1 8 path functions, Path functions for positioning blocks – HEIDENHAIN TNC 310 (286 140) Pilot User Manual
Page 18
1 8
Path Functions
Page 19
Page 22
Page 21
Page 21
Page 23
Path Functions for Positioning Blocks
See Programming: programming contours
Programming the Direction of Traverse
Regardless of whether the tool or the workpiece is actually moving,
you always program as if the tool is moving and the workpiece is
stationary.
Entering the Target Positions
Target positions can be entered in Cartesian or polar coordinates
either as absolute or incremental values, or with both absolute and
incremental values in the same block.
Entries in the Positioning Block
A complete positioning block contains the following data:
Path function
Coordinates of the contour element end points (target position)
Radius compensation RR/RL/R0
Feed rate F
Miscellaneous function M
Before you execute a part program, always pre-position the tool
to prevent the possibility of damaging the tool or workpiece.
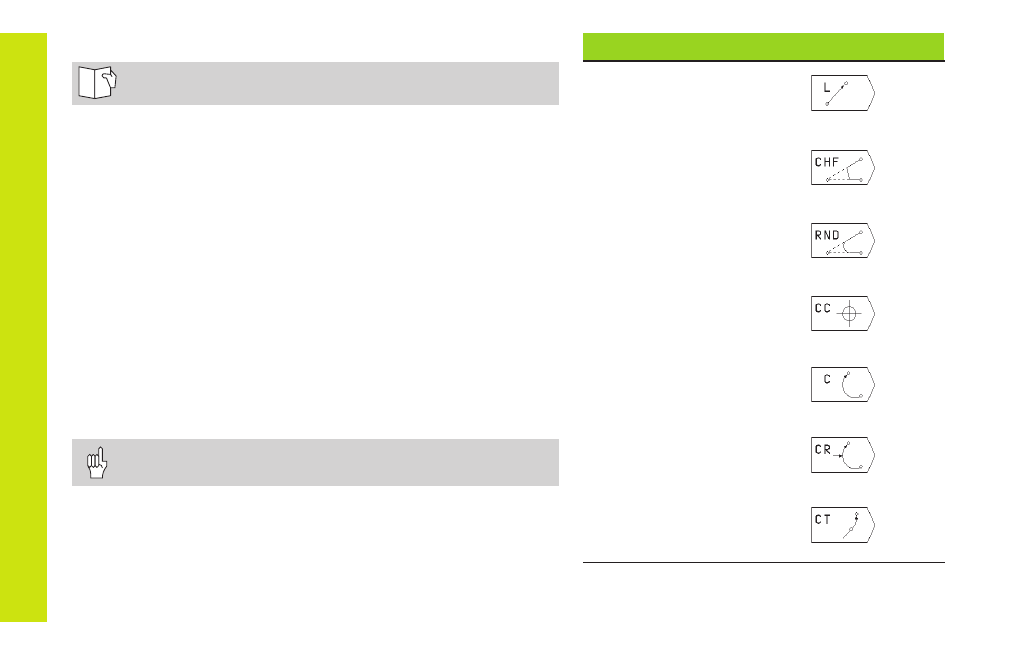
Path Functions
Straight line
Chamfer
between two
straight lines
Corner rounding
Circle center
or pole for
polar coordinates
Circular path
around the
circle center CC
Circular path with
known radius
Circular path with
tangential connection
to previous contour
Page 20
Page 20
