Simulated testing – Rice Lake BCi Belt Scale - Installation and Operation Manual Version 2.03 User Manual
Page 59
Installation & Operation Manual - Calibration
53
Simulated Testing
A simulated load test consisting of at least three consecutive test runs should be conducted as soon as possible,
but not more than 12 hours after the completion of the material test, to establish the factor to relate the results of
the simulated load test to the results of the material tests. The results of the simulated load test should repeat
within 0.1 percent.
Simulated testing is used only with auto calibration of the integrator.
There are two different simulated load testing techniques that can be used. They are:
•
Roller test chains
•
Static test weights
There are several advantages and disadvantages to each of the list simulated testing techniques. They are listed
below.
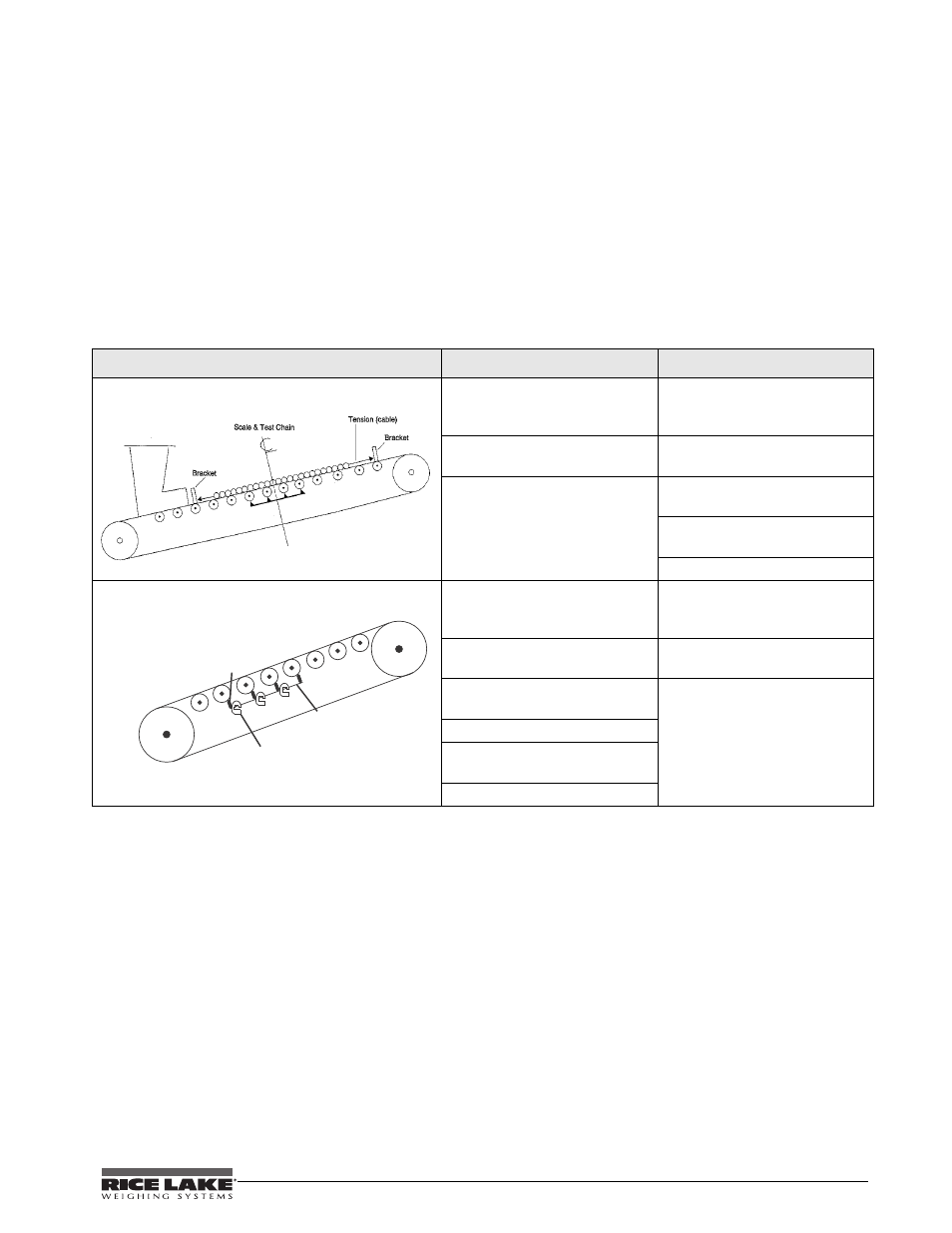
Table 5-2. Advantages and Disadvantages to Simulated Testing
Simulated Testing Type
Advantages
Disadvantages
Roller (chain)
Simulates some conveyor belt
effects
Chains do not provide a traceable
conveyor scale calibration
standard.
Acceptable simulated test
Heavy chains are difficult to
handle.
Conveyor belt must be stopped
to apply and remove.
Linearity test requires several
chains.
Chains are costly.
Static
Test Weights (3)
Belt Scale
Test Weight Brackets
Simulates some conveyor belt
effects
Weights do not provide a
traceable conveyor scale
calibration standard
Easy to apply
Does not simulate conveyor belt
effects
Conveyor belt does not have to
be stopped to apply
Linearity test is easy to perform
Detect load cell failures, and
applies force to the load cell
Acceptable simulated test
