3 spi interface pins, Timer registers, 1 registers – Cypress enCoRe CY7C602xx User Manual
Page 47: 1 free running counter
CY7C601xx, CY7C602xx
Document 38-16016 Rev. *E
Page 47 of 68
17.3 SPI Interface Pins
The SPI interface uses the P1.3–P1.6 pins. These pins are configured using the P1.3 and P1.4–P1.6 configuration.
18. Timer Registers
All timer functions of the enCoRe II LV are provided by a single timer block. The timer block is asynchronous from the CPU clock.
The 16-bit free running counter is used as the time base for timer captures and also as a general time base by software.
18.1 Registers
18.1.1 Free Running Counter
The 16-bit free running counter is clocked by the Timer Capture Clock (TCAPCLK). It is read in software for use as a general
purpose time base. When reading the low order byte, the high order byte is registered. Reading the high order byte reads this
register allowing the CPU to read the 16-bit value atomically (loads all bits at one time). The free running timer generates an
interrupt at 1024
μs rate when clocked by a 4 MHz source. It also generates an interrupt when the free running counter overflow
occurs—every 16.384 ms (with a 4 MHz source). This extends the length of the timer.
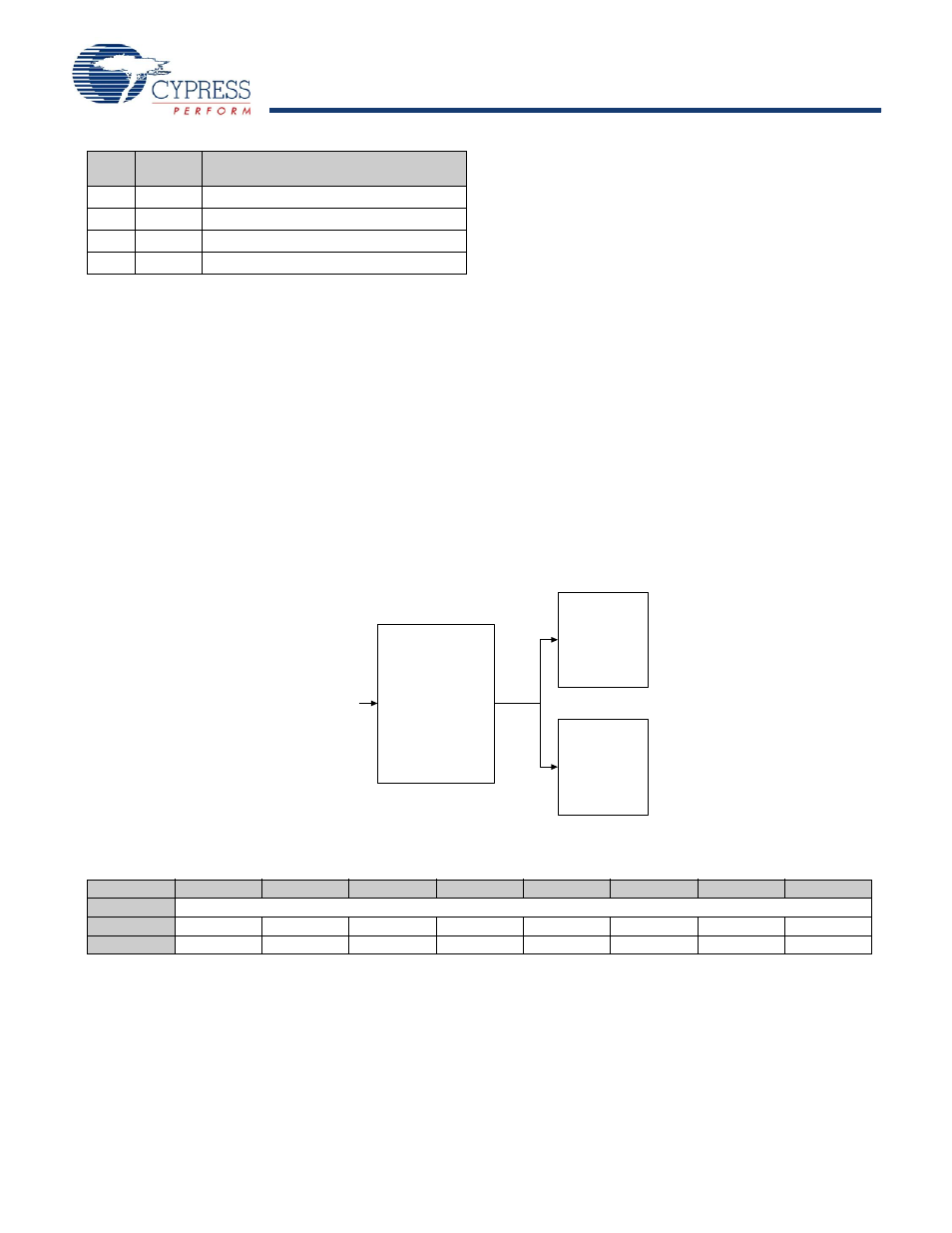
Figure 18-1. 16-Bit Free Running Counter Block Diagram
Table 17-4. SPI SCLK Frequency
SCLK
Select
CPUCLK
Divisor
SCLK Frequency when
CPUCLK = 12 MHz
00
6
2 MHz
01
12
1 MHz
10
48
250 kHz
11
96
125 kHz
Tim er C apture
C lock
16-bit Free
R unning C ounter
O verflow
Interrupt/W rap
Interrupt
1024-µs
Tim er
Interrupt
Table 18-1. Free Running Timer Low Order Byte (FRTMRL) [0x20] [R/W]
Bit #
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
Field
Free Running Timer [7:0]
Read/Write
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
Default
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
Bit [7:0]: Free Running Timer [7:0]
This register holds the low order byte of the 16-bit free running timer. Reading this register moves the high order byte into a
holding register allowing an automatic read of all 16 bits simultaneously.
For reads, the actual read occurs in the cycle when the low order is read. For writes, the actual time the write occurs is the cycle
when the high order is written.
When reading the free running timer, the low order byte is read first and the high order second. When writing, the low order byte
is written first then the high order byte.
