1 disk array groups, Figure 2.5 sample raid-1 layout – Compaq 9900 User Manual
Page 37
Hitachi Lightning 9900™ User and Reference Guide
23
2.3.1 Disk Array Groups
The disk array group is the basic unit of storage capacity for the 9900. Each array group is
attached to both ACPs of an ACP pair via eight fibre paths, which enables all disk drives in
the array group to be accessed simultaneously by the ACP pair. All disk drives in an array
group must have the same logical capacity. Each array frame has two canister mounts, and
each canister mount can have up to 48 physical disk drives.
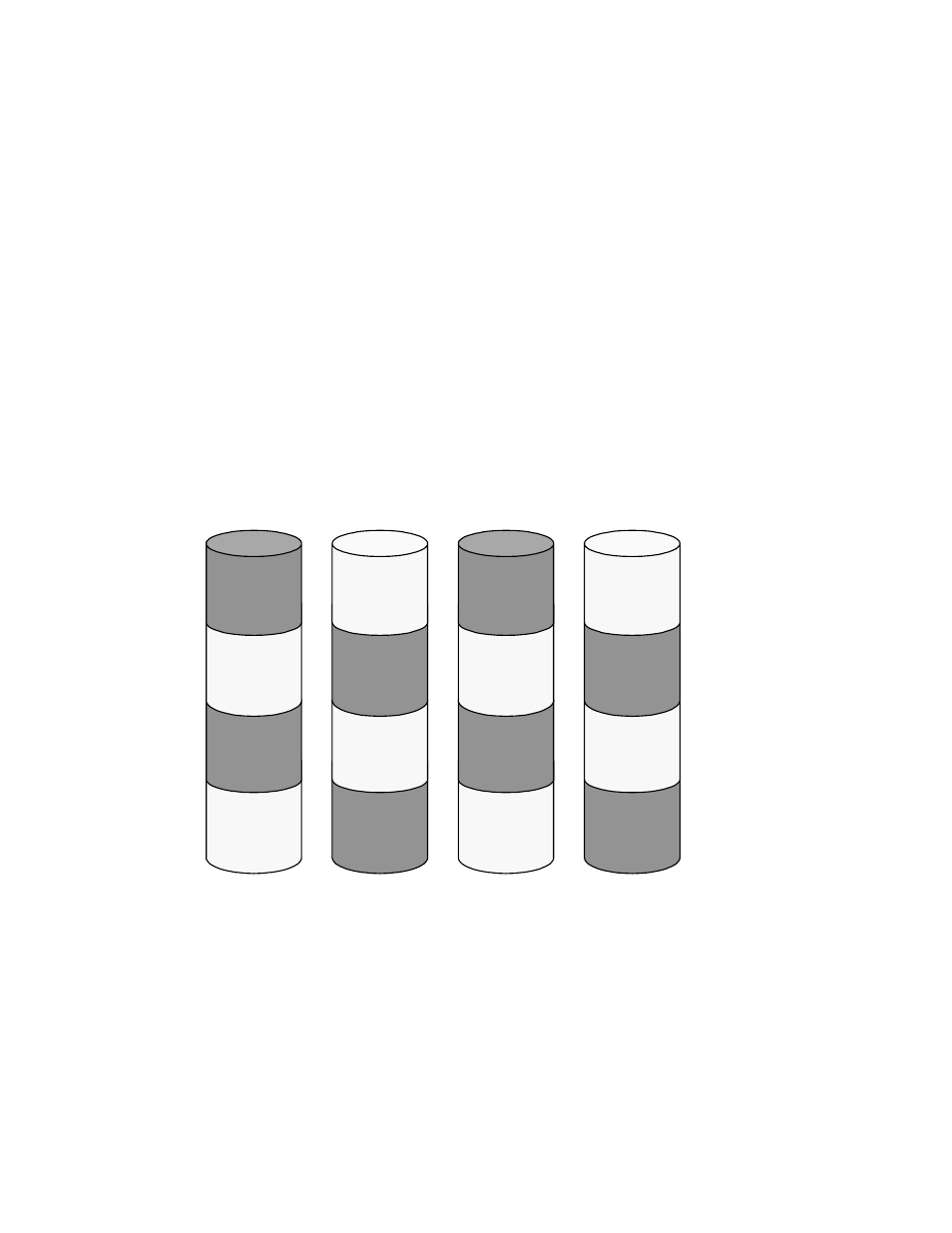
The 9900 supports both RAID-1 and RAID-5 array groups. Figure 2.5 illustrates a sample RAID-
1 layout. A RAID-1 array group consists of two pair of disk drives in a mirrored configuration,
regardless of disk drive capacity. Data is striped to two drives and mirrored to the other two
drives. The stripe consists of two data chunks. The primary and secondary stripes are
toggled back and forth across the physical disk drives for high performance. Each data chunk
consists of either eight logical tracks (S/390
®
) or 768 logical blocks (open systems). A failure
in a drive causes the corresponding mirrored drive to take over for the failed drive. Although
the RAID-5 implementation is appropriate for many applications, the RAID-1 option on the
all-open 9900 subsystem is ideal for workloads with low cache-hit ratios.
Track 32
to
Track 39
Track 32
to
Track 39
Track 40
to
Track 47
Track 56
to
Track 63
Track 48
to
Track 55
Track 48
to
Track 55
Track 40
to
Track 47
Track 56
to
Track 63
RAID-1 using 2D + 2D and S/390
®
LDEVs
Track 0
to
Track 7
Track 0
to
Track 7
Track 8
to
Track 15
Track 24
to
Track 31
Track 16
to
Track 23
Track 16
to
Track 23
Track 8
to
Track 15
Track 24
to
Track 31
Figure 2.5
Sample RAID-1 Layout
A RAID-5 array group consists of four disk drives. The data is written across the four hard
drives in a stripe that has three data chunks and one parity chunk. Each chunk contains
either eight logical tracks (S/390
®
) or 768 logical blocks (open systems). The enhanced RAID-
5+ implementation in the 9900 subsystem minimizes the write penalty incurred by standard
RAID-5 implementations by keeping write data in cache until an entire stripe can be built
and then writing the entire data stripe to the disk drives.
