Dsl parameter details – EXFO MaxTester DSL User Manual
Page 37
MaxTester DSL
31
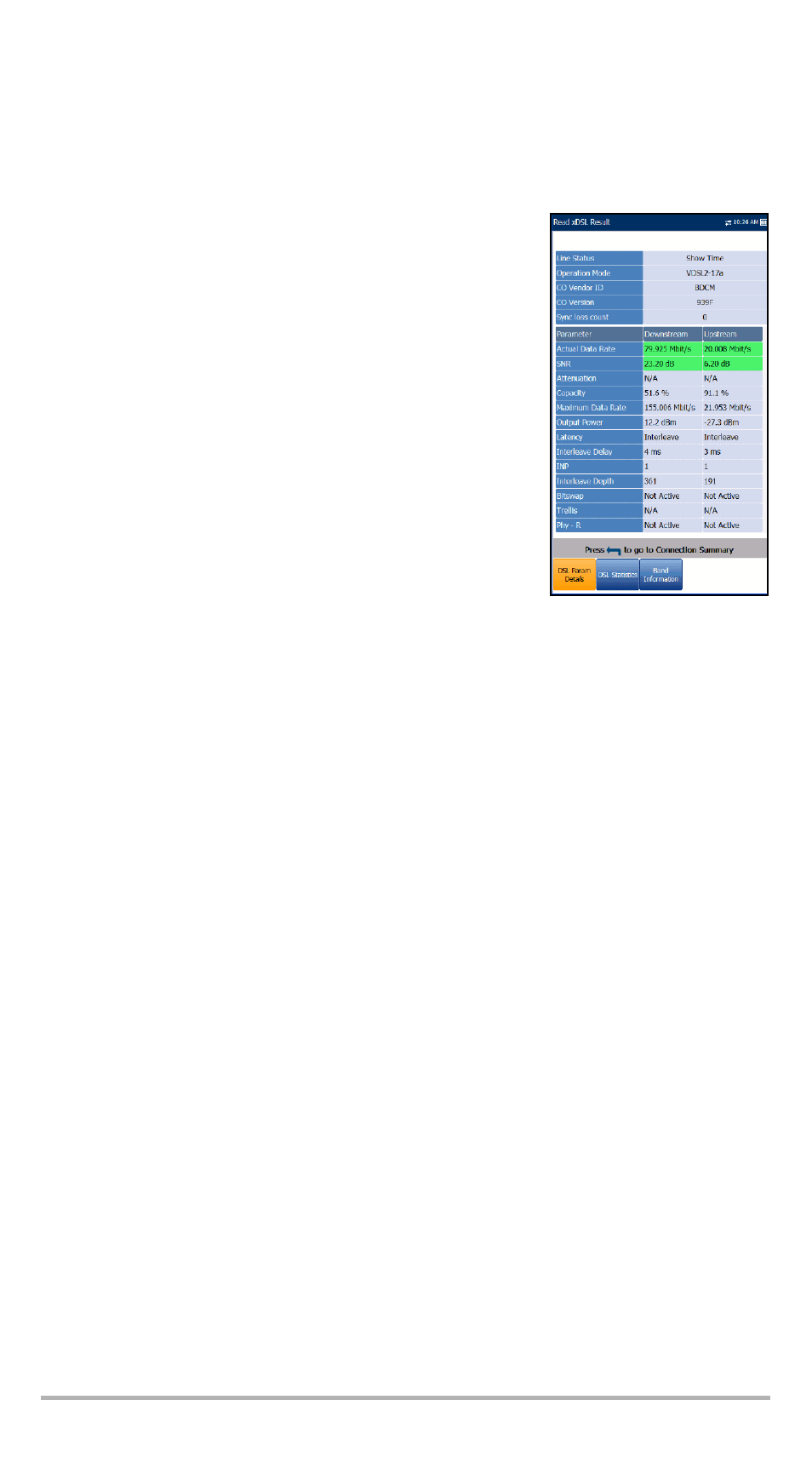
DSL Parameter Details
The DSL Param Details tab displays the Downstream and Upstream parameter
results configured in the xDSL tests.
³
Line Status displays the status of the line under test
during negotiation with the DSLAM. The value
changes from Idle /Activate /Handshake /Training
/Show Time for ADSL2+ or VDSL2 mode.
³
Operation Mode is the DSL mode of operation as
negotiated between the unit and the DSLAM.
³
CO Vendor ID is a unique 4-digit alphanumeric
identifier of the DSL chipset manufacturer used on the
CO (central office) side.
³
CO Version is the version number of the unique
alphanumeric identifier of the DSL chipset used on
the CO side.
³
Sync loss count is the number of times the unit lost
synchronization.
³
Parameters - Downstream/Upstream
³
Actual Data Rate displays the values at which the unit and CO are
connected, as negotiated during the training phase. The values should
represent what the CO was set to, unless the DSL link is being subjected to
high levels of noise/crosstalk, and are typically what the DSLAM has been
set to, whether interleaved or fast.
³
SNR is the signal-to-noise ratio margin measured on the line.
³
Attenuation is line attenuation measured during the training phase.
³
Capacity is the capacity of the line as a ratio of achieved bit rate over the
maximum attainable bit rate presented as a percentage (%). A high value
could mean that the link is nearing its maximum capabilities while a low
value could mean the link is being under utilized (sometimes intentionally –
verify your local DSLAM setup).
³
Maximum Data Rate displays the maximum attainable bit rates that the
circuit can handle as determined by the remote terminal and CO during the
training phase. Values can be greater than the actual bit rate.
³
Output Power is the current transmit power level that is a measure of the
aggregated transmit power.
³
Latency is the path type, Fast or Interleave, set by the service provider at
the CO. The use of the interleaved path means greater delay in the delivery
of data but it is less susceptible to noise or crosstalk due to increased
Reed-Solomon coding and FEC (forward error checking). The use of the
fast path means little or no delay in the delivery of data but it is more
susceptible to noise and crosstalk.
³
Interleave Delay defines the mapping (relative spacing) between
subsequent input bytes at the interleave input and their placement in the bit
stream at the interleave output.
³
INP is the level of impulse noise protection.
