4 control unit (cu) images, lvis, and lus, 1 cu images, 2 logical volume image (lvis) – Compaq 9900 User Manual
Page 45: 3 logical unit (lu) type, Table 3.1 capacities of standard lu types
Hitachi Lightning 9900™ User and Reference Guide
31
3.4 Control Unit (CU) Images, LVIs, and LUs
3.4.1 CU Images
The 9900 subsystem supports the following logical CU images (emulation types): 3990-3,
3990-6E, and 2105. The 9900 subsystem is configured with one logical CU image for each 256
devices (one storage subsystem ID (SSID) for each 64 or 256 devices) to provide a maximum
of sixteen CU images per subsystem. The S/390
®
data management features of the 9900
subsystem may have restrictions on CU image compatibility. FICON™ support requires
2105-F20 emulation. For further information on CU image support, please contact your
Hitachi Data Systems account team.
3.4.2 Logical Volume Image (LVIs)
The 9900 subsystem supports the following S/390
®
LVI types: 3390-1, -2, -3, -3R, -9; 3380-E,
-J, -K. The LVI configuration of the subsystem depends on the RAID implementation and
physical disk drive capacities. See section 4.1 for further information on LVI configurations.
3.4.3 Logical Unit (LU) Type
The 9900 subsystem currently supports the following LU types: OPEN-3, OPEN-8, OPEN-K,
OPEN-9, OPEN-E, OPEN-L, and OPEN-M. Table 3.1 lists the capacities for each standard LU
type. The 9900 also allows users to configure custom-size LUs which are smaller than
standard LUs as well as size-expanded LUs which are larger than standard LUs. LU Size
Expansion (LUSE) volumes can range in size from 3.748 (OPEN-K*2) to 524.448 GB (OPEN-
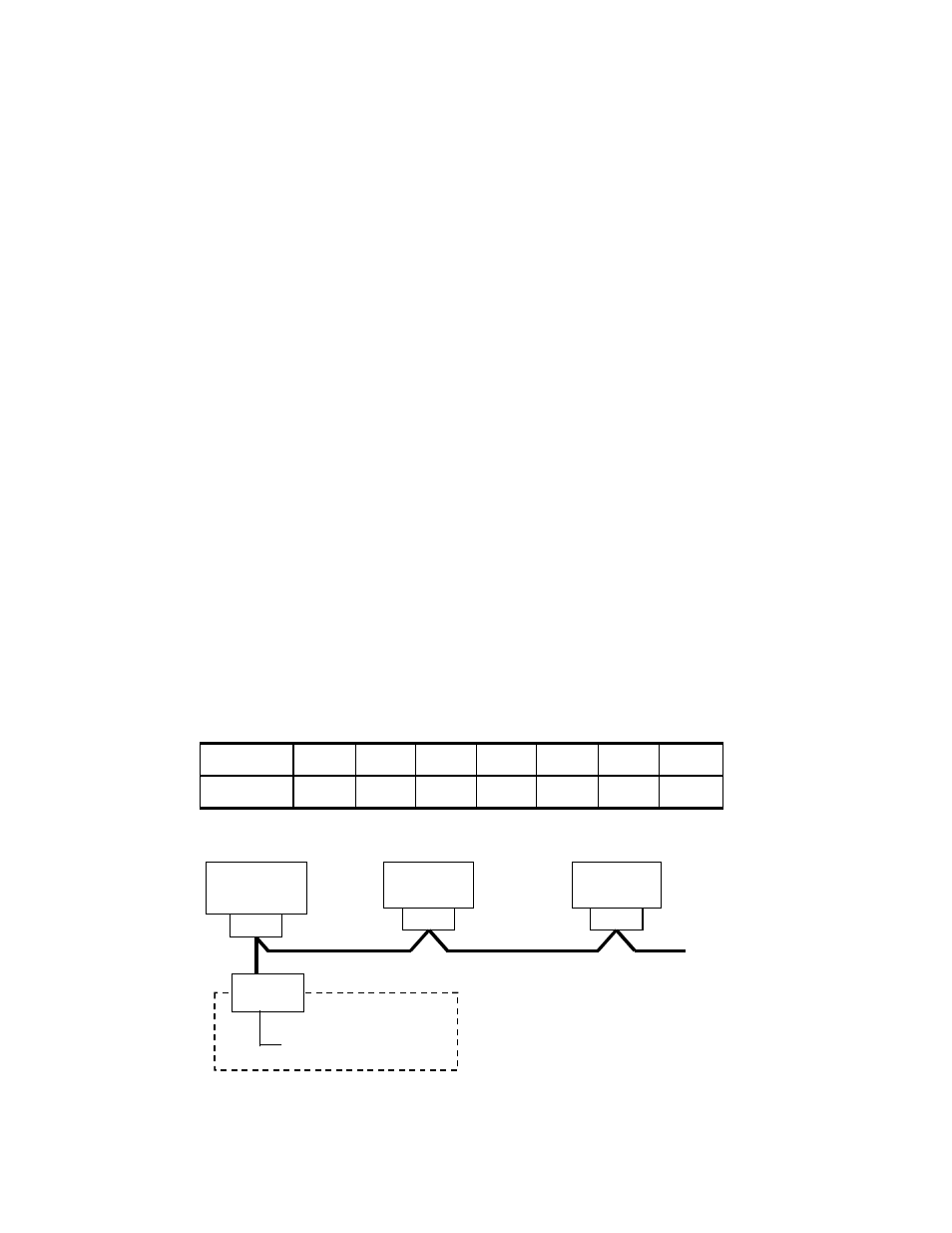
E*36). Each LU is identified by target ID (TID) and LU number (LUN) (see Figure 3.1). Each
9900 fibre-channel port supports addressing capabilities for up to 256 LUNs.
Table 3.1
Capacities of Standard LU Types
LU Type
OPEN-K OPEN-3 OPEN-8 OPEN-9 OPEN-E OPEN-L OPEN-M
Capacity (GB)
1.881 2.461 7.347 7.384 14.568 36.450 47.185
One 9900
fibre port
LUN 0 to 255
Host
Initiator ID
Target ID
Target ID
Other Fibre
device
Other Fibre
device
Each fibre TID must be
unique and within the range
from 0 to EF (hexadecimal).
Figure 3.1
Fibre-Channel Device Addressing
