Manual mode connections – Aviom 6416o User Manual
Page 76
67
b
uildiNg
A
P
ro
64 N
etwork
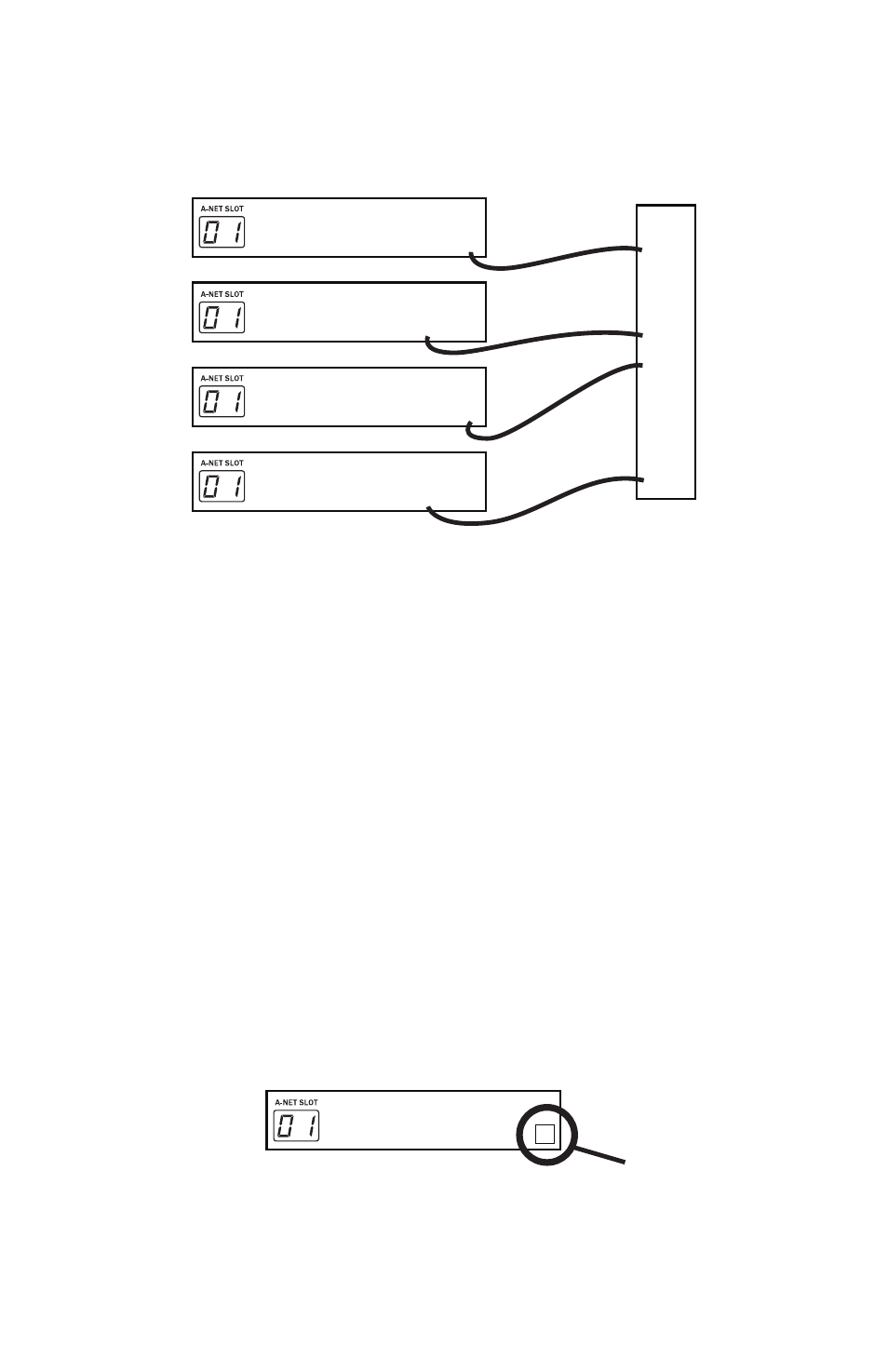
Example 4: One input module and three output modules connected using an
MH10 in Auto Mode
B A
B A
Input
B A
Output
B A
Input
B A
Output
B A
Input
B A
Input
B A
Output
1 2
Merger
3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
B A
B A
Input
B A
Output
B A
Input
B A
Output
B A
Input
B A
Input
B A
Output
1 2
Merger
3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
B A
B A
Input
B A
Output
B A
Input
B A
Output
B A
Input
B A
Input
B A
Output
1 2
Merger
3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
B A
B A
Input
B A
Output
B A
Input
B A
Output
B A
Input
B A
Input
B A
Output
1 2
Merger
3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
B A
B A
Input
B A
O
utput
B A
Input
B A
O
utput
B A
Input
B A
Input
B A
O
utput
1
2
M
er
ger
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
In Auto Mode, modules can be connected to any port on the MH10.
Note that in the example, it does not matter which A‑Net port (A or B) on the
I/O modules is connected to the MH10. Likewise, on the MH10, the choice
of A‑Net port (1 through 10) does not matter. Any audio made active on the
Pro64 input module in the diagram will be available to all output modules.
Manual Mode Connections
When creating bidirectional networks that require more than 64 channels
(at 48kHz), Manual Mode is the answer. Unlike Auto Mode, Manual Mode
requires that the user pay attention to which A‑Net port (A or B) is used
when connecting network cables to each module. As implemented in the
Pro64 Series of products, A‑Net is a truly bidirectional stream of up to 64x64
channels at all times.
In the examples that follow, the diagrams will indicate the specific A‑Net port
on an I/O module that is in use with a square as shown below. Input modules
such as the 6416i can send active audio channels to Port A, Port B, or both
Ports A and B.
B A
B A
Input
B A
Output
B A
Input
B A
Output
B A
Input
B A
Input
B A
Output
1 2
Merger
3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Port A is being used to send active audio inputs into the network, indicated
by the square surrounding the “A” Port.
