Shared rx/tx clock, Shared ref/tx clock – Altera HyperTransport MegaCore Function User Manual
Page 34
3–8
Chapter 3: Specifications
HyperTransport MegaCore Function Specification
HyperTransport MegaCore Function User Guide
© November 2009
Altera Corporation
Preliminary
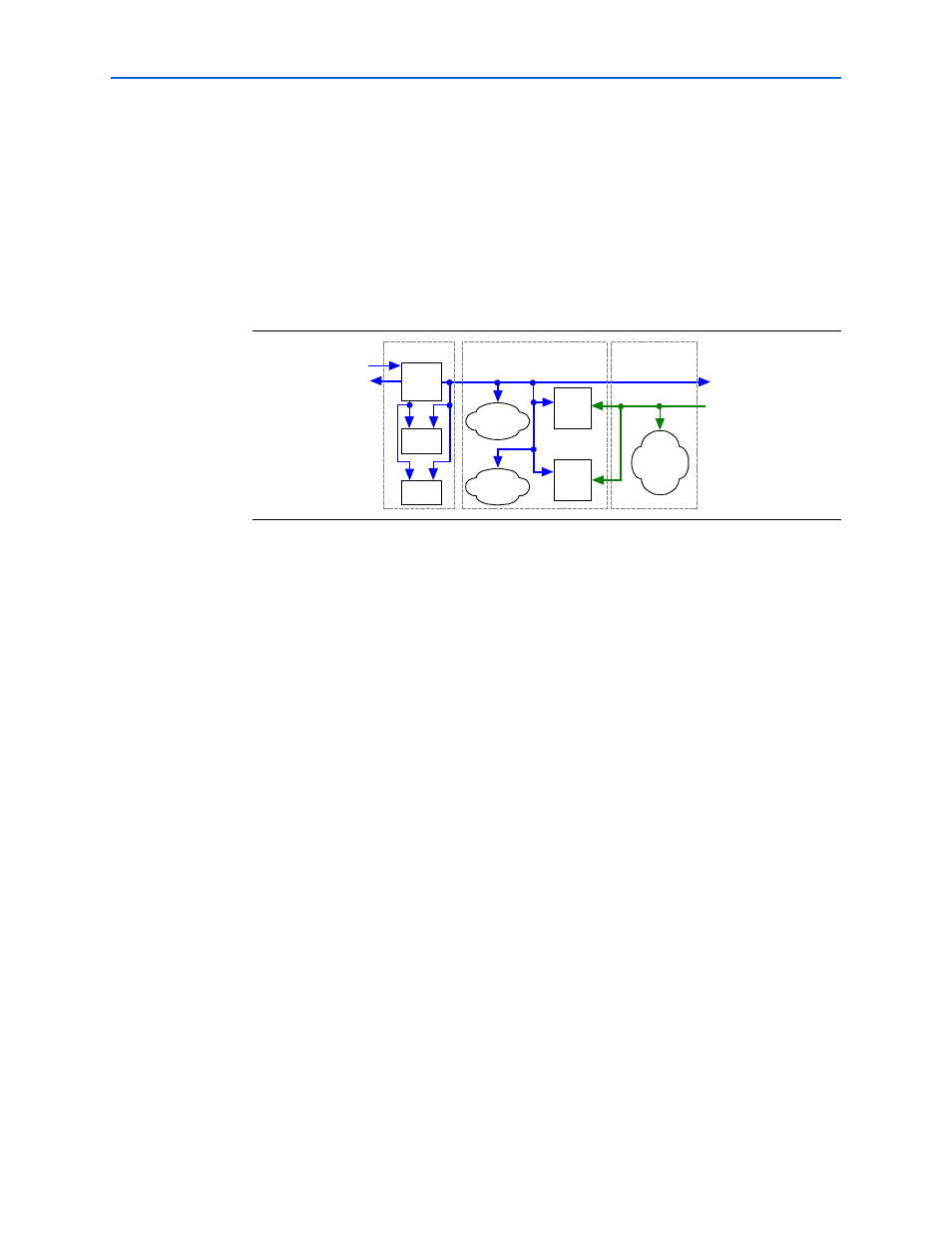
Shared Rx/Tx Clock
When you turn on the Shared Rx/Tx Clock option, the Rx alignment logic, protocol
interface logic, and Tx alignment logic operate as independent clock domains with
synchronization FIFO buffers buffering data between the modules, as shown in
. The Rx and Tx clocks share the same PLL, and are synchronous. This
implementation provides the most flexible design because the reference clock
(
RefClk
) frequency and phase can be determined by other requirements the user
application may impose, and the HT Tx link clock is always synchronous with the HT
Rx link clock.
The Tx sync and Rx sync FIFO buffers consume logic resources and add latency to the
HyperTransport MegaCore function. This increased latency can limit the link
throughput if the attached HT device has a small number of buffer credits. The
latency increases the turnaround time for receiving a new buffer credit after
transmitting a packet.
The design must meet the following clock frequency requirements when using the
Shared Rx/Tx Clock
option:
■
The frequency of
RefClk
must be greater than or equal to
RxLnkClkD4
.
■
When
RefClk
and
RxLnkClkD4
are nominally equal but are derived from
different sources,
RefClk
must be no more than 2,000 ppm slower than
RxLnkClkD4
.
1
Failing to meet these requirements will result in system failure due to Tx sync FIFO
buffer underflow or Rx sync FIFO buffer overflow.
In most designs, you would not connect
RxLnkClkD4
to anything external to the
HyperTransport MegaCore function, but it is provided for monitoring purposes if
needed.
Shared Ref/Tx Clock
The Shared Ref/Tx Clock option reduces the latency through the HyperTransport
MegaCore function by eliminating the Tx sync FIFO buffer. The MegaCore function
uses
RxLnkClkD4
for the Rx alignment logic only, and uses the
RefClk
for the rest of
the logic, including the Tx alignment logic, as shown in
Figure 3–5. Shared Rx/Tx Clock Option
RxClk_i
Rx
Alignment
Logic
Tx
Alignment
Logic
Rx
Sync
FIFO
RefClk
Phy
Synch & Alignment
Protocol Interface
Protocol
Interface
Logic
Rx
SerDes
RxLnkClkD4
PLL
÷4
TxClk_o
Tx
SerDes
Tx
Sync
FIFO
×
1
×
2
