2 f undamentals of path functions – HEIDENHAIN TNC 620 (73498x-01) User Manual
Page 172
172
Programming: Programming contours
6.2 F
undamentals of path functions
Circles and circular arcs
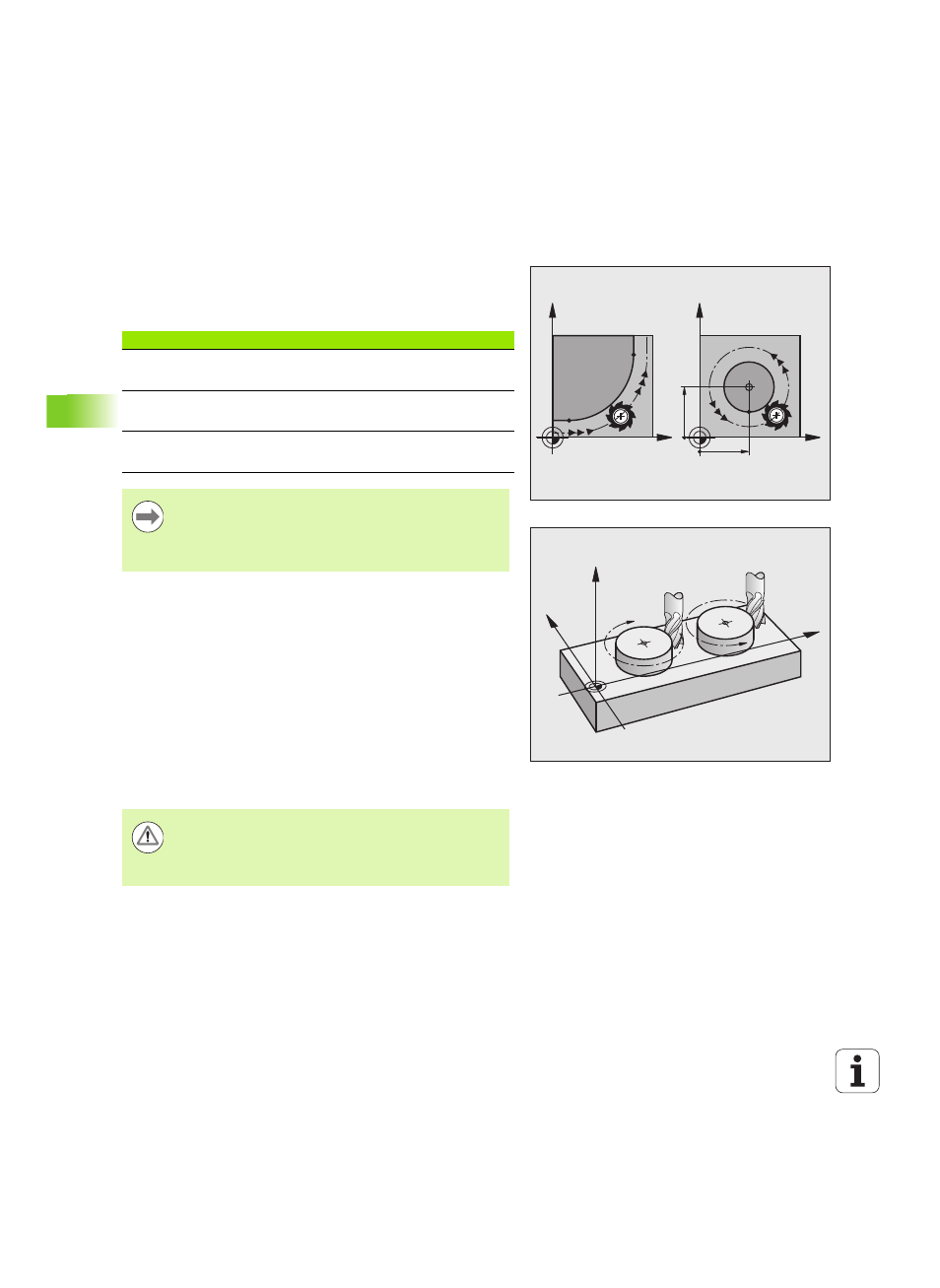
The TNC moves two axes simultaneously on a circular path relative to
the workpiece. You can define a circular movement by entering the
circle center CC.
When you program a circle, the control assigns it to one of the main
planes. This plane is defined automatically when you set the spindle
axis during a TOOL CALL:
Direction of rotation DR for circular movements
When a circular path has no tangential transition to another contour
element, enter the direction of rotation as follows:
Clockwise direction of rotation: DR-
Counterclockwise direction of rotation: DR+
Radius compensation
The radius compensation must be in the block in which you move to
the first contour element. You cannot activate radius compensation in
a circle block. Activate it beforehand in a straight-line block (see "Path
contours—Cartesian coordinates", page 182) or approach block (APPR
block, see "Contour approach and departure", page 174).
Pre-positioning
X
Y
X
Y
CC
X
CC
Y
CC
Spindle axis
Main plane
Z
XY, also
UV, XV, UY
Y
ZX, also
WU, ZU, WX
X
YZ, also
VW, YW, VZ
You can program circles that do not lie parallel to a main
plane by using the function for tilting the working plane
(see User's Manual for Cycles, Cycle 19, WORKING
PLANE) or Q parameters (see "Principle and overview",
page 236).
CC
CC
DR
DR+
X
Z
Y
Danger of collision!
Before running a part program, always pre-position the
tool to prevent the possibility of damaging it or the
workpiece.
