Ab c d arm null pot – Measurement Computing CIO-EXP-GP User Manual
Page 35
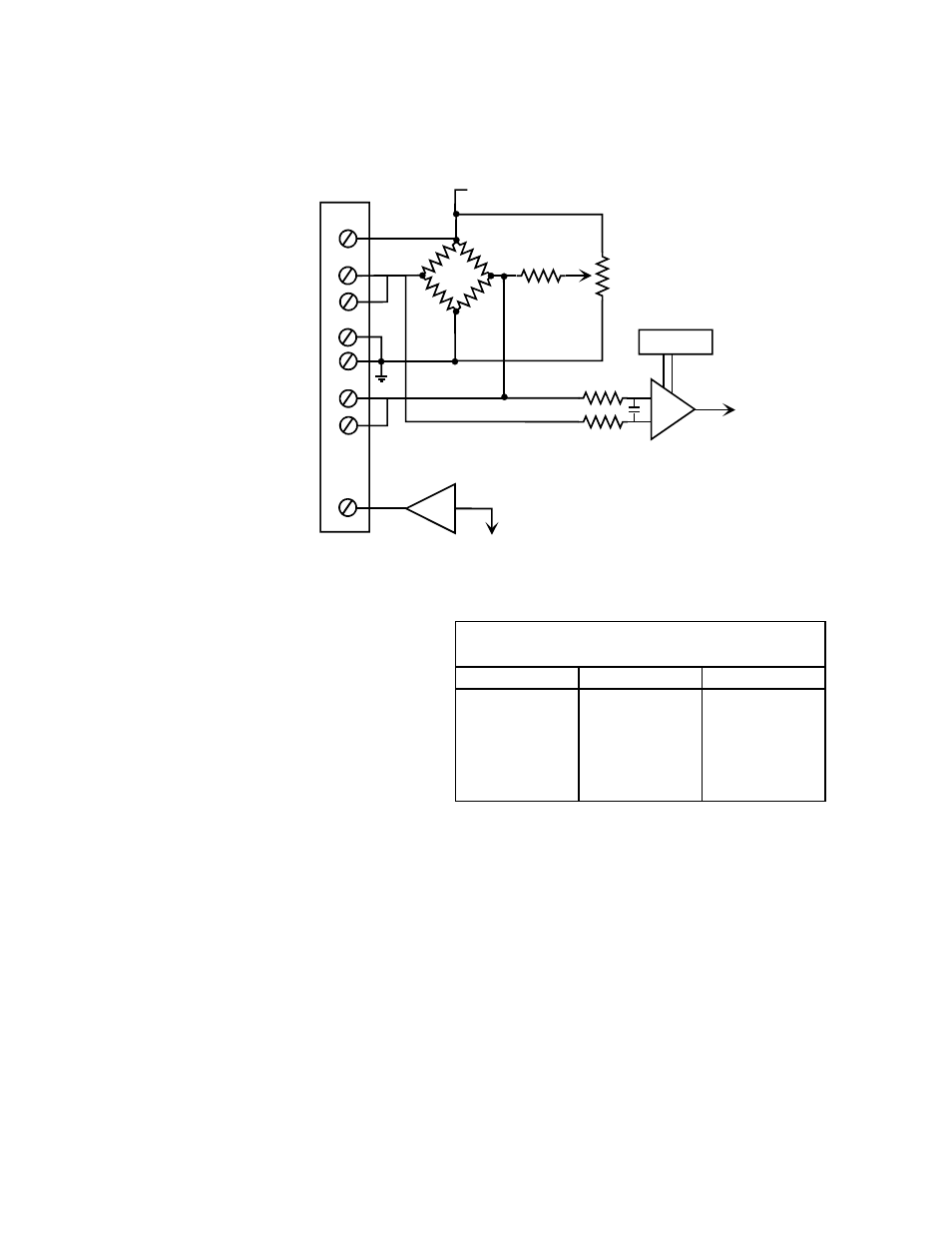
this bridge or the entire bridge. Examples of each of these configurations follow. Figure 7-6 is a
schematic of the bridge circuit.
GAIN SW
AMP
EXCITATION VOLAGE (+)
CURRENT SOURCE
VOLTAGE REFERENCE
TO CHANNEL
MULTIPLEXOR
EXCITATION. VOLTS (+)
SENSE LOW (-)
EXCITATION CURRENT (-)
EXCITATION VOLTS (-)
SENSE HIGH (+)
EXCITATION CURRENT (+)
SENSE LOW (-)
SENSE HIGH (+)
80Hz Low
Pass Filter
A
B
C
D
Arm
Null Pot
Figure 7-6. Bridge Circuit
- Volts
+ Volts
+ Volts
- Volts
+ Volts
- Volts
- Volts
+ Volts
A
B
C
D
- Ohms
+ Ohms
Leg
This table shows how the measurement at the
A/D board varies with respect to an increase
or decrease of the resistance in one of the legs
of the bridge.
Resistance Change vs. Sense Voltage
Change
Read the table by selecting the leg you are interested in and looking across that row to the ±Volts
indication under the column heading for the expected change in resistance. For example, if you are
interested in leg ‘A’ and want to know what the relative change in volts at the A/D board will be if the
resistance is increased, look under + Ohms. The measured voltage will increase.
7.8.1
Bridge Completion Resistors
You likely will have to install bridge-completion resistors on the CIO-EXP-GP board to match the
resistance of the external gauge. Refer to Table 7-2 for their identities and locations.
If you are using a ¼ bridge then you will have to install three precision resistors to complete the
bridge.
If you are using a ½ bridge then you will need to install two resistors to complete the bridge.
If you are using a full bridge, there are no resistors to install.
31
