than many
on the market.
The MS Series is built on the same platform as our popular ME and RD Series modifi ed sine
wave inverters—allowing for an easy upgrade to a pure sine wave inverter from the original ME
or RD Series installation. This standard platform also helps reduce cost by using standard parts/
accessories across many models. Magnum accessories such as the Advanced Remote Control (ME-
ARC), Standard Remote Control (ME-RC), Automatic Generator Start - Networked (ME-AGS-N),
and Battery Monitor Kit (ME-BMK) can be used.
TIME
VOLTAGE
40
80
0
120
40
160
200
80
120
160
200
Modified
Sine Wave
Sine Wave
Square Wave
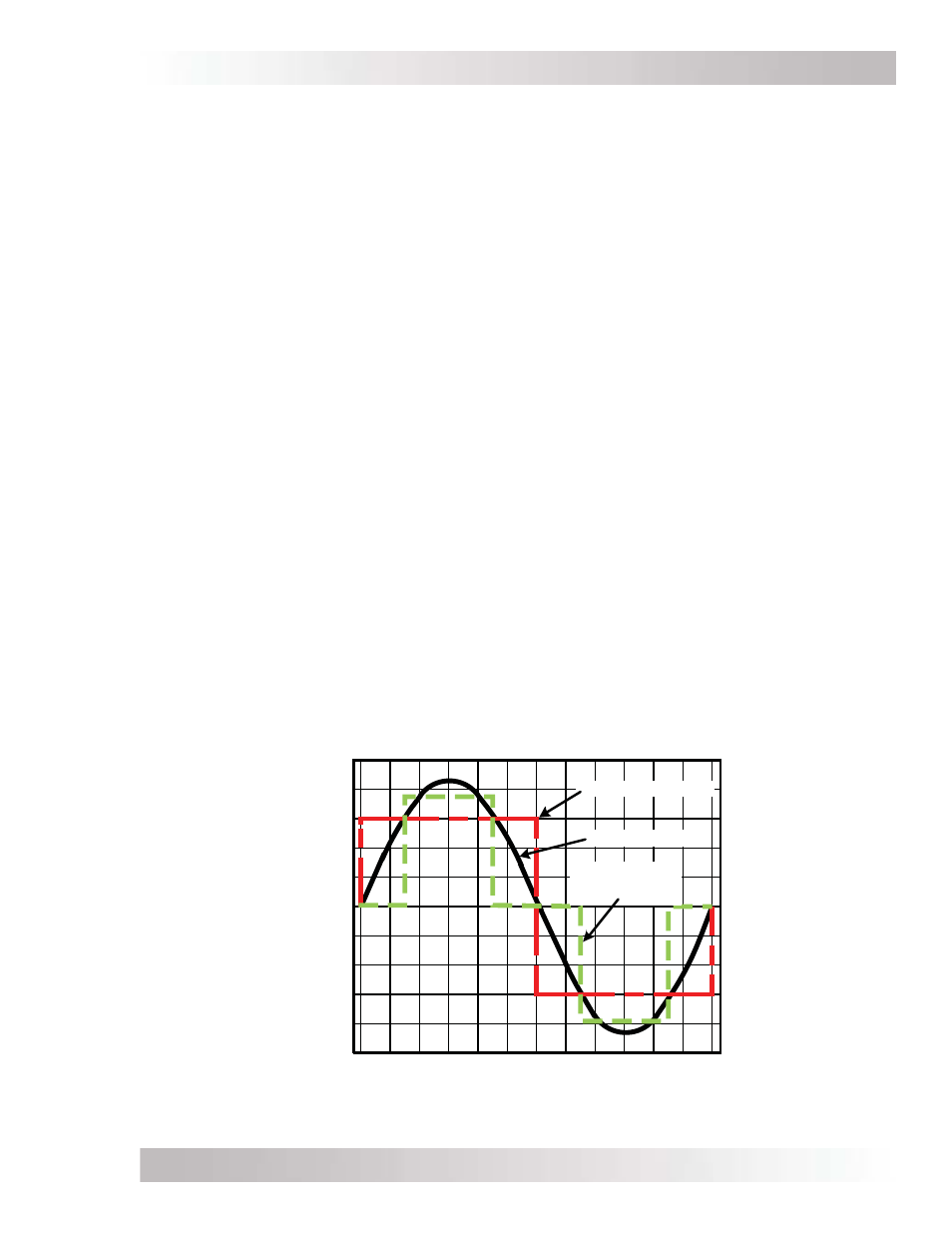
1.3.1 Output Waveform
The inverter’s output waveform is the shape of the wave that alternating current makes as its
voltage rises and falls with time (see Figure 1-5 below). The three basic output waveforms are:
• Modifi ed Sine Wave – Also referred to as a “quasi sine wave” or a “modifi ed square wave”.
This output looks like a one-step staircase and the waveform changes its width to continually
provide the correct RMS output voltage regardless of the battery voltage. Most loads that run
from a sine wave will also run from a modifi ed sine wave. However, things such as clocks and
furnace controllers may have trouble.
• Sine
Wave – An AC waveform that looks like rolling waves on water. It rises and falls smoothly
with time. The grid puts out a sine waveform. Any plug-in AC equipment will operate from a
sine wave output inverter.
• Square Wave – The simplest AC waveform. Some types of equipment behave strangely
when powered from a square wave inverter.
Figure 1-5, AC Waveforms
