B burst mode measurements – EXFO PSO-100 Series Optical Sampling Oscilloscopes User Manual
Page 113
Optical Sampling Oscilloscope
105
B Burst Mode Measurements
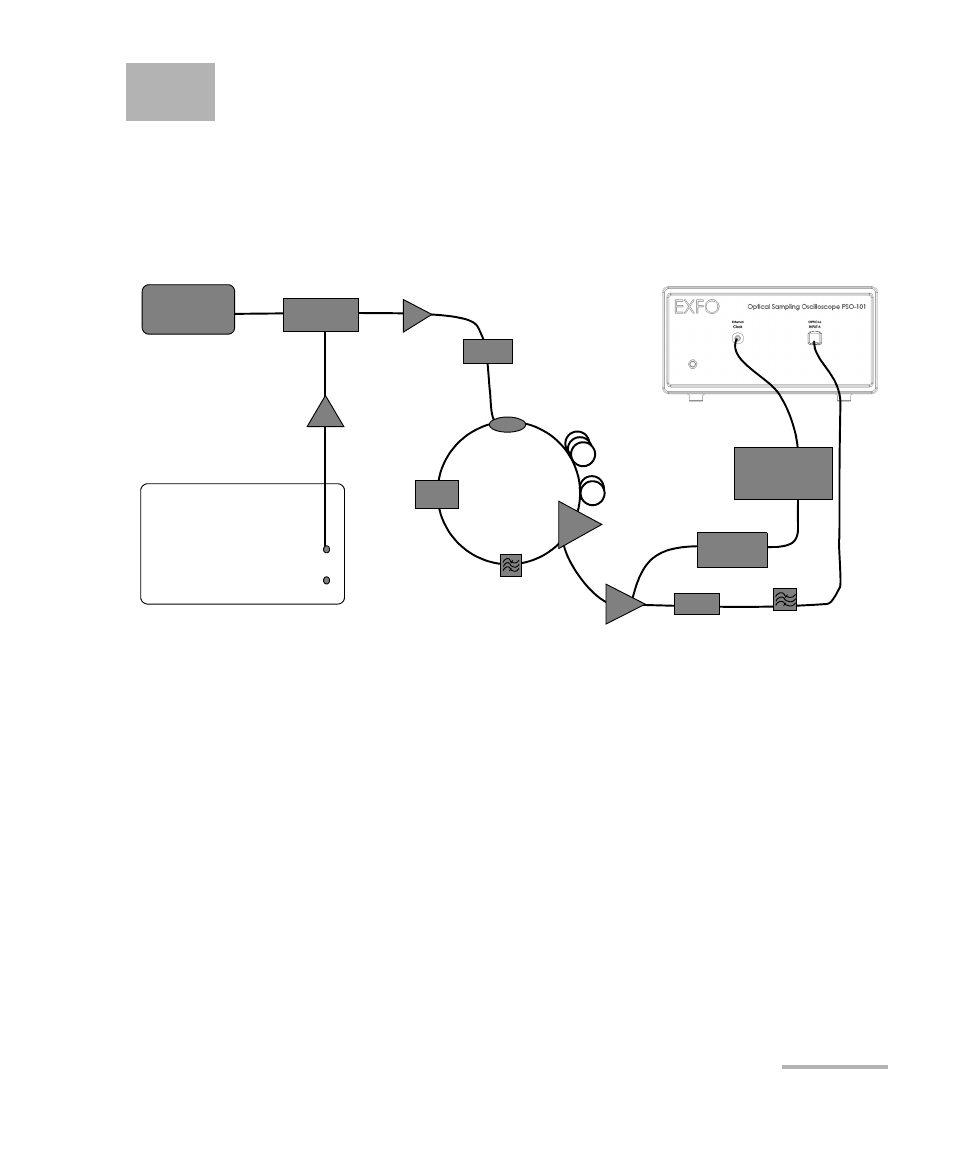
The burst mode is very useful for example in circulating loop experiments.
For this function to work, you must have the external clock option.
In the figure below, we see an example with 42.3 Gb/s NRZ data
modulation that come in bursts from a circulating loop.
The first acousto-optic modulator (AOM) chops the data into bursts with a
duration to exactly fill the loop (in this case 31.3 km of fiber). The AOM
inside the loop is used for emptying the loop after N circulations, when a
new burst is injected into the loop.
In this way, a near continuous data stream is circulating in the loop. The
output signal from the loop constitutes of bursts originating from
circulation number 1,2,…,N. With the last AOM, you select which
circulation to monitor. The signal frequency (or sub-rate) clock (in this
case from the clock recovery circuit) is inserted on the external clock input
and the optical signal from the loop is inserted to the sampler.
Clock and
Data Recovery
(CDR)
EDFA
10 GHz clock
Optical
bandpass
filter
AOM
10 %
27 km SMF
40 Gb/s
Receiver
Driver Amplifier
Roundtrip
selector
Laser
1550 nm
Empty loop
EDFA
Chop data
into bursts
4.3 km DCF
Optical
bandpass
filter
AOM
AOM
10 %
10 GHz clock
40 Gb/s output
Agilent ParBERT 81250
Pattern Generator
Mach-Zender
modulator
EDFA
